Abstract
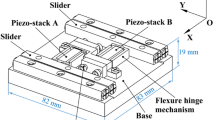
In this paper, the stick-slip motion of a new type of micro-robot with two perpendicular vibratory actuators is studied which is based on the friction drive principle. The actuators are based on piezo-electric phenomenon which are driven by a harmonic voltage, and both of them are mounted on the micro-robot body. These actuators cause the micro-robot moves forward or backward due to the specified phase difference between the voltages applied to vertical and horizontal actuators. Since the dynamics of the actuators affects on the micro-robot motion, so to derive the equations of motion the coupled dynamics between the body of robot and vibratory masses of actuators are considered, and the motion dynamics of the micro-robot is investigated by considering the piezo-actuators effects. After deriving the governing equations of motion, the operative parameters of the piezo-actuated micro-robot, which affect the motion dynamics, are defined in non-dimensional forms and studied for the first time. The Fourier expansion method is used to analyze the numerical results, and the discussion about the motion characteristics of the micro-robot is presented by defining the mean velocity and performance coefficient of the micro-robot stick-slip motion. At last, a simple practical model of this micro-robot is designed and fabricated with two Langevin-type piezo-electric actuators, and then the motion capability of the micro-robot is verified qualitatively by test.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ebefors, T., Stemme, G.: Microrobotics. In: Gad-el Hak, M. (ed.) The MEMS Handbook, pp 28.1–28.42. CRC Press, Boca Raton, RL (2005)
Zhang, Z.M., et al.: Piezoelectric friction-inertia actuator–a critical review and future perspective. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 62(5–8), 669–685 (2012)
Breguet, J.-M., et al.: A review on actuation principles for few cubic millimeter sized mobile micro-robots. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on New Actuators (Actuator 2006). Bremen, Germany (2006)
Donald, B.R., et al.: An untethered, electrostatic, globally controllable MEMS micro-robot. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 15(1), 1–15 (2006)
Bergbreiter, S., Pister, K.S.J.: Design of an autonomous jumping microrobot. In: Robotics and Automation, 2007 IEEE International Conference on (2007)
Go, G., et al.: Manipulation of micro-particles using a magnetically actuated microrobot. Mechatronics 23(8), 1037–1043 (2013)
Driesen, W., et al.: Friction based locomotion module for mobile MEMS robots. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2007. IROS 2007 (2007)
Mohebbi, M.H., et al.: Omnidirectional walking microrobot realized by thermal microactuator arrays. In: ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. New York, NY (2001)
De Ambroggi, F., Fortuna, L., Muscato, G.: PLIF: piezo light intelligent flea -new micro-robots controlled by self-learning techniques. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, ICRA (1997)
Eigoli, A.K., Vossoughi, G.R.: Locomotion modes of a novel piezo-driven microrobot: Analytical modeling and performance evaluation. Mech. Mach. Theory 52, 248–266 (2012)
Weida, L., et al.: Analysis and experiment of stick-slip motion principle in a legged microrobot. In: 2011 6th International Forum on Strategic Technology (IFOST) (2011)
Breguet, J.M., et al.: Applications of Piezo-actuated micro-robots in micro-biology and material science. In: Mechatronics and Automation, 2007. ICMA 2007. International Conference on (2007)
Kim, B., et al.: An earthworm-like micro robot using shape memory alloy actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 125(2), 429–437 (2006)
Shi, Y., et al.: The locomotion systems for self-propelled endoscopes: a review and a new proposal. In: Proceedings of the 5th IASTED International Conference Biomedical Engineering. Innsbruck, Austria (2007)
Wang, W., et al.: Autonomous control of micro flying robot. J. Vib. Control 16(4), 555–570 (2010)
Lester, B.T., et al.: Review and perspectives: shape memory alloy composite systems. Acta Mech. 226(12), 3907–3960 (2015)
Ikegami, T., et al.: Motion analysis of a micro-actuator using three piezoelectric actuators. In: 2006 International Symposium on Micro-NanoMechatronics and Human Science (2006)
Vartholomeos, P., Papadopoulos, E.: Dynamics, design and simulation of a novel microrobotic platform employing vibration microactuators. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 128(1), 122–133 (2005)
Chatterjee, S., Chatterjee, S., Singha, T.K.: On the generation of steady motion using fast-vibration. J. Sound Vib. 283, 1187–1204 (2005)
Voyiadjis, G.Z., et al.: Friction coefficient evaluation using physically based viscoplasticity model at the contact region during high velocity sliding. Acta Mech. 213(1), 39–52 (2010)
Kardan, I., et al.: Stick-slip conditions in the general motion of a planar rigid body. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 27(9), 2577–2583 (2013)
van de Vrande, B.L., van Campen, D.H., de Kraker, A.: An approximate analysis of dry-friction-induced stick-slip vibrations by a smoothing procedure. Nonlinear Dyn. 19(2), 159–171 (1999)
Bowen, Z., et al.: The dynamics study of the stick-slip driving system based on LuGre dynamic friction model. In: 2011 International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA) (2011)
Nguyen, H.X., Edeler, C., Fatikow, S.: Contact mechanics modeling of piezo-actuated stick-slip microdrives. Phys. Mesomech. 15(5), 280–286 (2012)
Seigler, T., Salehian, A.: Analysis of friction controlled motion. J. Vib. Control 17(12), 1893–1904 (2011)
Eigoli, A., Vossoughi, G.: Dynamic analysis of microrobots with Coulomb friction using harmonic balance method. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 1357–1371 (2012)
Jalili, H., Vossoughi, G., Salarieh, H.: Motion analysis of a vibrational microrobot with two perpendicular harmonic actuators and deriving the design parameters in stick-slip mode. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 11(2), 021003–021003 (2015)
Jalili, H., Vossoughi, G., Salarieh, H.: Motion analysis of a vibrational micro-robot with two perpendicular harmonic actuators and deriving the design parameters in stick-slip-jump mode. J. Sound Vib. 372, 266–282 (2016)
Jalili, H., Salarieh, H., Vossoughi, G.: Chaos study of a vibratory micro-robot in hybrid motion. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 1–24 (2015)
Nishimura, T., Hosaka, H., Morita, T.: Resonant-type smooth impact drive mechanism (SIDM) actuator using a bolt-clamped Langevin transducer. Ultrasonics 52(1), 75–80 (2012)
Abidi, K., Sabanovic, A., Yesilyurt S.: Sliding-mode based force control of a piezoelectric actuator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, 2004. ICM ’04 (2004)
Burden, R.L., Faires, J.D.: Numerical analysis. 5th ed. PWS-Kent, Boston, MA (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jalili, H., Salarieh, H. & Vossoughi, G. Study of a piezo-electric actuated vibratory micro-robot in stick-slip mode and investigating the design parameters. Nonlinear Dyn 89, 1927–1948 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3562-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-017-3562-6