Abstract
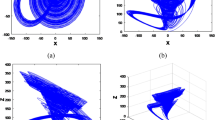
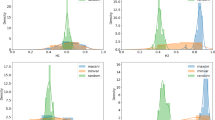
This paper introduced a new method to exploit chaotic, sparse representations of nonlinear time series data. The methodology of the algorithm included two steps. First, the proposed method applied the fractal theory to estimate optimal dimension in a compressive sensing of a time series, and sparse data were concentrated on a pseudo-orbit trajectory. Second, the chaotic trajectory was extracted from the data obtained from the first step by employing a chaos prediction method. To verify the efficiency of the proposed method, the algorithm is applied to three categories, consisting of chaotic noise reduction, signal compression, and image compression. The experimental results indicated that the proposed method outperformed other state-of-the-art methods with up to a 95% reduction in errors. Moreover, the results demonstrated that sparse, chaotic representation was most effective in signal and image compression.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yokoya, N., Iwasaki, A.: Object detection based on sparse representation and Hough voting for optical remote sensing imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 8(5), 2053–2062 (2015)
Qian, C., Xu, Z.: Robust visual tracking via sparse representation under subclass discriminant constraint. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 26(7), 1293–1307 (2014)
Su, H., Xing, F., Yang, L.: Robust cell detection of histopathological brain tumor images using sparse reconstruction and adaptive dictionary selection. IEEE Trans. Med. imaging 35(6), 1575–1586 (2016)
Zhou, N., Li, H., Wang, D., Pan, S., Zhou, Z.: Image compression and encryption scheme based on 2D compressive sensing and fractional Mellin transform. Opt. Commun. 343, 10–21 (2015)
Zhou, N., Zhang, A., Zheng, F., Gong, L.: Novel image compression-encryption hybrid algorithm based on key-controlled measurement matrix in compressive sensing. Opt. Laser Technol. 62, 152–160 (2014)
Qaisar, S., Bilal, R.M., Iqbal, W., Naureen, M., Lee, S.: Compressive sensing: from theory to applications, a survey. J. Commun. Netw. 15(5), 443–456 (2013)
Farmer, M.E.: A chaos theoretic analysis of motion and illumination in video sequences. J. Multimed. 2(2), 53–64 (2007)
Gan, C.B., Lei, H.: A new procedure for exploring chaotic attractors in nonlinear dynamical systems under random excitations. Acta Mech. Sin. 27(4), 593–601 (2011)
Upadhyay, R.K., Iyengar, S.R.: Introduction to Mathematical Modeling and Chaotic Dynamics. CRC Press, Hoboken (2013)
Andrievskii, B.R., Fradkov, A.L.: Control of chaos: methods and applications. I. Methods. Autom. Remote Control 64(5), 673–713 (2003)
Das, S.: Chaotic patterns in the discrete-time dynamics of social foraging swarms with attractant-repellent profiles: an analysis. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(3), 1399–1417 (2015)
Messerotti, M., Zuccarello, F., Guglielmino, S.L., Bothmer, V., Lilensten, J., Noci, G., Storini, G., Lundstedt, H.: Solar weather event modelling and prediction. Space Sci. Rev. 147(3–4), 121–185 (2009)
Wang, X., Liu, C., Xu, D., Liu, C.: Image encryption scheme using chaos and simulated annealing algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn. 84(3), 1417–1429 (2016)
Mittal, A.K., Singh, U.P., Tiwari, A., Dwivedi, S., Joshi, M.K., Tripathi, K.C.: Short-term predictions by statistical methods in regions of varying dynamical error growth in a chaotic system. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 127(4), 457–465 (2015)
Tongue, B.H., Gu, K.: Interpolated cell mapping of dynamical systems. J. Appl. Mech. 55(2), 461–466 (1988)
Asif, M.S., Romberg, J.: Sparse recovery of streaming signals using \(\text{ l }_1 \)-homotopy. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(16), 4209–4223 (2014)
Wu, J., Lu, J., Wang, J.: Application of chaos and fractal models to water quality time series prediction. Environ. Model. Softw. 24(5), 632–636 (2009)
Kulp, C.W.: Detecting chaos in irregularly sampled time series. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 23(3), 033110 (2013)
Casdagli, M.: Nonlinear forecasting, chaos and statistics. In: Modeling Complex Phenomena. The seventh Triennial Symposium on Transportation Analysis (TRISTAN VII). pp. 131–152. Springer, New York (1992)
Wang, J., Shi, Q.: Short-term traffic speed forecasting hybrid model based on chaos-wavelet analysis-support vector machine theory. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 27, 219–232 (2013)
Dhanya, C.T.: Nagesh Kumar, D.: Nonlinear ensemble prediction of chaotic daily rainfall. Adv. Water Resour. 33(3), 327–347 (2010)
An, X., Jiang, D., Zhao, M., Liu, C.: Short-term prediction of wind power using EMD and chaotic theory. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(2), 1036–1042 (2012)
Petkov, B.H., Vitale, V., Mazzola, M., Lanconelli, C., Lupi, A.: Chaotic behaviour of the short-term variations in ozone column observed in Arctic. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 26(1), 238–249 (2015)
Li, M.W., Geng, J., Han, D.F., Zheng, T.J.: Ship motion prediction using dynamic seasonal RvSVR with phase space reconstruction and the chaos adaptive efficient FOA. Neurocomputing 174, 661–680 (2016)
Kayacan, E., Ulutas, B., Kaynak, O.: Grey system theory-based models in time series prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(2), 1784–1789 (2010)
Du, H., Smith, L.A.: Rising above chaotic likelihoods. arXiv preprint arXiv:1410.2568
Dabby, D.S.: Musical variations from a chaotic mapping. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 6(2), 95–107 (1996)
Du, H., Leonard, A.S.: Pseudo-orbit data assimilation. Part II: assimilation with imperfect models. J. Atmos. Sci. 71(2), 483–495 (2014)
Bilotta, E., Pantano, P., Stranges, F.: A gallery of Chua attractors. Part I. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 17(1), 1–60 (2007)
Mu, C., Zhang, F., Shu, Y., Zhou, S.: On the boundedness of solutions to the Lorenz-like family of chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(2), 987–996 (2012)
Bisaillon, P., Sandhu, R., Khalil, M., Pettit, C., Poirel, D., Sarkar, A.: Bayesian parameter estimation and model selection for strongly nonlinear dynamical systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(3), 1061–1080 (2015)
Khalil, M., Sarkar, A., Adhikari, S.: Nonlinear filters for chaotic oscillatory systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 55(1–2), 113–137 (2009)
Du, H., Leonard, A.S.: Pseudo-orbit data assimilation. Part I: the perfect model scenario. J. Atmos. Sci. 71(2), 469–482 (2014)
Liu, Z., Elezzabi, A.Y., Zhao, H.V.: Maximum frame rate video acquisition using adaptive compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 21(11), 1704–1718 (2011)
Malioutov, D.M., Sanghavi, S.R., Willsky, A.S.: Sequential compressed sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 4(2), 435–444 (2010)
Blumensath, T.: Compressed sensing with nonlinear observations and related nonlinear optimization problems. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 59(6), 3466–3474 (2013)
Tillmann, A.M., Pfetsch, M.E.: The computational complexity of the restricted isometry property, the nullspace property and related concepts, in compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 60(2), 1248–1259 (2014)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Leinonen, M., Codreanu, M., Juntti, M.: Sequential compressed sensing with progressive signal reconstruction in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 14(3), 1622–1635 (2015)
Sugihara, G., May, R.: Nonlinear forecasting as a way of distinguishing chaos from measurement error in time series. Nature 344(6268), 734–741 (1990)
Tsonis, A.A., Elsner, J.B.: Nonlinear prediction as a way of distinguishing chaos from random fractal sequences. Nature 358, 217–220 (1992)
Wales, D.J.: Calculating the rate of loss of information from chaotic time series by forecasting. Nature 350, 485–488 (1991)
Anderson, T.W.: An Introduction to Multivariate Statistical Analysis, vol. 2. Wiley, Hoboken (1958)
Yang, D., Liu, Z., Zhou, J.: Chaos optimization algorithms based on chaotic maps with different probability distribution and search speed for global optimization. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 19(4), 1229–1246 (2014)
Fertig, E.J., Harlim, J., Hunt, B.R.: A comparative study of 4D-VAR and a 4D ensemble Kalman filter: perfect model simulations with Lorenz-96. Tellus 59, 96–100 (2007)
Wright, S.J., Nowak, R.D., Figueiredo, M.A.: Sparse reconstruction by separable approximation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(7), 2479–2493 (2009)
Yang, J., Zhang, Y.: Alternating direction algorithms for \(\text{ l }_1 \)-problems in compressive sensing. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 33(1), 250–278 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdechiri, M., Faez, K., Amindavar, H. et al. The chaotic dynamics of high-dimensional systems. Nonlinear Dyn 87, 2597–2610 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3213-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-3213-3