Abstract
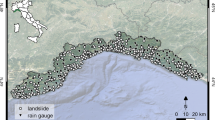
In this paper, the updating of rainfall thresholds for landslide early warning systems (EWSs) is presented. Rainfall thresholds are widely used in regional-scale landslide EWSs, but the efficiency of those systems can decrease during the time, so a periodically updating should be required to keep their functionality. The updating of 12 of the 25 thresholds used in the EWS of Tuscany region (central Italy) is presented, and a comparison between performances of new and previous thresholds has been made to highlight the need of their periodical update. The updating has been carried out by collecting ca. 1200 new landslide reports (from 2010 to March 2013) and their respective rainfall data, collected by 332 rain gauges. The comparison has been made by the use of several statistical indexes and showed a marked increasing in the performances of the new thresholds with respect to previous ones.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostini A, Tofani V, Nolesini T, Gigli G, Tanteri L, Rosi A, Cardellini S, Casagli N (2014) A new appraisal of the Ancona landslide based on geotechnical investigations and stability modeling. Q J Eng Geol Hydrogeol 47:29–43. doi:10.1144/qjegh2013-028
Ahmad R (2003) Developing early warning systems in Jamaica: rainfall thresholds for hydrological hazards. In: National disaster management conference, Ocho Rios, St. Ann, Jamaica, 9–10 September 2003
Aleotti P (2004) A warning system for rainfall-induced shallow failures. Eng Geol 73:247–265
Arnone E, Pumo D, Viola F, Noto LV, La Loggia G (2013) Rainfall statistics changes in Sicily. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 17:2449–2458
Brunetti MT, Peruccacci S, Rossi M, Luciani S, Valigi D, Guzzetti F (2010) Rainfall thresholds for the possible occurrence of landslides in Italy. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 10:447–458. doi:10.5194/nhess-10-447-2010
Brunsden D (1973) The application of system theory to the study of mass movement. Geol Appl Idrogeoeol 8:185–207
Caine N (1980) The rainfall intensity—duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows. Geogr Ann 62:23–27
Cannon SH, Gartner JE, Wilson RC, Bowers JC, Laber JL (2008) Storm rainfall conditions for floods and debris flows from recently burned areas in southwestern Colorado and southern California. Geomorphology 96:250–269
Carrara A, Sorriso-Valvo M, Reali C (1982) Analysis of landslide form and incidence by statistical techniques, Southern Italy. Catena 9:35–62
Catani F, Lagomarsino D, Segoni S, Tofani V (2013) Landslide susceptibility estimation by random forests technique: sensitivity and scaling issues. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13:2815–2831
Chen HX, Wang JD (2014) Regression analyses for the minimum intensity-duration conditions of continuous rainfall for mudflows triggering in Yan’an, northern Shaanxi (China). Bull Eng Geol Environ 73:917–928
Crosta GB (1989) A study of slope movements caused by heavy rainfall in Valtellina (Italy–July 1987). In: Cancelli A (ed) Proceedings 6th international conference, and field workshop on Landslides ALPS 90, vol 79b. Ricerca Scientifica ed Educazione Permanente, Milano, pp 247–258
Floris M, D’Alpaos A, Squarzoni C, Genevois R, Marani M (2010) Recent changes in rainfall characteristics and their influence on thresholds for debris flow triggering in the Dolomitic area of Cortina d’Ampezzo, north-eastern Italian Alps. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 10:571–580
Garcia-Urquia E, Axelsson K (2015) Rainfall thresholds for the occurrence of urban landslides in Tegucigalpa, Honduras: an application of the critical rainfall intensity. Geogr Ann Ser A Phys Geogr 97:61–83
Giannecchini R, Galanti Y, D’Amato Avanzi G (2012) Critical rainfall thresholds for triggering shallow landslides in the Serchio River Valley (Tuscany, Italy). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 12:829–842
Gioia E, Speranza G, Appiotti F, Ferretti M, Marincioni F (2015) Rainfall threshold and landslides in the post-orogenic complex of the Esino River Basin, central Italy. In: Lollino G, Giordan D, Crosta G, Corominas J, Azzam R, Wasowski J, Sciarra N (eds) Engineering geology for society and territory, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 1553–1556
Guzzetti F, Peruccaci S, Rossi M, Stark CP (2007) Rainfall thresholds for the initiation of landslides in central and southern Europe. Meteorol Atmos Phys 98:239–267
Guzzetti F, Peruccacci S, Rossi M, Stark CP (2008) The rainfall intensity–duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: an update. Landslides 5:3–17
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. In: Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA
ISPRA (2014) Soil consumption in Italy, ISPRA, Rome (in Italian). http://www.isprambiente.gov.it/files/pubblicazioni/rapporti/Rapporto_Consumo_di_Suolo_in_Italia_2014.pdf. Accessed 07 December 2014
Lagomarsino D, Segoni S, Fanti R, Catani F (2013) Updating and tuning a regional-scale landslide early warning system. Landslides 10:91–97
Lee ML, Ng KY, Huang YF, Li WC (2014) Rainfall-Induced Landslides in Hulu Kelang Area, Malaysia. Nat Hazards 70(1):353–375
Maracchi G, Genesio L, Magno R, Ferrari R, Crisci A, Bottai L (2005) The diagrams of the climate in Tuscany. CNR-Ibimet, LAMMA-CRES, Florence (In Italian)
Martelloni G, Segoni S, Fanti R, Catani F (2012) Rainfall thresholds for the forecasting of landslide occurrence at regional scale. Landslides 9:485–495
Melillo M, Brunetti MT, Peruccacci S, Gariano SL, Guzzetti F (2014) An algorithm for the objective reconstruction of rainfall events responsible for landslides. Landslides. doi:10.1007/s10346-014-0471-3
Mercogliano P, Segoni S, Rossi G, Sikorsky B, Tofani V, Schiano P, Catani F, Casagli N (2013) Brief communication: a prototype forecasting chain for rainfall induced shallow landslides. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13:771–777
Rapetti F, Vittorini S (1994) Rainfall in Tuscany: observation about extreme events. Riv Geogr Ital 101:47–76 (in Italian)
Rosi A, Segoni S, Catani F, Casagli N (2012) Statistical and environmental analyses for the definition of a regional rainfall thresholds system for landslide triggering in Tuscany (Italy). J Geogr Sci 22:617–629
Rossi G, Catani F, Leoni L, Segoni S, Tofani V (2013) HIRESSS: a physically based slope stability simulator for HPC applications. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 13:151–166
Segoni S, Rossi G, Rosi A, Catani F (2014a) Landslides triggered by rainfall: a semiautomated procedure to define consistent intensity-duration thresholds. Comput Geosci 63:123–131
Segoni S, Rosi A, Rossi G, Catani F, Casagli N (2014b) Analysing the relationship between rainfalls and landslides to define a mosaic of triggering thresholds for regional scale warning systems. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 14:2637–2648
Segoni S, Battistini A, Rossi G, Rosi A, Lagomarsino D, Catani F, Moretti S, Casagli N (2014c) Technical Note: an operational landslide early warning system at regional scale based on space–time variable rainfall thresholds. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci Discuss 2:6599–6622
Tiranti D, Rabuffetti D (2010) Estimation of rainfall thresholds triggering shallow landslides for an operational warning system implementation. Landslides 7:471–481
Vessia G, Parise M, Brunetti MT, Peruccacci S, Rossi M, Vennari C, Guzzetti F (2014) Automated reconstruction of rainfall events responsible for shallow landslides. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 14:2399–2408
Zêzere JL, Trigo RM, Trigo IF (2005) Shallow and deep landslides induced by rainfall in the Lisbon region (Portugal): assessment of relationships with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 5:331–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosi, A., Lagomarsino, D., Rossi, G. et al. Updating EWS rainfall thresholds for the triggering of landslides. Nat Hazards 78, 297–308 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1717-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-015-1717-7