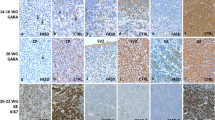
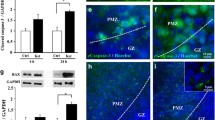
Abstract
GABAergic Interneuronal migration constitutes an essential process during corticogenesis. Derived from progenitor cells located in the proliferative zones of the ventral telencephalon, newly generated GABAergic Interneuron migrate to their cortical destinations. Cortical dysfunction associated with defects in neuronal migration results in severe developmental consequences. There is growing evidence linking prenatal ethanol exposure to abnormal GABAergic interneuronal migration and subsequent cortical dysfunction. Investigating the pathophysiological mechanisms behind disrupted GABAergic interneuronal migration encountered with prenatal alcohol exposure is crucial for understanding and managing fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. This review explores the molecular pathways regulating GABAergic interneuronal cortical migration that might be altered by prenatal ethanol exposure thus opening new avenues for further research in this topic.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Powell EM, Campbell DB, Stanwood GD, Davis C, Noebels JL, Levitt P (2003) Genetic disruption of cortical interneuron development causes region- and GABA cell type-specific deficits, epilepsy, and behavioral dysfunction. J Neurosci 23(2):622–631
Bartolini G, Ciceri G, Marin O (2013) Integration of GABAergic interneurons into cortical cell assemblies: lessons from embryos and adults. Neuron 79(5):849–864. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.08.014
Lodato S, Rouaux C, Quast KB, Jantrachotechatchawan C, Studer M, Hensch TK, Arlotta P (2011) Excitatory projection neuron subtypes control the distribution of local inhibitory interneurons in the cerebral cortex. Neuron 69(4):763–779. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.01.015
Le Magueresse C, Monyer H (2013) GABAergic interneurons shape the functional maturation of the cortex. Neuron 77(3):388–405. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2013.01.011
Varju P, Katarova Z, Madarasz E, Szabo G (2001) GABA signalling during development: new data and old questions. Cell Tissue Res 305(2):239–246
Rossignol E (2011) Genetics and function of neocortical GABAergic interneurons in neurodevelopmental disorders. Neural Plast 2011:649325. doi:10.1155/2011/649325
Reiner O, Karzbrun E, Kshirsagar A, Kaibuchi K (2016) Regulation of neuronal migration, an emerging topic in autism spectrum disorders. J Neurochem 136(3):440–456. doi:10.1111/jnc.13403
Lewis DA (2000) GABAergic local circuit neurons and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31(2–3):270–276
Guerrini R, Dobyns WB, Barkovich AJ (2008) Abnormal development of the human cerebral cortex: genetics, functional consequences and treatment options. Trends Neurosci 31(3):154–162. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2007.12.004
Guerrini R, Parrini E (2010) Neuronal migration disorders. Neurobiol Dis 38(2):154–166. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2009.02.008
Lewis DA, Curley AA, Glausier JR, Volk DW (2012) Cortical parvalbumin interneurons and cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Trends Neurosci 35(1):57–67. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2011.10.004
Kato M, Dobyns WB (2003) Lissencephaly and the molecular basis of neuronal migration. Hum Mol Genet 12 Spec No 1:R89–R96
Crandall JE, Hackett HE, Tobet SA, Kosofsky BE, Bhide PG (2004) Cocaine exposure decreases GABA neuron migration from the ganglionic eminence to the cerebral cortex in embryonic mice. Cereb Cortex 14(6):665–675. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhh027
Cuzon VC, Yeh PW, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Yeh HH (2008) Ethanol consumption during early pregnancy alters the disposition of tangentially migrating GABAergic interneurons in the fetal cortex. J Neurosci 28(8):1854–1864. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5110-07.2008
Skorput AG, Gupta VP, Yeh PW, Yeh HH (2015) Persistent interneuronopathy in the prefrontal cortex of young adult Offspring exposed to ethanol in utero. J Neurosci 35(31):10977–10988. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1462-15.2015
Isayama RN, Leite PE, Lima JP, Uziel D, Yamasaki EN (2009) Impact of ethanol on the developing GABAergic system. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 292 (12):1922–1939. doi:10.1002/ar.20966
Kawaguchi Y, Kubota Y (1997) GABAergic cell subtypes and their synaptic connections in rat frontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 7(6):476–486
Lee S, Hjerling-Leffler J, Zagha E, Fishell G, Rudy B (2010) The largest group of superficial neocortical GABAergic interneurons expresses ionotropic serotonin receptors. J Neurosci 30(50):16796–16808. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1869-10.2010
Fogarty M, Grist M, Gelman D, Marin O, Pachnis V, Kessaris N (2007) Spatial genetic patterning of the embryonic neuroepithelium generates GABAergic interneuron diversity in the adult cortex. J Neurosci 27(41):10935–10946. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1629-07.2007
Gelman DM, Martini FJ, Nobrega-Pereira S, Pierani A, Kessaris N, Marin O (2009) The embryonic preoptic area is a novel source of cortical GABAergic interneurons. J Neurosci 29(29):9380–9389. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0604-09.2009
Gelman DM, Marin O (2010) Generation of interneuron diversity in the mouse cerebral cortex. Eur J Neurosci 31(12):2136–2141. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07267.x
Wonders CP, Anderson SA (2006) The origin and specification of cortical interneurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(9):687–696. doi:10.1038/nrn1954
Welagen J, Anderson S (2011) Origins of neocortical interneurons in mice. Dev Neurobiol 71(1):10–17. doi:10.1002/dneu.20857
de Carlos JA, Lopez-Mascaraque L, Valverde F (1996) Dynamics of cell migration from the lateral ganglionic eminence in the rat. J Neurosci 16(19):6146–6156
Marin O (2013) Cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling the migration of neocortical interneurons. Eur J Neurosci 38(1):2019–2029. doi:10.1111/ejn.12225
Wichterle H, Turnbull DH, Nery S, Fishell G, Alvarez-Buylla A (2001) In utero fate mapping reveals distinct migratory pathways and fates of neurons born in the mammalian basal forebrain. Development 128(19):3759–3771
Yozu M, Tabata H, Nakajima K (2005) The caudal migratory stream: a novel migratory stream of interneurons derived from the caudal ganglionic eminence in the developing mouse forebrain. J Neurosci 25(31):7268–7277. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2072-05.2005
Rubin AN, Alfonsi F, Humphreys MP, Choi CK, Rocha SF, Kessaris N (2010) The germinal zones of the basal ganglia but not the septum generate GABAergic interneurons for the cortex. J Neurosci 30(36):12050–12062. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6178-09.2010
Tanaka DH, Nakajima K (2012) Migratory pathways of GABAergic interneurons when they enter the neocortex. Eur J Neurosci 35(11):1655–1660. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08111.x
Miyoshi G, Butt SJ, Takebayashi H, Fishell G (2007) Physiologically distinct temporal cohorts of cortical interneurons arise from telencephalic Olig2-expressing precursors. J Neurosci 27(29):7786–7798. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1807-07.2007
Del Rio JA, Soriano E, Ferrer I (1992) Development of GABA-immunoreactivity in the neocortex of the mouse. J Comp Neurol 326(4):501–526. doi:10.1002/cne.903260403
Rymar VV, Sadikot AF (2007) Laminar fate of cortical GABAergic interneurons is dependent on both birthdate and phenotype. J Comp Neurol 501(3):369–380. doi:10.1002/cne.21250
Faux C, Rakic S, Andrews W, Britto JM (2012) Neurons on the move: migration and lamination of cortical interneurons. Neurosignals 20(3):168–189. doi:10.1159/000334489
Liu JS (2011) Molecular genetics of neuronal migration disorders. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 11(2):171–178. doi:10.1007/s11910-010-0176-5
Faux C, Rakic S, Andrews W, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Parnavelas JG (2010) Differential gene expression in migrating cortical interneurons during mouse forebrain development. J Comp Neurol 518(8):1232–1248. doi:10.1002/cne.22271
Kelsom C, Lu W (2013) Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons. Cell Biosci 3(1):19. doi:10.1186/2045-3701-3-19
Bagnard D, Vaillant C, Khuth ST, Dufay N, Lohrum M, Puschel AW, Belin MF, Bolz J, Thomasset N (2001) Semaphorin 3A-vascular endothelial growth factor-165 balance mediates migration and apoptosis of neural progenitor cells by the recruitment of shared receptor. J Neurosci 21(10):3332–3341
Senturk A, Pfennig S, Weiss A, Burk K, Acker-Palmer A (2011) Ephrin Bs are essential components of the reelin pathway to regulate neuronal migration. Nature 472(7343):356–360. doi:10.1038/nature09874
Lussier SJ, Stevens HE (2016) Delays in GABAergic interneuron development and behavioral inhibition after prenatal stress. Dev Neurobiol. doi:10.1002/dneu.22376
Manent JB, Jorquera I, Mazzucchelli I, Depaulis A, Perucca E, Ben-Ari Y, Represa A (2007) Fetal exposure to GABA-acting antiepileptic drugs generates hippocampal and cortical dysplasias. Epilepsia 48(4):684–693. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01056.x
Naimi TS, Lipscomb LE, Brewer RD, Gilbert BC (2003) Binge drinking in the preconception period and the risk of unintended pregnancy: implications for women and their children. Pediatrics 111(5 Pt 2):1136–1141
May PA, Gossage JP (2001) Estimating the prevalence of fetal alcohol syndrome. A summary. Alcohol Res Health 25(3):159–167
Tan CH, Denny CH, Cheal NE, Sniezek JE, Kanny D (2015) Alcohol use and binge drinking among women of childbearing age - United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 64(37):1042–1046. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm6437a3
Maier SE, West JR (2001) Drinking patterns and alcohol-related birth defects. Alcohol Res Health 25(3):168–174
Peadon E, Elliott EJ (2010) Distinguishing between attention-deficit hyperactivity and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders in children: clinical guidelines. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 6:509–515
Fryer SL, McGee CL, Matt GE, Riley EP, Mattson SN (2007) Evaluation of psychopathological conditions in children with heavy prenatal alcohol exposure. Pediatrics 119(3):e733–e741. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-1606
Knopik VS, Sparrow EP, Madden PA, Bucholz KK, Hudziak JJ, Reich W, Slutske WS, Grant JD, McLaughlin TL, Todorov A, Todd RD, Heath AC (2005) Contributions of parental alcoholism, prenatal substance exposure, and genetic transmission to child ADHD risk: a female twin study. Psychol Med 35(5):625–635
Schneider ML, Moore CF, Adkins MM (2011) The effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on behavior: rodent and primate studies. Neuropsychol Rev 21(2):186–203. doi:10.1007/s11065-011-9168-8
Marquardt K, Sigdel R, Caldwell K, Brigman JL (2014) Prenatal ethanol exposure impairs executive function in mice into adulthood. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(12):2962–2968. doi:10.1111/acer.12577
Miller MW (1993) Migration of cortical neurons is altered by gestational exposure to ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 17(2):304–314
Miller MW (1986) Effects of alcohol on the generation and migration of cerebral cortical neurons. Science 233(4770):1308–1311
Miller MW (2006) Effect of prenatal exposure to ethanol on glutamate and GABA immunoreactivity in macaque somatosensory and motor cortices: critical timing of exposure. Neuroscience 138(1):97–107. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.10.060
Bailey CD, Brien JF, Reynolds JN (2004) Chronic prenatal ethanol exposure alters the proportion of GABAergic neurons in layers II/III of the adult guinea pig somatosensory cortex. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26(1):59–63. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2003.08.002
Moore DB, Quintero MA, Ruygrok AC, Walker DW, Heaton MB (1998) Prenatal ethanol exposure reduces parvalbumin-immunoreactive GABAergic neuronal number in the adult rat cingulate cortex. Neurosci Lett 249(1):25–28
Knoflach F, Hernandez MC, Bertrand D (2016) GABAA receptor-mediated neurotransmission: not so simple after all. Biochem Pharmacol 115:10–17. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.014
Misgeld U, Bijak M, Jarolimek W (1995) A physiological role for GABAB receptors and the effects of baclofen in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol 46(4):423–462
Wu C, Sun D (2015) GABA receptors in brain development, function, and injury. Metab Brain Dis 30(2):367–379. doi:10.1007/s11011-014-9560-1
Braat S, Kooy RF (2015) The GABAA receptor as a therapeutic target for neurodevelopmental disorders. Neuron 86(5):1119–1130. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.042
Manent JB, Demarque M, Jorquera I, Pellegrino C, Ben-Ari Y, Aniksztejn L, Represa A (2005) A noncanonical release of GABA and glutamate modulates neuronal migration. J Neurosci 25(19):4755–4765. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0553-05.2005
Smith KM, Maragnoli ME, Phull PM, Tran KM, Choubey L, Vaccarino FM (2014) Fgfr1 inactivation in the mouse telencephalon results in impaired maturation of interneurons expressing parvalbumin. PLoS ONE 9(8):e103696. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103696
Cuzon VC, Yeh PW, Cheng Q, Yeh HH (2006) Ambient GABA promotes cortical entry of tangentially migrating cells derived from the medial ganglionic eminence. Cereb Cortex 16(10):1377–1388. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj084
Cuzon Carlson VC, Yeh HH (2011) GABAA receptor subunit profiles of tangentially migrating neurons derived from the medial ganglionic eminence. Cereb Cortex 21(8):1792–1802. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhq247
Inada H, Watanabe M, Uchida T, Ishibashi H, Wake H, Nemoto T, Yanagawa Y, Fukuda A, Nabekura J (2011) GABA regulates the multidirectional tangential migration of GABAergic interneurons in living neonatal mice. PLoS ONE 6(12):e27048. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027048
Behar TN, Smith SV, Kennedy RT, McKenzie JM, Maric I, Barker JL (2001) GABA(B) receptors mediate motility signals for migrating embryonic cortical cells. Cereb Cortex 11(8):744–753
Behar TN, Schaffner AE, Scott CA, O’Connell C, Barker JL (1998) Differential response of cortical plate and ventricular zone cells to GABA as a migration stimulus. J Neurosci 18(16):6378–6387
Bony G, Szczurkowska J, Tamagno I, Shelly M, Contestabile A, Cancedda L (2013) Non-hyperpolarizing GABAB receptor activation regulates neuronal migration and neurite growth and specification by cAMP/LKB1. Nat Commun 4:1800. doi:10.1038/ncomms2820
Furukawa T, Yamada J, Akita T, Matsushima Y, Yanagawa Y, Fukuda A (2014) Roles of taurine-mediated tonic GABAA receptor activation in the radial migration of neurons in the fetal mouse cerebral cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 8:88. doi:10.3389/fncel.2014.00088
Heck N, Kilb W, Reiprich P, Kubota H, Furukawa T, Fukuda A, Luhmann HJ (2007) GABA-A receptors regulate neocortical neuronal migration in vitro and in vivo. Cereb Cortex 17(1):138–148. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhj135
Rheims S, Represa A, Ben-Ari Y, Zilberter Y (2008) Layer-specific generation and propagation of seizures in slices of developing neocortex: role of excitatory GABAergic synapses. J Neurophysiol 100(2):620–628. doi:10.1152/jn.90403.2008
Kumar S, Fleming RL, Morrow AL (2004) Ethanol regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptors: genomic and nongenomic mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther 101(3):211–226. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.12.001
Santhakumar V, Wallner M, Otis TS (2007) Ethanol acts directly on extrasynaptic subtypes of GABAA receptors to increase tonic inhibition. Alcohol 41(3):211–221. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2007.04.011
Lobo IA, Harris RA (2008) GABA(A) receptors and alcohol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 90(1):90–94. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2008.03.006
Janigro D, Schwartzkroin PA (1988) Effects of GABA and baclofen on pyramidal cells in the developing rabbit hippocampus: an ‘in vitro’ study. Brain Res 469(1–2):171–184
Lopez-Bendito G, Shigemoto R, Kulik A, Paulsen O, Fairen A, Lujan R (2002) Expression and distribution of metabotropic GABA receptor subtypes GABABR1 and GABABR2 during rat neocortical development. Eur J Neurosci 15(11):1766–1778
Behar TN, Schaffner AE, Scott CA, Greene CL, Barker JL (2000) GABA receptor antagonists modulate postmitotic cell migration in slice cultures of embryonic rat cortex. Cereb Cortex 10(9):899–909
Lopez-Bendito G, Lujan R, Shigemoto R, Ganter P, Paulsen O, Molnar Z (2003) Blockade of GABA(B) receptors alters the tangential migration of cortical neurons. Cereb Cortex 13(9):932–942
Crandall JE, McCarthy DM, Araki KY, Sims JR, Ren JQ, Bhide PG (2007) Dopamine receptor activation modulates GABA neuron migration from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex. J Neurosci 27(14):3813–3822. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5124-06.2007
Trantham-Davidson H, Chandler LJ (2015) Alcohol-induced alterations in dopamine modulation of prefrontal activity. Alcohol 49(8):773–779. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2015.09.001
Engel JA, Jerlhag E (2014) Alcohol: mechanisms along the mesolimbic dopamine system. Prog Brain Res 211:201–233. doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-63425-2.00009-X
Fabio MC, Vivas LM, Pautassi RM (2015) Prenatal ethanol exposure alters ethanol-induced Fos immunoreactivity and dopaminergic activity in the mesocorticolimbic pathway of the adolescent brain. Neuroscience 301:221–234. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.06.003
Rex EB, Rankin ML, Ariano MA, Sibley DR (2008) Ethanol regulation of D(1) dopamine receptor signaling is mediated by protein kinase C in an isozyme-specific manner. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(12):2900–2911. doi:10.1038/npp.2008.16
Zhou R, Wang S, Zhu X (2012) Prenatal ethanol exposure alters synaptic plasticity in the dorsolateral striatum of rat offspring via changing the reactivity of dopamine receptor. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42443. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042443
Ungerer M, Knezovich J, Ramsay M (2013) In utero alcohol exposure, epigenetic changes, and their consequences. Alcohol Res 35(1):37–46
Kim P, Choi CS, Park JH, Joo SH, Kim SY, Ko HM, Kim KC, Jeon SJ, Park SH, Han SH, Ryu JH, Cheong JH, Han JY, Ko KN, Shin CY (2014) Chronic exposure to ethanol of male mice before mating produces attention deficit hyperactivity disorder-like phenotype along with epigenetic dysregulation of dopamine transporter expression in mouse offspring. J Neurosci Res 92(5):658–670. doi:10.1002/jnr.23275
Kleiber ML, Diehl EJ, Laufer BI, Mantha K, Chokroborty-Hoque A, Alberry B, Singh SM (2014) Long-term genomic and epigenomic dysregulation as a consequence of prenatal alcohol exposure: a model for fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. Front Genet 5:161. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00161
Kim P, Park JH, Choi CS, Choi I, Joo SH, Kim MK, Kim SY, Kim KC, Park SH, Kwon KJ, Lee J, Han SH, Ryu JH, Cheong JH, Han JY, Ko KN, Shin CY (2013) Effects of ethanol exposure during early pregnancy in hyperactive, inattentive and impulsive behaviors and MeCP2 expression in rodent offspring. Neurochem Res 38(3):620–631. doi:10.1007/s11064-012-0960-5
Perkins A, Lehmann C, Lawrence RC, Kelly SJ (2013) Alcohol exposure during development: impact on the epigenome. Int J Dev Neurosci 31(6):391–397. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.03.010
Chen WG, Chang Q, Lin Y, Meissner A, West AE, Griffith EC, Jaenisch R, Greenberg ME (2003) Derepression of BDNF transcription involves calcium-dependent phosphorylation of MeCP2. Science 302(5646):885–889. doi:10.1126/science.1086446
Martinowich K, Hattori D, Wu H, Fouse S, He F, Hu Y, Fan G, Sun YE (2003) DNA methylation-related chromatin remodeling in activity-dependent BDNF gene regulation. Science 302(5646):890–893. doi:10.1126/science.1090842
Horike S, Cai S, Miyano M, Cheng JF, Kohwi-Shigematsu T (2005) Loss of silent-chromatin looping and impaired imprinting of DLX5 in Rett syndrome. Nat Genet 37(1):31–40. doi:10.1038/ng1491
Tuncdemir SN, Fishell G, Batista-Brito R (2015) miRNAs are essential for the survival and maturation of cortical interneurons. Cereb Cortex 25(7):1842–1857. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht426
Gardiner AS, Gutierrez HL, Luo L, Davies S, Savage DD, Bakhireva LN, Perrone-Bizzozero NI (2016) Alcohol use during pregnancy is associated with specific alterations in microRNA levels in maternal serum. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40(4):826–837. doi:10.1111/acer.13026
Balaraman S, Lunde ER, Sawant O, Cudd TA, Washburn SE, Miranda RC (2014) Maternal and neonatal plasma microRNA biomarkers for fetal alcohol exposure in an ovine model. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(5):1390–1400. doi:10.1111/acer.12378
Guo Y, Chen Y, Carreon S, Qiang M (2012) Chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and its removal induce a different miRNA expression pattern in primary cortical neuronal cultures. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 36(6):1058–1066. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01689.x
Ignacio C, Mooney SM, Middleton FA (2014) Effects of Acute Prenatal Exposure to Ethanol on microRNA Expression are Ameliorated by Social Enrichment. Front Pediatr 2:103. doi:10.3389/fped.2014.00103
Miranda RC, Pietrzykowski AZ, Tang Y, Sathyan P, Mayfield D, Keshavarzian A, Sampson W, Hereld D (2010) MicroRNAs: master regulators of ethanol abuse and toxicity? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 34(4):575–587. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01126.x
Sathyan P, Golden HB, Miranda RC (2007) Competing interactions between micro-RNAs determine neural progenitor survival and proliferation after ethanol exposure: evidence from an ex vivo model of the fetal cerebral cortical neuroepithelium. J Neurosci 27(32):8546–8557. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1269-07.2007
Wang LL, Zhang Z, Li Q, Yang R, Pei X, Xu Y, Wang J, Zhou SF, Li Y (2009) Ethanol exposure induces differential microRNA and target gene expression and teratogenic effects which can be suppressed by folic acid supplementation. Hum Reprod 24(3):562–579. doi:10.1093/humrep/den439
Marin O, Rubenstein JL (2003) Cell migration in the forebrain. Annu Rev Neurosci 26:441–483. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.26.041002.131058
Metin C, Baudoin JP, Rakic S, Parnavelas JG (2006) Cell and molecular mechanisms involved in the migration of cortical interneurons. Eur J Neurosci 23(4):894–900. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04630.x
Powell EM, Mars WM, Levitt P (2001) Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor is a motogen for interneurons migrating from the ventral to dorsal telencephalon. Neuron 30(1):79–89
Polleux F, Whitford KL, Dijkhuizen PA, Vitalis T, Ghosh A (2002) Control of cortical interneuron migration by neurotrophins and PI3-kinase signaling. Development 129(13):3147–3160
Canty AJ, Dietze J, Harvey M, Enomoto H, Milbrandt J, Ibanez CF (2009) Regionalized loss of parvalbumin interneurons in the cerebral cortex of mice with deficits in GFRalpha1 signaling. J Neurosci 29(34):10695–10705. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2658-09.2009
Pozas E, Ibanez CF (2005) GDNF and GFRalpha1 promote differentiation and tangential migration of cortical GABAergic neurons. Neuron 45(5):701–713. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2005.01.043
Ceccanti M, Mancinelli R, Tirassa P, Laviola G, Rossi S, Romeo M, Fiore M (2012) Early exposure to ethanol or red wine and long-lasting effects in aged mice. A study on nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor. Neurobiol Aging 33(2):359–367. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.03.005
Tyler CR, Allan AM (2014) Prenatal alcohol exposure alters expression of neurogenesis-related genes in an ex vivo cell culture model. Alcohol 48(5):483–492. doi:10.1016/j.alcohol.2014.06.001
Heaton MB, Mitchell JJ, Paiva M, Walker DW (2000) Ethanol-induced alterations in the expression of neurotrophic factors in the developing rat central nervous system. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 121(1):97–107
Light KE, Brown DP, Newton BW, Belcher SM, Kane CJ (2002) Ethanol-induced alterations of neurotrophin receptor expression on Purkinje cells in the neonatal rat cerebellum. Brain Res 924(1):71–81
Ahmadiantehrani S, Barak S, Ron D (2014) GDNF is a novel ethanol-responsive gene in the VTA: implications for the development and persistence of excessive drinking. Addict Biol 19(4):623–633. doi:10.1111/adb.12028
Sanchez Vega MC, Chong S, Burne TH (2013) Early gestational exposure to moderate concentrations of ethanol alters adult behaviour in C57BL/6 J mice. Behav Brain Res 252:326–333. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2013.06.003
Diaz MR, Vollmer CC, Zamudio-Bulcock PA, Vollmer W, Blomquist SL, Morton RA, Everett JC, Zurek AA, Yu J, Orser BA, Valenzuela CF (2014) Repeated intermittent alcohol exposure during the third trimester-equivalent increases expression of the GABA(A) receptor delta subunit in cerebellar granule neurons and delays motor development in rats. Neuropharmacology 79:262–274. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.11.020
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my sincere thanks and appreciation to Dr. Seena Ajit, Drexel University College of Medicine for her continuous support and encouragement. I acknowledge the help of Diana Winters in editing the review. The author is a recipient of the Fulbright Foreign Student Program fellowship funded by the US Department of State, Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs and Dean’s Fellowship for Excellence in Collaborative or Themed Research, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences and Professional Studies, Drexel University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shenoda, B.B. An Overview of the Mechanisms of Abnormal GABAergic Interneuronal Cortical Migration Associated with Prenatal Ethanol Exposure. Neurochem Res 42, 1279–1287 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2169-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2169-5