Abstract
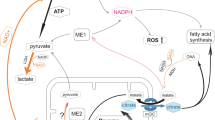
Citrate is key constituent of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, serves as substrate for fatty acid and sterol biosynthesis, and functions as a key regulator of intermediary energy metabolism. Ursula Sonnewald had initiated studies using for the first time both proton- and 13C-NMR to investigate metabolic processes in cultured neurons and astrocytes resulting in the important observation that citrate was specifically synthesized in and released from astrocytes in large amounts which is in keeping with the high concentration found in the CSF. The aim of this review is to highlight the possible roles of citrate in physiological and pathophysiological processes in the CNS. An interesting feature of citrate is its ability to chelate Ca2+, Mg2+ and Zn2+and thereby playing a pivotal role as an endogenous modulator of glutamate receptors and in particular the NMDA subtypes of these receptors in the CNS. Besides its presence in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) citrate is also found in high amounts in prostate fluid reaching concentrations as high as 180 mM and here Zn2+ seems also to play an important role, which makes prostate cells interesting for comparison of features of citrate and Zn2+ between these cells and cells in the CNS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Srere PA (1992) The molecular physiology of citrate. Curr Top Cell Regul 33:261–275
Glusker JP (1992) Structural aspects of citrate biochemistry. Curr Top Cell Regul 33:169–184
Iacobazzi V, Infantino V (2014) Citrate—new functions for an old metabolite. Biol Chem 395:387–399
Schousboe A, Westergaard N, Waagepetersen HS, Larsson OM, Bakken IJ, Sonnewald U (1997) Trafficking between glia and neurons of TCA cycle intermediates and related metabolites. Glia 21:99–105
Westergaard N, Banke T, Wahl P, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A (1995) Citrate modulates the regulation by Zn2+ of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated channel current and neurotransmitter release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3367–3370
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Krane J, Unsgard G, Petersen SB, Schousboe A (1991) First direct demonstration of preferential release of citrate from astrocytes using [13C]NMR spectroscopy of cultured neurons and astrocytes. Neurosci Lett 128:235–239
Sonnewald U, Risan AG, Hole HB, Westergaard N, Qu H (2002) Citrate, beneficial or deleterious in the CNS? Neurochem Res 27:155–159
Mycielska ME, Milenkovic VM, Wetzel CH, Rummele P, Geissler EK (2015) Extracellular citrate in health and disease. Curr Mol Med 15:884–891
Sonnewald U, Petersen SB, Krane J, Westergaard N, Schousboe A (1992) 1 H NMR study of cortex neurons and cerebellar granule cells on microcarriers and their PCA extracts: lactate production under hypoxia. Magn Reson Med 23:166–171
Badar-Goffer RS, Bachelard HS, Morris PG (1990) Cerebral metabolism of acetate and glucose studied by 13 C-n.m.r. spectroscopy. A technique for investigating metabolic compartmentation in the brain. Biochem J 266:133–139
Schousboe A, Walls AB, Bak LK, Waagepetersen HS (2015) Astroglia and brain metabolism: focus on energy and neurotransmitter amino acid homeostasis. In: Verkhratsky A, Parpura V (eds) Colloquium series onneuroglia in biology and medicine from physiology to disease. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences, San Rafael, pp 1–63
Fonnum F, Johnsen A, Hassel B (1997) Use of fluorocitrate and fluoroacetate in the study of brain metabolism. Glia 21:106–113
Hassel B, Westergaard N, Schousboe A, Fonnum F (1995) Metabolic differences between primary cultures of astrocytes and neurons from cerebellum and cerebral cortex. Effects of fluorocitrate. Neurochem Res 20:413–420
Hassel B, Bachelard H, Jones P, Fonnum F, Sonnewald U (1997) Trafficking of amino acids between neurons and glia in vivo. Effects of inhibition of glial metabolism by fluoroacetate. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:1230–1238
Miyake S, Yamashita T, Taniguchi M, Tamatani M, Sato K, Kawai Y, Senba E, Mitsuda N, Hori O, Yamaguchi A, Tohyama M (2002) Expression of mitochondrial tricarboxylate carrier TCC mRNA and protein in the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 100:67–73
Gnoni GV, Priore P, Geelen MJ, Siculella L (2009) The mitochondrial citrate carrier: metabolic role and regulation of its activity and expression. IUBMB Life 61:987–994
Munday MR (2002) Regulation of mammalian acetyl-CoA carboxylase. Biochem Soc Trans 30:1059–1064
Lopes-Cardozo M, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (1986) Acetoacetate and glucose as lipid precursors and energy substrates in primary cultures of astrocytes and neurons from mouse cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 46:773–778
Schmoll D, Fuhrmann E, Gebhardt R, Hamprecht B (1995) Significant amounts of glycogen are synthesized from 3-carbon compounds in astroglial primary cultures from mice with participation of the mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase isoenzyme. Eur J Biochem 227:308–315
Nieweg K, Schaller H, Pfrieger FW (2009) Marked differences in cholesterol synthesis between neurons and glial cells from postnatal rats. J Neurochem 109:125–134
Yu AC, Drejer J, Hertz L, Schousboe A (1983) Pyruvate carboxylase activity in primary cultures of astrocytes and neurons. J Neurochem 41:1484–1487
Shank RP, Bennett GS, Freytag SO, Campbell GL (1985) Pyruvate carboxylase: an astrocyte-specific enzyme implicated in the replenishment of amino acid neurotransmitter pools. Brain Res 329:364–367
Lovatt D, Sonnewald U, Waagepetersen HS, Schousboe A, He W, Lin JH, Han X, Takano T, Wang S, Sim FJ, Goldman SA, Nedergaard M (2007) The transcriptome and metabolic gene signature of protoplasmic astrocytes in the adult murine cortex. J Neurosci 27:12255–12266
Murin R, Cesar M, Kowtharapu BS, Verleysdonk S, Hamprecht B (2009) Expression of pyruvate carboxylase in cultured oligodendroglial, microglial and ependymal cells. Neurochem Res 34:480–489
Westergaard N, Sonnewald U, Unsgard G, Peng L, Hertz L, Schousboe A (1994) Uptake, release, and metabolism of citrate in neurons and astrocytes in primary cultures. J Neurochem 62:1727–1733
Westergaard N, Sonnewald U, Schousboe A (1994) Release of alpha-ketoglutarate, malate and succinate from cultured astrocytes: possible role in amino acid neurotransmitter homeostasis. Neurosci Lett 176:105–109
Yodoya E, Wada M, Shimada A, Katsukawa H, Okada N, Yamamoto A, Ganapathy V, Fujita T (2006) Functional and molecular identification of sodium-coupled dicarboxylate transporters in rat primary cultured cerebrocortical astrocytes and neurons. J Neurochem 97:162–173
Sonnewald U, Westergaard N, Schousboe A, Svendsen JS, Unsgard G, Petersen SB (1993) Direct demonstration by [13C]NMR spectroscopy that glutamine from astrocytes is a precursor for GABA synthesis in neurons. Neurochem Int 22:19–29
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2001) Multiple compartments with different metabolic characteristics are involved in biosynthesis of intracellular and released glutamine and citrate in astrocytes. Glia 35:246–252
Meshitsuka S, Aremu DA (2008) (13)C heteronuclear NMR studies of the interaction of cultured neurons and astrocytes and aluminum blockade of the preferential release of citrate from astrocytes. J Biol Inorg Chem 13:241–247
Kaufman EE, Driscoll BF (1992) Carbon dioxide fixation in neuronal and astroglial cells in culture. J Neurochem 58:258–262
Petroff OA, Yu RK, Ogino T (1986) High-resolution proton magnetic resonance analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurochem 47:1270–1276
Levine J, Panchalingam K, Rapoport A, Gershon S, McClure RJ, Pettegrew JW (2000) Increased cerebrospinal fluid glutamine levels in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:586–593
Musteata M, Nicolescu A, Solcan G, Deleanu C (2013) The 1 H NMR profile of healthy dog cerebrospinal fluid. PLoS ONE 8:e81192
Monaghan DT, Jane DE (2009) Pharmacology of NMDA receptors. In: Van Dongen AM (ed) Biology of the NMDA receptor. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Clarke DD (1991) Fluoroacetate and fluorocitrate: mechanism of action. Neurochem Res 16:1055–1058
Goldberg ND, Passonneau JV, Lowry OH (1966) Effects of changes in brain metabolism on the levels of citric acid cycle intermediates. J Biol Chem 241:3997–4003
Hassel B, Sonnewald U, Unsgard G, Fonnum F (1994) NMR spectroscopy of cultured astrocytes: effects of glutamine and the gliotoxin fluorocitrate. J Neurochem 62:2187–2194
Hornfeldt CS, Larson AA (1990) Seizures induced by fluoroacetic acid and fluorocitric acid may involve chelation of divalent cations in the spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol 179:307–313
Harrison NL, Gibbons SJ (1994) Zn2+: an endogenous modulator of ligand- and voltage-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 33:935–952
Salazar G, Craige B, Love R, Kalman D, Faundez V (2005) Vglut1 and ZnT3 co-targeting mechanisms regulate vesicular zinc stores in PC12 cells. J Cell Sci 118:1911–1921
Smidt K, Rungby J (2012) ZnT3: a zinc transporter active in several organs. Biometals 25:1–8
Assaf SY, Chung SH (1984) Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature 308:734–736
Howell GA, Welch MG, Frederickson CJ (1984) Stimulation-induced uptake and release of zinc in hippocampal slices. Nature 308:736–738
Charton G, Rovira C, Ben-Ari Y, Leviel V (1985) Spontaneous and evoked release of endogenous Zn2+ in the hippocampal mossy fiber zone of the rat in situ. Exp Brain Res 58:202–205
Peters S, Koh J, Choi DW (1987) Zinc selectively blocks the action of N-methyl-D-aspartate on cortical neurons. Science 236:589–593
Eimerl S, Schramm M (1993) Potentiation of 45Ca uptake and acute toxicity mediated by the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor: the effect of metal binding agents and transition metal ions. J Neurochem 61:518–525
Smart TG, Xie X, Krishek BJ (1994) Modulation of inhibitory and excitatory amino acid receptor ion channels by zinc. Prog Neurobiol 42:393–441
Radford RJ, Lippard SJ (2013) Chelators for investigating zinc metalloneurochemistry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17:129–136
Mayer ML, Vyklicky L Jr, Westbrook GL (1989) Modulation of excitatory amino acid receptors by group IIB metal cations in cultured mouse hippocampal neurones. J Physiol 415:329–350
Rassendren FA, Lory P, Pin JP, Nargeot J (1990) Zinc has opposite effects on NMDA and non-NMDA receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron 4:733–740
Koh JY, Choi DW (1988) Zinc alters excitatory amino acid neurotoxicity on cortical neurons. J Neurosci 8:2164–2171
Larson AA, Kitto KF (1999) Chelation of zinc in the extracellular area of the spinal cord, using ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium-calcium salt or dipicolinic acid, inhibits the antinociceptive effect of capsaicin in adult mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:759–765
Wong EH, Kemp JA, Priestley T, Knight AR, Woodruff GN, Iversen LL (1986) The anticonvulsant MK-801 is a potent N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7104–7108
Kavanagh JP (1994) Isocitric and citric acid in human prostatic and seminal fluid: implications for prostatic metabolism and secretion. Prostate 24:139–142
Franklin RB, Ma J, Zou J, Guan Z, Kukoyi BI, Feng P, Costello LC (2003) Human ZIP1 is a major zinc uptake transporter for the accumulation of zinc in prostate cells. J Inorg Biochem 96:435–442
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2016) A comprehensive review of the role of zinc in normal prostate function and metabolism; and its implications in prostate cancer. Arch Biochem Biophys 611:100–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westergaard, N., Waagepetersen, H.S., Belhage, B. et al. Citrate, a Ubiquitous Key Metabolite with Regulatory Function in the CNS. Neurochem Res 42, 1583–1588 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2159-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2159-7