Abstract
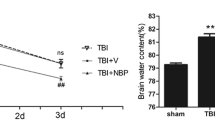
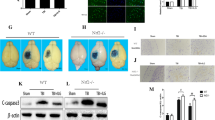
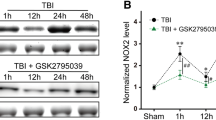
Previous studies have indicated oxidative stress and inflammatory injury as significant contributors to the secondary damage associated with traumatic brain injury (TBI). Ursolic acid (UA) has been demonstrated to exert anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects on cerebral ischemia by activating the nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway. However, the effects of UA on TBI remain unclear. The aim of this study is to evaluate the potential roles of UA in the activation of the Nrf2 pathway using an experimental TBI model and the underlying mechanism. Wild-type (WT) and Nrf2(−/−) mice were divided into eight groups: (1) sham; (2) TBI; (3) TBI + vehicle; (4) TBI + 50 mg/kg UA; (5) TBI + 100 mg/kg UA; (6) TBI + 150 mg/kg UA; (7) TBI + Nrf2(−/−) + vehicle; (8) TBI + Nrf2(−/−) + UA. All mice underwent the TBI with the exception of the sham group. The neurologic outcomes of the mice were evaluated at 24 h after TBI, as well as the expression of Nrf2, NQO1, HO1,SOD, GPx, and MDA. Treatment of UA significantly ameliorated brain edema and the neurological insufficiencies after TBI. In addition, UA treatment markedly strengthened the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 protein and increased the expression of NQO1 and HO1. Moreover, UA significantly increased the expression of AKT, an Nrf2 upstream factor, suggesting that UA play a neuroprotective role through the activation of the Nrf2-ARE signal pathway. On the contrary, UA showed no neuroprotective effect on the Nrf2(−/−) mice. These data indicated that UA increases the activity of antioxidant enzymes and attenuated brain injury via Nrf2 factor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R (2008) Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurol 7:728–741
Werner C, Engelhard K (2007) Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Br J Anaesth 99:4–9
Cornelius C, Crupi R, Calabrese V, Graziano A, Milone P, Pennisi G, Radak Z, Calabrese EJ, Cuzzocrea S (2013) Traumatic brain injury: oxidative stress and neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:836–853
Kobayashi MY, Yamamoto M (2006) Nrf2-Keap1 regulation of cellular defense mechanisms against electrophiles and reactive oxygen species. Adv Enzyme Regul 46:113–140
Kandhare AD, Bodhankar SL, Mohan V, Thakurdesai PA (2015) Effect of glycosides based standardized fenugreek seed extract in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats: decisive role of Bax, Nrf2, NF-kappaB, Muc5ac, TNF-alpha and IL-1beta. Chemi Biol Interact 237:151–165
Wang B, Zhu X, Kim Y, Li J, Huang S, Saleem S, Li RC, Xu Y, Dore S, Cao W (2012) Histone deacetylase inhibition activates transcription factor Nrf2 and protects against cerebral ischemic damage. Free Radic Biol Med 52:928–936
de Vries HE, Witte M, Hondius D, Rozemuller AJ, Drukarch B, Hoozemans J, van Horssen J (2008) Nrf2-induced antioxidant protection: a promising target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in neurodegenerative disease? Free Radic Biol Med 45:1375–1383
Itoh K, Tong KI, Yamamoto M (2004) Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles. Free Radic Biol Med 36:1208–1213
Zhang M, An C, Gao Y, Leak RK, Chen J, Zhang F (2013) Emerging roles of Nrf2 and phase II antioxidant enzymes in neuroprotection. Prog Neurobiol 100:30–47
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Yu F, Chan PH (2006) Akt/GSK3beta survival signaling is involved in acute brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Stroke 37:2140–2146
Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F, de Bono JS, Workman P (2008) Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8:393–412
Xu Y, Duan C, Kuang Z, Hao Y, Jeffries JL, Lau GW (2013) Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyocyanin activates NRF2-ARE-mediated transcriptional response via the ROS-EGFR-PI3K-AKT/MEK-ERK MAP kinase signaling in pulmonary epithelial cells. PLoS One 8:e72528
Gong YQ, Huang W, Li KR, Liu YY, Cao GF, Cao C, Jiang Q (2016) SC79 protects retinal pigment epithelium cells from UV radiation via activating Akt-Nrf2 signaling. Oncotarget 7:60123–60132
Lee YJ, Jeong HY, Kim YB, Lee YJ, Won SY, Shim JH, Cho MK, Nam HS, Lee SH (2012) Reactive oxygen species and PI3K/Akt signaling play key roles in the induction of Nrf2-driven heme oxygenase-1 expression in sulforaphane-treated human mesothelioma MSTO-211 H cells. Food Chem Toxicol 50:116–123
Baskaran R, Poornima P, Priya LB, Huang CY, Padma VV (2016) Neferine prevents autophagy induced by hypoxia through activation of Akt/mTOR pathway and Nrf2 in muscle cells. Biomed Pharmacother 83:1407–1413
Liu DY, Zhang YL, Wei YZ, Liu GY, Liu YF, Gao QM, Zou LP, Zeng WJ, Zhang N (2016) Activation of AKT pathway by Nrf2/PDGFA feedback loop contributes to HCC progression. Oncotarget. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11700
Cui T, Li JZ, Kayahara H, Ma L, Wu LX, Nakamura K (2006) Quantification of the polyphenols and triterpene acids in chinese hawthorn fruit by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 54:4574–4581
Yang Y, Li C, Xiang X, Dai Z, Chang J, Zhang M, Cai H, Zhang H, Zhang M, Guo Y, Wu Z (2014) Ursolic acid prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis induced by heat stress in mouse cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 67:103–111
Wang X, Zhang F, Yang L, Mei Y, Long H, Zhang X, Zhang J, Qimuge S, Su X (2011) Ursolic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:419343
Lee J, Lee HI, Seo KI, Cho HW, Kim MJ, Park EM, Lee MK (2014) Effects of ursolic acid on glucose metabolism, the polyol pathway and dyslipidemia in non-obese type 2 diabetic mice. Indian J Exp Biol 52:683–691
Flierl MA, Stahel PF, Beauchamp KM, Morgan SJ, Smith WR, Shohami E (2009) Mouse closed head injury model induced by a weight-drop device. Nat Protoc 4:1328–1337
Li L, Zhang X, Cui L, Wang L, Liu H, Ji H, Du Y (2013) Ursolic acid promotes the neuroprotection by activating Nrf2 pathway after cerebral ischemia in mice. Brain Res 1497:32–39
Zhang T, Su J, Guo B, Zhu T, Wang K, Li X (2014) Ursolic acid alleviates early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage by suppressing TLR4-mediated inflammatory pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 23:585–591
Beni-Adani L, Bassan M, Gibney G, Berenneman DE, Gozes J, Shohami E (2000) Activity-dependent neurotrophic protein is neuroprotective in a mouse model of closed head injury [abstract]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:57–63
Wei W, Wang H, Wu Y, Ding K, Li T, Cong Z, Xu J, Zhou M, Huang L, Ding H, Wu H (2015) Alpha lipoic acid inhibits neural apoptosis via a mitochondrial pathway in rats following traumatic brain injury. Neurochem Int 87:85–91
Xu J, Wang H, Ding K, Zhang L, Wang C, Li T, Wei W, Lu X (2014) Luteolin provides neuroprotection in models of traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 71:186–195
Ding K, Wang H, Xu J, Li T, Zhang L, Ding Y, Zhu L, He J, Zhou M (2014) Melatonin stimulates antioxidant enzymes and reduces oxidative stress in experimental traumatic brain injury: the Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway as a potential mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med 73:1–11
Rodriguez-Rodriguez A, Egea-Guerrero JJ, Murillo-Cabezas F, Carrillo-Vico A (2014) Oxidative stress in traumatic brain injury. Curr Med Chem 21:1201–1211
Smith JA, Park S, Krause JS, Banik NL (2013) Oxidative stress, DNA damage, and the telomeric complex as therapeutic targets in acute neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int 62:764–775
Ansari MA, Roberts KN, Scheff SW (2008) A time course of contusion-induced oxidative stress and synaptic proteins in cortex in a rat model of TBI. J Neurotrauma 25:513–526
Hou Z, Luo W, Sun X, Hao S, Zhang Y, Xu F, Wang Z, Liu B (2012) Hydrogen-rich saline protects against oxidative damage and cognitive deficits after mild traumatic brain injury. Brain Res Bull 88:560–565
Liu W, Tan X, Shu L, Sun H, Song J, Jin P, Yu S, Sun M, Jia X (2012) Ursolic acid inhibits cigarette smoke extract-induced human bronchial epithelial cell injury and prevents development of lung cancer. Molecules 17:9104–9115
Ma JQ, Ding J, Zhang L, Liu CM (2015) Protective effects of ursolic acid in an experimental model of liver fibrosis through Nrf2/ARE pathway. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 39:188–197
Yan W, Wang HD, Feng XM, Ding YS, Jin W, Tang K (2009) The expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 in the rat brain after traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 66:1431–1435
Miller DM, Wang JA, Buchanan AK, Hall ED (2014) Temporal and spatial dynamics of nrf2-antioxidant response elements mediated gene targets in cortex and hippocampus after controlled cortical impact traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurotrauma 31:1194–1201
Acknowledgments
This study was grant-supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (Grant No. 81371357).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, H., Wang, H., Zhu, L. et al. Ursolic Acid Ameliorates Early Brain Injury After Experimental Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice by Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Neurochem Res 42, 337–346 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2077-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-2077-8