Abstract
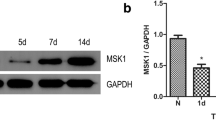
The Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway plays an important role in central and peripheral neurons in functions such as dendritic arborization, neuronal polarity, and axon assembly. However, emerging evidence also shows that up-regulation of this signaling pathway may lead to the development of spinal cord injury. The present study aimed to determine the effects of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway inhibition on properties of spinal cord-injured neurons. First, neurons from spinal cord-injured C57BL/6 J mouse pups and sham-operated C57BL/6 J mouse pups were harvested. Then, immunofluorescence, western blotting, cell adhesion and cell migration assays, and DiI labeling were employed to investigate the effect of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway inhibition on spinal cord-injured neurons. Immunofluorescence results of synapse formation indicated that the experimental spinal cord injury model was successfully established. Western blot results identified upregulated Erk phosphorylation in the spinal cord-injured neurons, and also showed that U0126 inhibited phosphorylation of Erk, which is a downstream kinase in the Ras/Raf signaling pathway. Additionally, cell migration and adhesion was significantly increased in the spinal cord-injured neurons. DiI labeling results also showed an increased formation of mature spines after inhibition of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling. Taken together, these results suggested that the Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway could serve as an effective treatment target for spinal cord injury.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knoller N, Auerbach G, Fulga V, Zelig G, Attias J, Bakimer R, Marder JB, Yoles E, Belkin M, Schwartz M, Hadani M (2005) Clinical experience using incubated autologous macrophages as a treatment for complete spinal cord injury: phase I study results. J Neurosurg Spine 3:173–181
Jones LL, Oudega M, Bunge MB, Tuszynski MH (2001) Neurotrophic factors, cellular bridges and gene therapy for spinal cord injury. J Physiol 533:83–89
Christie KJ, Zochodne D (2013) Peripheral axon regrowth: new molecular approaches. Neuroscience 240:310–324
Cui Q (2006) Actions of neurotrophic factors and their signaling pathways in neuronal survival and axonal regeneration. Mol Neurobiol 33:155–179
Chan KM, Gordon T, Zochodne DW, Power HA (2014) Improving peripheral nerve regeneration: from molecular mechanisms to potential therapeutic targets. Exp Neurol 261:826–835
Mazzoni IE, Said FA, Aloyz R, Miller FD, Kaplan D (1999) Ras regulates sympathetic neuron survival by suppressing the p53-mediated cell death pathway. J Neurosci 19:9716–9727
Arevalo JC, Wu SH (2006) Neurotrophin signaling: many exciting surprises! Cell Mol Life Sci: CMLS 63:1523–1537
Huang EJ, Reichardt LF (2001) Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:677–736
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129:1261–1274
Atwal JK, Massie B, Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2000) The TrkB-Shc site signals neuronal survival and local axon growth via MEK and P13-kinase. Neuron 27:265–277
Namikawa K, Honma M, Abe K, Takeda M, Mansur K, Obata T, Miwa A, Okado H, Kiyama H (2000) Akt/protein kinase B prevents injury-induced motoneuron death and accelerates axonal regeneration. J Neurosci 20:2875–2886
Sun Z, Wen Y, Mao Q, Hu L, Li H, Sun Z, Wang D (2010) [Adenosine-triphosphate promoting repair of spinal cord injury by activating mammalian target of rapamycin/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 signal pathway in rats]. Zhongguo xiu fu chong jian wai ke za zhi = Zhongguo xiufu chongjian waike zazhi. Chin J Repar Reconstr Surg 24:165–171
Kanno H, Ozawa H, Sekiguchi A, Yamaya S, Tateda S, Yahata K, Itoi E (2012) The role of mTOR signaling pathway in spinal cord injury. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex) 11:3175–3179
Bramanti V, Grasso S, Tibullo D, Giallongo C, Raciti G, Viola M, Avola R (2015) Modulation of extracellular signal-related kinase, cyclin D1, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and vimentin expression in estradiol-pretreated astrocyte cultures treated with competence and progression growth factors. J Neurosci Res 93:1378–1387
Leevers SJ, Marshall CJ (1992) Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J 11:569–574
Bramanti V, Grasso S, Tibullo D, Giallongo C, Pappa R, Brundo MV, Tomassoni D, Viola M, Amenta F, Avola R (2016) Neuroactive molecules and growth factors modulate cytoskeletal protein expression during astroglial cell proliferation and differentiation in culture. J Neurosci Res 94:90–98
Li G, Marlin MC (2015) Rab family of GTPases. Methods Mol Biol (Clifton, NJ) 1298:1–15
Liu A, Prenger MS, Norton DD, Mei L, Kusiak JW, Bai G (2001) Nerve growth factor uses Ras/ERK and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascades to up-regulate the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor 1 promoter. J Biol Chem 276:45372–45379
Lo LW, Cheng JJ, Chiu JJ, Wung BS, Liu YC, Wang DL (2001) Endothelial exposure to hypoxia induces Egr-1 expression involving PKCalpha-mediated Ras/Raf-1/ERK1/2 pathway. J Cell Physiol 188:304–312
Guaiquil VH, Pan Z, Karagianni N, Fukuoka S, Alegre G, Rosenblatt MI (2014) VEGF-B selectively regenerates injured peripheral neurons and restores sensory and trophic functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:17272–17277
Lesuisse C, Martin LJ (2002) Immature and mature cortical neurons engage different apoptotic mechanisms involving caspase-3 and the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:935–950
Stanciu M, Wang Y, Kentor R, Burke N, Watkins S, Kress G, Reynolds I, Klann E, Angiolieri MR, Johnson JW, DeFranco DB (2000) Persistent activation of ERK contributes to glutamate-induced oxidative toxicity in a neuronal cell line and primary cortical neuron cultures. J Biol Chem 275:12200–12206
Minano A, Xifro X, Perez V, Barneda-Zahonero B, Saura CA, Rodriguez-Alvarez J (2008) Estradiol facilitates neurite maintenance by a Src/Ras/ERK signalling pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci 39:143–151
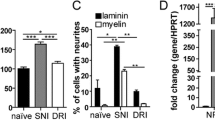
Cao FJ, Zhang X, Liu T, Li XW, Malik M, Feng SQ (2013) Up-regulation of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling in the spinal cord impairs neural cell migration, neurogenesis, synapse formation, and dendritic spine development. Chin Med J 126:3879–3885
Yang K, Cao F, Sheikh AM, Malik M, Wen G, Wei H, Ted Brown W, Li X (2013) Up-regulation of Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling impairs cultured neuronal cell migration, neurogenesis, synapse formation, and dendritic spine development. Brain Struct Funct 218:669–682
Weiss S, Dunne C, Hewson J, Wohl C, Wheatley M, Peterson AC, Reynolds BA (1996) Multipotent CNS stem cells are present in the adult mammalian spinal cord and ventricular neuroaxis. J Neurosci 16:7599–7609
Hering H, Lin CC, Sheng M (2003) Lipid rafts in the maintenance of synapses, dendritic spines, and surface AMPA receptor stability. J Neurosci 23:3262–3271
Jaworski J, Kapitein LC, Gouveia SM, Dortland BR, Wulf PS, Grigoriev I, Camera P, Spangler SA, Di Stefano P, Demmers J, Krugers H, Defilippi P, Akhmanova A, Hoogenraad CC (2009) Dynamic microtubules regulate dendritic spine morphology and synaptic plasticity. Neuron 61:85–100
Hozumi Y, Watanabe M, Otani K, Goto K (2009) Diacylglycerol kinase beta promotes dendritic outgrowth and spine maturation in developing hippocampal neurons. BMC Neurosci 10:99
McKinney BC, Grossman AW, Elisseou NM, Greenough WT (2005) Dendritic spine abnormalities in the occipital cortex of C57BL/6 Fmr1 knockout mice. Am J Med Genet Part B Neuropsychiatr Genet 136b:98–102
Chappell WH, Steelman LS, Long JM, Kempf RC, Abrams SL, Franklin RA, Basecke J, Stivala F, Donia M, Fagone P, Malaponte G, Mazzarino MC, Nicoletti F, Libra M, Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Mijatovic S, Montalto G, Cervello M, Laidler P, Milella M, Tafuri A, Bonati A, Evangelisti C, Cocco L, Martelli AM, McCubrey JA (2011) Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3 K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR inhibitors: rationale and importance to inhibiting these pathways in human health. Oncotarget 2:135–164
Kumar V, Zhang MX, Swank MW, Kunz J, Wu GY (2005) Regulation of dendritic morphogenesis by Ras-PI3 K-Akt-mTOR and Ras-MAPK signaling pathways. J Neurosci 25:11288–11299
Chen J, Rusnak M, Lombroso PJ, Sidhu A (2009) Dopamine promotes striatal neuronal apoptotic death via ERK signaling cascades. Eur J Neurosci 29:287–306
Luo JM, Cen LP, Zhang XM, Chiang SW, Huang Y, Lin D, Fan YM, van Rooijen N, Lam DS, Pang CP, Cui Q (2007) PI3 K/akt, JAK/STAT and MEK/ERK pathway inhibition protects retinal ganglion cells via different mechanisms after optic nerve injury. Eur J Neurosci 26:828–842
Zhou Y, Pernet V, Hauswirth WW, Di Polo A (2005) Activation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway by AAV gene transfer protects retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma. Mol Ther 12:402–412
O’Brien DE, Alter BJ, Satomoto M, Morgan CD, Davidson S, Vogt SK, Norman ME, Gereau GB, Demaro JA 3rd, Landreth GE, Golden JP, Gereau RW 4th (2015) ERK2 alone drives inflammatory pain but cooperates with ERK1 in sensory neuron survival. J Neurosci 35:9491–9507
de Bernardo S, Canals S, Casarejos MJ, Solano RM, Menendez J, Mena MA (2004) Role of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase in neuronal cell death induced by glutathione depletion in neuron/glia mesencephalic cultures. J Neurochem 91:667–682
Lu KT, Cheng NC, Wu CY, Yang YL (2008) NKCC1-mediated traumatic brain injury-induced brain edema and neuron death via Raf/MEK/MAPK cascade. Crit Care Med 36:917–922
Akesson E, Wolmer-Solberg N, Cederarv M, Falci S, Odeberg J (2009) Human neural stem cells and astrocytes, but not neurons, suppress an allogeneic lymphocyte response. Stem Cell Res 2:56–67
Zhong J (2016) RAS and downstream RAF-MEK and PI3K-AKT signaling in neuronal development, function and dysfunction. Biol Chem 397:215–222
Campbell M, Allen WE, Sawyer C, Vanhaesebroeck B, Trimble ER (2004) Glucose-potentiated chemotaxis in human vascular smooth muscle is dependent on cross-talk between the PI3 K and MAPK signaling pathways. Circ Res 95:380–388
Kasai H, Fukuda M, Watanabe S, Hayashi-Takagi A, Noguchi J (2010) Structural dynamics of dendritic spines in memory and cognition. Trends Neurosci 33:121–129
Zoghbi HY (2003) Postnatal neurodevelopmental disorders: meeting at the synapse? Science (New York, NY) 302:826–830
Valiente M, Marin O (2010) Neuronal migration mechanisms in development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:68–78
Shi C, Lu J, Wu W, Ma F, Georges J, Huang H, Balducci J, Chang Y, Huang Y (2011) Endothelial cell-specific molecule 2 (ECSM2) localizes to cell-cell junctions and modulates bFGF-directed cell migration via the ERK-FAK pathway. PLoS ONE 6:e21482
Rico B, Beggs HE, Schahin-Reed D, Kimes N, Schmidt A, Reichardt LF (2004) Control of axonal branching and synapse formation by focal adhesion kinase. Nat Neurosci 7:1059–1069
Knafo S, Esteban JA (2012) Common pathways for growth and for plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 22:405–411
Bos JL (2005) Linking rap to cell adhesion. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17:123–128
Asaki C, Usuda N, Nakazawa A, Kametani K, Suzuki T (2003) Localization of translational components at the ultramicroscopic level at postsynaptic sites of the rat brain. Brain Res 972:168–176
Takei N, Inamura N, Kawamura M, Namba H, Hara K, Yonezawa K, Nawa H (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent local activation of translation machinery and protein synthesis in neuronal dendrites. J Neurosci 24:9760–9769
Luo L (2002) Actin cytoskeleton regulation in neuronal morphogenesis and structural plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:601–635
Bar-Sagi D, Hall A (2000) Ras and Rho GTPases: a family reunion. Cell 103:227–238
Wu GY, Deisseroth K, Tsien RW (2001) Spaced stimuli stabilize MAPK pathway activation and its effects on dendritic morphology. Nat Neurosci 4:151–158
Koh YH, Ruiz-Canada C, Gorczyca M, Budnik V (2002) The Ras1-mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway regulates synaptic plasticity through fasciclin II-mediated cell adhesion. J Neurosci 22:2496–2504
Takahashi H, Yamazaki H, Hanamura K, Sekino Y, Shirao T (2009) Activity of the AMPA receptor regulates drebrin stabilization in dendritic spine morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 122:1211–1219
Patterson MA, Szatmari EM, Yasuda R (2010) AMPA receptors are exocytosed in stimulated spines and adjacent dendrites in a Ras-ERK-dependent manner during long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15951–15956
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation for Young Scholars of China (81401784) and the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (81330042), the Special Program for Sino-Russian Joint Research Sponsored by the Ministry of Science and Technology, China (2014DFR31210), and the Key Program Sponsored by the Tianjin Science and Technology Committee, China (13RCGFSY19000, 14ZCZDSY00044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Dongdong Xu, Fujiang Cao are Co-first authors and contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Cao, F., Sun, S. et al. Inhibition of the Ras/Raf/ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Restores Cultured Spinal Cord-Injured Neuronal Migration, Adhesion, and Dendritic Spine Development. Neurochem Res 41, 2086–2096 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1921-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-016-1921-1