Abstract
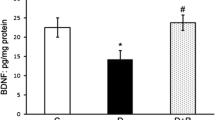
Neurodegeneration is an early event in the diabetic retina which may lead to diabetic retinopathy. One of the potential pathways in damaging retinal neurons is the activation of renin angiotensin system including angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) in the diabetic retina. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of telmisartan, an AT1R blocker on retinal level of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF) and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), glutathione (GSH) and caspase activity in the diabetic rats. The dysregulated levels of these factors are known to cause neurodegeneration in diabetic retina. Three weeks streptozotocin induced diabetic rats were orally treated or untreated with telmisartan (10 mg/kg/day). After 4 weeks of treatments, the levels of BDNF and GSH were found to be increased systemically in the sera as well as in the retina of diabetic rats compared to untreated rats as measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and biochemical techniques (p < 0.05). The caspase-3 activity in the telmisartan treated diabetic retina was decreased compared to untreated diabetic rats (p < 0.05). Western blotting experiments showed the expression levels of BDNF, CNTF and TH were increased compared to untreated diabetic rats (p < 0.05). Thus, our findings show a beneficial effect of AT1R blocker telmisartan in efficiently increasing neurotrophic support, endogenous antioxidant GSH content, and decreasing signs of apoptosis in diabetic retina.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthews DR, Stratton IM, Aldington SJ, Holman RR, Kohner EM (2004) Risks of progression of retinopathy and vision loss related to tight blood pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: UKPDS 69. Arch Ophthalmol 122:1631–1640
Clermont A, Bursell SE, Feener EP (2006) Role of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy: effects of blood pressure control and beyond. J Hypertens Suppl 24:S73–S80
Sjølie AK (2007) Prospects for angiotensin receptor blockers in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1:S31–S39
Gurley SB, Coffman TM (2007) The renin-angiotensin system and diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27:144–152
Satofuka S, Ichihara A, Nagai N, Noda K, Ozawa Y, Fukamizu A, Tsubota K, Itoh H, Oike Y, Ishida S (2009) (Pro)renin receptor-mediated signal transduction and tissue renin-angiotensin system contribute to diabetes-induced retinal inflammation. Diabetes 58:1625–1633
Nagai N, Izumi-Nagai K, Oike Y, Koto T, Satofuka S, Ozawa Y, Yamashiro K, Inoue M, Tsubota K, Umezawa K, Ishida S (2007) Suppression of diabetes-induced retinal inflammation by blocking the angiotensin II type 1 receptor or its downstream nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:4342–4350
Danser AH, van-den-Dorpel MA, Deinum J, Derkx FH, Franken AA, Peperkamp E, de-Jong PT, Schalekamp MA (1989) Renin, prorenin, and immunoreactive renin in vitreous fluid from eyes with and without diabetic retinopathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68:160–167
Funatsu H, Yamashita H, Nakanishi Y, Hori S (2002) Angiotensin II and vascular endothelial growth factor in the vitreous fluid of patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol 86:311–315
Chaturvedi N, Porta M, Klein R, Orchard T, Fuller J, Parving HH, Bilous R, Sjølie AK (2008) DIRECT programme study group: effect of candesartan on prevention (DIRECT-Prevent 1) and progression (DIRECT-Protect 1) of retinopathy in type 1 diabetes: randomised, placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 372:1394–1402
Mauer M, Zinman B, Gardiner R, Suissa S, Sinaiko A, Strand T, Drummond K, Donnelly S, Goodyer P, Gubler MC, Klein R (2009) Renal and retinal effects of enalapril and losartan in type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 361:40–51
Ola MS, Nawaz MI, Siddiquei MM, Al-Amro S, Abu El-Asrar AM (2012) Recent advances in understanding the biochemical and molecular mechanism of diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Complications 26:56–64
Barber AJ, Lieth E, Khin SA, Antonetti DA, Buchanan AG, Gardner TW (1998) Neural apoptosis in the retina during experimental and human diabetes. Early onset and effect of insulin. J Clin Invest 102:783–791
Mohr S, Xi X, Tang J, Kern TS (2002) Caspase activation in retinas of diabetic and galactosemic mice and diabetic patients. Diabetes 51:1172–1179
Kurihara T, Ozawa Y, Nagai N, Shinoda K, Noda K, Imamura Y, Tsubota K, Okano H, Oike Y, Ishida S (2008) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling contributes to synaptophysin degradation and neuronal dysfunction in the diabetic retina. Diabetes 57:2191–2198
Yang H, Hirooka K, Fukuda K, Shiraga F (2009) Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker in a rat model of chronic glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:5800–5804
Kurihara T, Ozawa Y, Shinoda K, Nagai N, Inoue M, Oike Y, Tsubota K, Ishida S, Okano H (2006) Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) blocker, telmisartan, via modulating AT1R and AT2R signaling in retinal inflammation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:5545–5552
Pd S, Drazba J, Shadrach K, Milsted A, Rungger-Brandle E, Nishiyama K, Miura S, Karnik S, Sears JE, Hollyfield JG (2007) Angiotensin II and its receptor subtypes in the human retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:3301–3311
Downie LE, Vessey K, Miller A, Ward MM, Pianta MJ, Vingrys AJ, Wilkinson-Berka JL, Fletcher EL (2009) Neuronal and glial cell expression of angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) and type 2 (AT2) receptors in the rat retina. Neuroscience 161:195–213
Griendling KK, Minieri CA, Ollerenshaw JD, Alexander RW (1994) Angiotensin II stimulates NADH and NADPH oxidase activity in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 74:1141–1148
Chen P, Guo AM, Edwards PA, Trick G, Scicli AG (2007) Role of NADPH oxidase and ANG II in diabetes-induced retinal leukostasis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1619–R1629
Silva KC, Rosales MA, Biswas SK, Lopes-de-Faria JB, Lopes-de-Faria JM (2009) Diabetic retinal neurodegeneration is associated with mitochondrial oxidative stress and is improved by an angiotensin receptor blocker in a model combining hypertension and diabetes. Diabetes 58:1382–1390
Ozawa Y, Kurihara T, Sasaki M, Ban N, Yuki K, Kubota S, Tsubota K (2011) Neural degeneration in the retina of the streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetes model. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:108328
Fujita T, Hirooka K, Nakamura T, Itano T, Nishiyama A, Nagai Y, Shiraga F (2012) Neuroprotective effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1-R) blocker via modulating AT1-R signaling and decreased extracellular glutamate levels. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 53:4099–4110
Kakuta H, Sudoh K, Sasamata M, Yamagishi S (2005) Telmisartan has the strongest binding affinity to angiotensin II type 1 receptor: comparison with other angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers. Int J Clin Pharmacol Res 25(1):41–46
Zou Z, Xi GL, Yuan HB, Zhu QF, Shi XY (2009) Telmisartan versus angiotension-converting enzyme inhibitors in the treatment of hypertension: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Hum Hypertens 23(5):339–349
Sleight P (2009) Clinical evidence from ONTARGET: the value of an angiotensin II receptor blocker and an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. J Hypertens Suppl 27(5):S23–S29
Chan SH, Wu CW, Chang AY, Hsu KS, Chan JY (2010) Transcriptional upregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rostral ventrolateral medulla by angiotensin II: significant in superoxide homeostasis and neural regulation of arterial pressure. Circ Res 107:1127–1139
Kishi T, Hirooka Y, Sunagawa K (2012) Sympathoinhibition caused by orally administeredtelmisartan through inhibition of the AT1 receptor in the rostralventrolateral medulla of hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res PMID: 22948091
Seki M, Tanaka T, Nawa H, Usui T, Fukuchi T, Ikeda K, Abe H, Takei N (2004) Involvement of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in early retinal neuropathy of streptozotocin-induceddiabetes in rats: therapeutic potential of brain-derived neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic amacrine cells. Diabetes 53:2412–2419
Sasaki M, Ozawa Y, Kurihara T, Kubota S, Yuki K, Noda K, Kobayashi S, Ishida S, Tsubota K (2010) Neurodegenerative influence of oxidative stress in the retina of a murine model of diabetes. Diabetologia 53:971–979
Ola MS, Nawaz MI, El-Asrar AA, Abouammoh M, Alhomida AS (2013a) Reduced Levels of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in the Serum of Diabetic Retinopathy Patients and in the Retina of Diabetic Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol PMID: 23271640
Lee TH, Yang JT, Kato H, Wu JH (2006) Hypertension downregulates the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the ischemic-vulnerable hippocampal CA1 and cortical areas after carotid artery occlusion. Brain Res 1116:31–38
Zacchigna S, Lambrechts D, carmeliet P (2008) Neurovascular signalling defects in neurodegeneration. Nat Rev 9:169–181
Pease ME, Zack DJ, Berlinicke C, Bloom K, Cone F, Wang Y, Klein RL, Hauswirth WW, Quigley HA (2009) Effect of CNTF on retinal ganglion cell survival in experimental glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:2194–2200
Grammatopoulos TN, Jones SM, Ahmadi FA, Hoover BR, Snell LD, Skoch J, Jhaveri VV, Poczobutt AM, Weyhenmeyer JA, Zawada WM (2007) Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist losartan, reduces MPTP-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. Mol Neurodegener 15(2):1
Mertens B, Varcin M, Michotte Y, Sarre S (2011) The neuroprotective action of candesartan is related to interference with the early stages of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced dopaminergic cell death. Eur J Neurosci 34:1141–1148
Ola MS, Nawaz MI, Khan HA, Alhomida AS (2013) Neurodegeneration and neuroprotection in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci 14:2559–2572
Miao X, Lv H, Wang B, Chen Q, Miao L, Su G, Tan Y (2013) Deletion of angiotensin II Type 1 receptor gene attenuates chronic alcohol-induced retinal ganglion cell death with preservation of VEGF expression. Curr Eye Res 38:185–193
Wilkinson-Berka JL (2006) Angiotensin and diabetic retinopathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38:752–765
Fletcher EL, Phipps JA, Ward MM, Vessey KA, Wilkinson-Berka JL (2010) The renin-angiotensin system in retinal health and disease: its influence on neurons, glia and the vasculature. Prog Retin Eye Res 29:284–311
Miller AG, Tan G, Binger KJ, Pickering RJ, Thomas MC, Nagaraj RH, Cooper ME, Wilkinson-Berka JL (2010) Candesartan attenuates diabetic retinal vascular pathology by restoring glyoxalase-I function. Diabetes 59:3208–3215
Kagota S, Tada Y, Nejime N, Nakamura K, Kunitomo M, Shinozuka K (2011) Telmisartan provides protection against development of impaired vasodilation independently of metabolic effects in SHRSP.Z-Lepr(fa)/IzmDmcr rats with metabolic syndrome. Can J PhysiolPharmacol 89:355–364
Krikov M, Thone-Reineke C, Müller S, Villringer A, Unger T (2008) Candesartan but not ramipril pretreatment improves outcome after stroke and stimulates neurotrophin BNDF/TrkB system in rats. J Hypertens 26:544–552
Gastinger MJ, Singh RS, Barber AJ (2006) Loss of cholinergic and dopaminergic amacrine cells in streptozotocin-diabetic rat and Ins2Akita-diabetic mouse retinas. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:3143–3150
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge funding from the Deanship of Scientific Research (RGP-VPP-052) at King Saud University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ola, M.S., Ahmed, M.M., Abuohashish, H.M. et al. Telmisartan Ameliorates Neurotrophic Support and Oxidative Stress in the Retina of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Neurochem Res 38, 1572–1579 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1058-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1058-4