Abstract
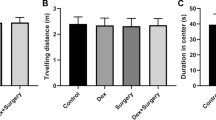
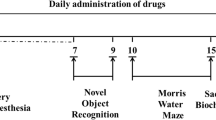
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is very common complication of surgery in aged individuals. Accumulated evidence suggests that neuroinflammation may be the underlying cause of POCD. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of ulinastatin (UTI) on neuroinflammation and on learning and memory of aged rats after anesthesia and surgery. Our results showed that anesthetic isoflurane increased the hippocampal mRNA level of IL-1β, while surgery of partial hepatectomy increased the hippocampal mRNA levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 as well as impaired rats’ spatial memory at day 7 post-surgery. UTI (10,000 U/kg, i.v.) decreased the anesthesia- and surgery-induced increases in mRNA levels of all three cytokines, but did not improve the rats’ impaired working memory. In conclusion, moderate and temporary suppression of UTI-induced inflammatory cytokines in hippocampus is not sufficient to alleviate the impairment of working memory.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dijkstra JB, Houx PJ, Jolles J (1999) Cognition after major surgery in the elderly: test performance and complaints. Br J Anaesth 82:867–874
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse N, Rasmussen LS (2009) Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 110:548–555
Rosczyk HA, Sparkman NL, Johnson RW (2008) Neuroinflammation and cognitive function in aged mice following minor surgery. Exp Gerontol 43:840–846
Newman S, Stygall J, Hirani S, Shaefi S, Maze M (2007) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after noncardiac surgery: a systematic review. Anesthesiology 106:572–590
Canet J, Raeder J, Rasmussen LS, Enlund M, Kuipers HM, Hanning CD, Jolles J, Korttila K, Siersma VD, Dodds C, Abildstrom H, Sneyd JR, Vila P, Johnson T, Munoz Corsini L, Silverstein JH, Nielsen IK, Moller JT (2003) Cognitive dysfunction after minor surgery in the elderly. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 47:1204–1210
Terrando N, Eriksson LI, Kyu Ryu J, Yang T, Monaco C, Feldmann M, Jonsson Fagerlund M, Charo IF, Akassoglou K, Maze M (2011) Resolving postoperative neuroinflammation and cognitive decline. Ann Neurol 70:986–995
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D, Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS, Maze M (2010) Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Ann Neuro 168:360–368
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM, Feldmann M, Maze M (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20518–20522
Cao XZ, Ma H, Wang JK, Liu F, Wu BY, Tian AY, Wang LL, Tan WF (2010) Postoperative cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation in the hippocampus triggered by surgical trauma are exacerbated in aged rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:1426–1432
Fang Y, Xu P, Gu C, Wang Y, Fu XJ, Yu WR, Yao M (2011) Ulinastatin improves pulmonary function in severe burn-induced acute lung injury by attenuating inflammatory response. J Trauma 71:1297–1304
Park KH, Lee KH, Kim H, Hwang SO (2010) The anti-inflammatory effects of ulinastatin in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock. J Korean Med Sci 25:128–134
Tsujino T, Komatsu Y, Isayama H, Hirano K, Sasahira N, Yamamoto N, Toda N, Ito Y, Nakai Y, Tada M, Matsumura M, Yoshida H, Kawabe T, Shiratori Y, Omata M (2005) Ulinastatin for pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a randomized, controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:376–383
Yano T, Anraku S, Nakayama R, Ushijima K (2003) Neuroprotective effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Anesthesiology 98:465–473
Iwama H, Ohmori S, Tsutsumi T (2000) Detectable concentrations of urinary trypsin inhibitor in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 12:29–32
Kamer AR, Galoyan SM, Haile M, Kline R, Boutajangout A, Li YS, Bekker A (2012) Meloxicam improves object recognition memory and modulates glial activation after splenectomy in mice. Eur J Anaesthesiol 29:332–337
He HJ, Wang Y, Le Y, Duan KM, Yan XB, Liao Q, Liao Y, Tong JB, Terrando N, Ouyang W (2012) Surgery upregulates high mobility group box-1 and disrupts the blood-brain barrier causing cognitive dysfunction in aged rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:994–1002
Wuri G, Wang DX, Zhou Y, Zhu SN (2011) Effects of surgical stress on long-term memory function in mice of different ages. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 55:474–485
Peng M, Wang YL, Wang FF, Chen C, Wang CY (2012) The cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor parecoxib inhibits surgery-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in the hippocampus in aged rats. J Surg Res 178:e1–e8
Tanaka H, Hashizume K, Enosawa S, Suzuki S (2003) Successful transplantation of a 20 % partial liver graft in rats: a technical innovation. J Surg Res 110:409–412
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Boost KA, Hofstetter C, Flondor M, Betz C, Homann M, Pfeilschifter J, Muehl H, Zwissler B (2006) Desflurane differentially affects the release of proinflammatory cytokines in plasma and bronchoalveolar fluid of endotoxemic rats. Int J Mol Med 17:1139–1144
Carlson NG, Wieggel WA, Chen J (1999) Inflammatory cytokines IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha impart neuroprotection to an excitotoxin through distinct pathways. J Immunol 163:3963–3968
Bingyang J, Jinping L, Mingzheng L, Guyan W, Zhengyi F (2007) Effects of urinary protease inhibitor on inflammatory response during on-pump coronary revascularisation. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 48:497–503
Steinman L (2010) Modulation of postoperative cognitive decline via blockade of inflammatory cytokines outside the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:20595–20596
Conflict of interest
The Author(s) declare(s) that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Yong-zhe, L., Ya-qun, M. et al. Ulinastatin Alleviates Neuroinflammation but Fails to Improve Cognitive Function in Aged Rats Following Partial Hepatectomy. Neurochem Res 38, 1070–1077 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1018-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1018-z