Abstract
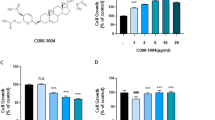
3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) is a compound extracted from Chinese celery and is used as an anti-hypertensive herbal medicine for treating stroke patients. The aim of this study is to demonstrate the effects and mechanisms of this compound through in vitro and in vivo experiments. Culture experiments were performed by adding hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to SH-SY5Y cells. From the MTT assay result, enhanced cell survival was observed with DL-NBP treatment, regardless of whether they are added before, simultaneously with or after the addition of H2O2. For the in vivo experiment, Spontaneously Hypertensive rats and Wistar Kyoto control rats with chronic cerebral ischemia, which were induced by bilateral transection of the common carotid arteries, were given DL-NBP. Their performances in the place navigation test and spatial probe test in the Morris Water Maze have significantly improved compared with the DL-NBP untreated animals, indicating an improvement in spatial learning and memory in the ischemic-animals. In addition, in the chick embryonic chorioallantoic membrane assay, angiogenesis was more vigorous under the effects of DL-NBP, together with increased expression of growth factors, VEGF, VEGF-receptor and bFGF. All these suggested that one of the mechanisms of DL-NBP might be ameliorating vascular dementia and promoting angiogenesis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gironi M, Bianchi A, Russo A, Alberoni M, Ceresa L, Angelini A, Cursano C, Mariani E, Nemni R, Kullmann C, Farina E, Martinelli Boneschi F (2011) Oxidative imbalance in different neurodegenerative diseases with memory impairment. Neurodegener Dis 8:129–137
Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, Decarli C, Greenberg SM, Iadecola C, Launer LJ, Laurent S, Lopez OL, Nyenhuis D, Petersen RC, Schneider JA, Tzourio C, Arnett DK, Bennett DA, Chui HC, Higashida RT, Lindquist R, Nilsson PM, Roman GC, Sellke FW, Seshadri S; American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention, and Council on Cardiovascular Surgery and Anesthesia (2011) Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 42:2672–2713
Román GC (2008) The epidemiology of vascular dementia. Handb Clin Neurol 89:639–658
Harrison DG, Gongora MC (2009) Oxidative stress and hypertension. Med Clin North Am 93:621–635
Bennetta S, Grantb MM, Aldreda S (2009) Oxidative stress in vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a common pathology. J Alzheimers Dis 17:245–257
Zini I, Tomasi A, Grimaldi R, Vannini V, Agnati LF (1992) Detection of free radicals during brain ischemia and reperfusion by spin trapping and microdialysis. Neurosci Lett 138:279–282
Li L, Zhang B, Tao Y, Wang Y, Wei H, Zhao J, Huang R, Pei Z (2009) DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects endothelial cells against oxidative/nitrosative stress, mitochondrial damage and subsequent cell death after oxygen glucose deprivation in vitro. Brain Res 1290:91–101
Bell RD, Zlokovic BV (2009) Neurovascular mechanisms and blood–brain barrier disorder in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 118:103–113
Deng WB, Feng YP (1997) Effect of DL-3-N-Butylphthalide on brain edema in rats subjected to focal cerebral ischemia. Chin Med Sci J 12:102–106
Huang JZ, Chen YZ, Su M, Zheng HF, Yang YP, Chen J, Liu CF (2010) Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide prevents oxidative damage and reduces mitochondrial dysfunction in an MPP+-induced cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 475:89–94
Xiong N, Huang J, Chen C, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Jia M, Zhang Z, Hou L, Yang H, Cao X, Liang Z, Zhang Y, Sun S, Lin Z, Wang T (2011) Dl-3-n-butylphthalide, a natural antioxidant, protects dopamine neurons in rotenone models for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.007
Li J, Li Y, Ogle M, Zhou X, Song M, Yu SP, Wei L (2010) DL-3-n-butylphthalide prevents neuronal cell death after focal cerebral ischemia in mice via the JNK pathway. Brain Res 1359:216–226
Peng Y, Xu SF, Chen G, Wang L, Feng Y, Wang X (2007) l-3-n-Butylphthalide improves cognitive impairment induced by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:902–910
Zhang T, Jia WP, Sun XJ (2010) 3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP) reduces apoptosis and enhances vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) up-regulation in diabetic rats. Neurol Res 32:1–7
Chong Z, Feng Y (1998) Protective effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on changes of regional cerebral blood flow and blood-brain barrier damage following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Chin Med J (Engl) 111:858–860
Li QF, Kong SY, Deji QZ, He L, Zhou D (2008) Effects of dl-3-n-butylphthalide on expression of VEGF and bFGF in rat brain with permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 39:84–88
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song WH (2011) Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. J Vis Exp 53:2920
Kirchner LM, Schmidt SP, Gruber BS (1996) Quantitation of angiogenesis in the chick chorioallantoic membrane model using fractal analysis. Microvasc Res 51:2–14
Watanabe H, Ni JW, Sakai Y, Matsumoto K, Murakami Y, Tohda M (1996) Permanent occlusion of bilateral internal carotid arteries produces cognitive deficits in two learning behavior tasks. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi 16:19–24
Murakami Y, Tanaka E, Sakai Y, Matsumoto K, Li HB, Watanabe H (1997) Tacrine improves working memory deficit caused by permanent occlusion of bilateral common carotid arteries in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 75:443–446
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11(1):47–60
Zeng G, Tang T, Wu HJ, You WH, Luo JK, Lin Y, Liang QH, Li XQ, Huang X, Yang QD (2010) Salvianolic acid B protects SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells from 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium-induced apoptosis. Biol Pharm Bull 33:1337–1342
Majesky MW (1996) A little VEGF goes a long way. Therapeutic angiogenesis by direct injection of vascular endothelial growth factor-encoding plasmid DNA. Circulation 94:3062–3064
Hopkins SP, Bulgrin JP, Sims RL, Bowman B, Donovan DL, Schmidt SP (1998) Controlled delivery of vascular endothelial growth factor promotes neovascularization and maintains limb function in a rabbit model of ischemia. J Vasc Surg 27:886–894
Wei P, Yu FQ, Chen XL, Tao SX, Han CS, Liu YX (2004) VEGF, bFGF and their receptors at the fetal-maternal interface of the rhesus monkey. Placenta 25:184–196
Przybylski M (2009) A review of the current research on the role of bFGF and VEGF in angiogenesis. J Wound Care 18:516–519
Webber MJ, Tongers J, Newcomb CJ, Marquardt KT, Bauersachs J, Losordo DW, Stupp SI (2011) Supramolecular nanostructures that mimic VEGF as a strategy for ischemic tissue repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:13438–13443
Zhang T, Yan W, Li Q, Fu J, Liu K, Jia W, Sun X, Liu X (2011) 3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) attenuated neuronal autophagy and amyloid-beta expression in diabetic mice subjected to brain ischemia. Neurol Res 33:396–404
Wei T, Ni Y, Hou J, Chen C, Zhao B, Xin W (2000) Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis in cerebellar granule cells: protection by Ginkgo biloba extract. Pharmacol Res 41:427–433
Xin W, Wei T, Chen C, Ni Y, Zhao B, Hou J (2000) Mechanisms of apoptosis in rat cerebellar granule cells induced by hydroxyl radicals and the effects of EGb761 and its constituents. Toxicology 148:103–110
Shi C, Yao Z, Xu J, Yew DT (2009) Effects of Ginko Extract (EGb761) on oxidative damage under different conditions of serum supply. J Bioenerg Biomembr 41:61–69
Shi C, Zhao L, Zhu B, Li Q, Yew DT, Yao Z, Xu J (2009) Dosage effects of EGb761 on hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact 180:389–397
Shi C, Wu F, Yew DT, Xu J, Zhu Y (2010) Bilobalide prevents apoptosis through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Apoptosis 15:715–727
Lestage P, Lockhart B, Roger A (2002) In vivo exploration of cerebral ischemia: use of neuroprotective agents in animal studies. Terapie 57:554–563
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Shijiazhuang Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. (Project Ref. No. 7010062).
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Lü, L., Chan, W.M. et al. Effects of DL-3-n-Butylphthalide on Vascular Dementia and Angiogenesis. Neurochem Res 37, 911–919 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0663-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-011-0663-3