Abstract
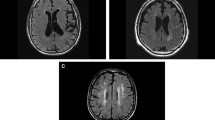
Supratentorial white matter is an important part of the brain and a major site of detrimental effects after whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT). It is not known if prevalence of metastases in white matter justifies standard inclusion of white matter in whole brain treatment. In this retrospective analysis we examined the frequency of metastasis in supratentorial deep cerebral white matter with cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Deep white matter (DWM) was defined as white matter in corpus callosum with forceps anterior and posterior and centrum semiovale. Lesions extending from grey matter, gyrus or ventricles into white matter were not classified as DWM metastases. Brain MRI of 198 patients from two centres were analyzed. In total 1330 metastases were counted and only 4.6 % were located in DWM. Metastases in DWM were small (median diameter 6 mm). Only 1/41 patients (2 %) with a singular metastasis had a DWM metastasis, 2/35 patients (6 %) with 2 metastases had a DWM metastasis, 14/79 patients (18 %) with 3–9 metastases and 12/43 patients (28 %) with >9 metastases had a single or more DWM metastases (p = 0.003). There appeared to be tumor related differences with renal cell carcinoma showing significantly more DWM metastasis (6/17, 35 %), than NSCLC (11/85, 13 %, p = 0.024), breast cancer (1/20, 5 %, p = 0.019) or colorectal cancer (0/10, 0 %, p = 0.033). Overall, relevant preservation of DWM from metastases, especially in oligometastatic disease, was shown. This implies that DWM in patients with only few brain metastases is unnecessarily damaged by conventional WBRT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soffietti R, Ruda R, Mutani R (2002) Management of brain metastases. J Neurol 10:1357–1369
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT, Posner JB (1988) Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol 7:741–744
Ge Y, Grossman RI, Babb JS, Rabin ML, Mannon LJ, Kolson DL (2002) Age-related total gray matter and white matter changes in normal adult brain. Part I: volumetric MR imaging analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 8:1327–1333
Klein B, Kuschinsky W, Schrock H, Vetterlein F (1986) Interdependency of local capillary density, blood flow, and metabolism in rat brains. Am J Physiol 6:1333–1340
Ellenbogen RG, Abdulrauf SI, Sekhar N (2012) Principles of neurological surgery. Saunders/Elsevier, Philadelphia
Correa DD, DeAngelis LM, Shi W, Thaler H, Glass A, Abrey LE (2004) Cognitive functions in survivors of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurology 4:548–555
Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, Arbuckle RB, Swint JM, Shiu AS, Maor MH, Meyers CA (2009) Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 11:1037–1044
Soffietti R, Kocher M, Abacioglu UM, Villa S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann R, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge Dirk, Mueller R, Tridello G, Collette L, Bottomley A (2013) A European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: quality-of-life results. J Clin Oncol 1:65–72
Eriksson PS, Perfilieva E, Bjork-Eriksson T, Alborn AM, Nordborg C, Peterson DA, Gage FH (1998) Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat Med 11:1313–1317
Gondi V, Tome WA, Mehta MP (2010) Why avoid the hippocampus? A comprehensive review. Radiother Oncol 3:370–376
DeAngelis LM, Delattre JY, Posner JB (1989) Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 6:789–796
Correa DD, Shi W, Abrey LE, Deangelis LM, Omuro AM, Deutsch MB, Thaler HT (2012) Cognitive functions in primary CNS lymphoma after single or combined modality regimens. Neuro Oncol 1:101–108
Fujii O, Tsujino K, Soejima T, Yoden E, Ichimiya Y, Sugimura K (2006) White matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging following whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases. Radiat Med 5:345–350
Monaco EA, Faraji AH, Berkowitz O, Parry PV, Hadelsberg U, Kano H, Niranjan A, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2013) Leukoencephalopathy after whole-brain radiation therapy plus radiosurgery versus radiosurgery alone for metastatic lung cancer. Cancer 1:226–232
Duffau H (2006) New concepts in surgery of WHO grade II gliomas: functional brain mapping, connectionism and plasticity—a review. J Neurooncol 1:77–115
Ius T, Angelini E, de Schotten Thiebaut, Michel Mandonnet E, Duffau H (2011) Evidence for potentials and limitations of brain plasticity using an atlas of functional resectability of WHO grade II gliomas: towards a “minimal common brain”. Neuroimage 3:992–1000
Irimia A, Horn Van, John D (2014) Systematic network lesioning reveals the core white matter scaffold of the human brain. Front Hum Neurosci 8:51
Jellinger KA (2013) Pathology and pathogenesis of vascular cognitive impairment-a critical update. Front Aging Neurosci 5:17
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 7347:298–307
Donnem T, Hu J, Ferguson M, Adighibe O, Snell C, Harris AL, Gatter KC, Pezzella F (2013) Vessel co-option in primary human tumors and metastases: an obstacle to effective anti-angiogenic treatment? Cancer Med 4:427–436
Adighibe O, Micklem K, Campo L, Ferguson M, Harris A, Pozos R, Gatter K, Pezzella F (2006) Is nonangiogenesis a novel pathway for cancer progression? A study using 3-dimensional tumour reconstructions. Br J Cancer 8:1176–1179
Budde MD, Gold E, Jordan EK, Frank JA (2012) Differential microstructure and physiology of brain and bone metastases in a rat breast cancer model by diffusion and dynamic contrast enhanced MRI. Clin Exp Metastasis 1:51–62
Helfrich I, Scheffrahn I, Bartling S, Weis J, Felbert V, Middleton M, Kato M, Ergün S, Augustin HG, Schadendorf D (2010) Resistance to antiangiogenic therapy is directed by vascular phenotype, vessel stabilization, and maturation in malignant melanoma. J Exp Med 3:491–503
Berghoff AS, Ilhan-Mutlu A, Dinhof C, Magerle M, Hackl M, Widhalm G, Hainfellner JA, Dieckmann K, Pichler J, Hutterer M, Melchardt T, Bartsch R, Zielinski CC, Birner P, Preusser M (2014) Differential role of angiogenesis and tumor cell proliferation in brain metastases according to primary tumor type: analysis of 639 cases. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. doi:10.1111/nan.12185 [Epub ahead of print]
Rades D, Pluemer A, Veninga T, Hanssens P, Dunst J, Schild SE (2007) Whole-brain radiotherapy versus stereotactic radiosurgery for patients in recursive partitioning analysis classes 1 and 2 with 1 to 3 brain metastases. Cancer 10:2285–2292
Kocher M, Soffietti R, Abacioglu U, Villà S, Fauchon F, Baumert BG, Fariselli L, Tzuk-Shina T, Kortmann R, Carrie C, Ben Hassel M, Kouri M, Valeinis E, van den Berge Dirk, Collette S, Collette L, Mueller R (2011) Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of one to three cerebral metastases: results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study. J Clin Oncol 2:134–141
Yamamoto M, Serizawa T, Shuto T, Akabane A, Higuchi Y, Kawagishi J, Yamanaka K, Sato Y, Jokura H, Yomo S, Nagano O, Kenai H, Moriki A, Suzuki S, Kida Y, Iwai Y, Hayashi M, Onishi H, Gondo M, Sato M, Akimitsu T, Kubo K, Kikuchi Y, Shibasaki T, Goto T, Takanashi M, Mori Y, Takakura K, Saeki N, Kunieda E, Aoyama H, Momoshima S, Tsuchiya K (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): a multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncology 4:387–395
Prokic V, Wiedenmann N, Fels F, Schmucker M, Nieder C, Grosu A (2013) Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases: a planning study on treatment concepts. Int J Rad Oncol Biol Physics 1:264–270
Gondi V, Pugh SL, Tome WA, Caine C, Corn B, Kanner A, Rowley H, Kundapur V, DeNittis A, Greenspoon JN, Konski AA, Bauman GS, Shah S, Shi W, Wendland M, Kachnic L, Mehta MP (2014) Preservation of memory with conformal avoidance of the hippocampal neural stem-cell compartment during whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases (RTOG 0933): a phase II multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol 32:3810–3816 [Epub ahead of print]
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Patient data was used anonymized. All patients gave informed consent to the use of their data for research purposes. This article does not contain any clinical studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seidel, C., Hambsch, P., Hering, K. et al. Analysis of frequency of deep white matter metastasis on cerebral MRI. J Neurooncol 123, 135–139 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1773-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1773-6