Abstract
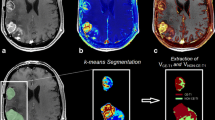
Bevacizumab, an antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor, is commonly used in the setting of recurrent glioblastoma (rGB). The aim of the present study was to evaluate whether dynamic-contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) derived microvascular permeability is related to bevacizumab treatment outcome in rGB. Twenty-two patients with rGB underwent DCE-MRI at a median of 2.6 weeks prior initializing bevacizumab therapy. Follow-up MRI-scans (DCE-MRI available for 19/22 patients) were obtained after a median of 9.9 weeks. The volume transfer constant (Ktrans)—an estimate related to microvascular permeability—at baseline and voxel-wise-reduction (VWR) in Ktrans at first follow-up were measured from the entire contrast-enhancing tumor (CET) and correlated with progression-free and overall survival (PFS, OS) using uni- and multivariate cox-regression (significance-level p < 0.05). Baseline Ktrans ranged from 0.050 to 0.205 min−1 (median, 0.109 min−1). The VWR in Ktrans ranged from 19.9 to 97.2 % (median, 89.4 %). Patients with lower baseline Ktrans and higher VWR in Ktrans showed significantly longer PFS and OS. Given the strong correlation of VWR in Ktrans and CET-volume changes (Spearman’s ρ = −0.73, p < 0.01) both variables were included in a multivariate model. Thereby, neither VWR in Ktrans nor CET-volume changes retained independent significance for PFS or OS. Pre-treatment Ktrans stratifies PFS and OS in patients with bevacizumab-treated rGB. Although early pharmacodynamics changes in Ktrans were not assessed, the VWR in Ktrans at first follow-up had no additional benefit over assessment of CET-volume changes. Further prospective trials are needed to confirm these findings and to elucidate the potential role of pre-treatment Ktrans as a predictive and/or prognostic biomarker.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong ET, Brem S (2008) Antiangiogenesis treatment for glioblastoma multiforme: challenges and opportunities. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 6:515–522
Jain RK, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT (2007) Angiogenesis in brain tumours. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:610–622. doi:10.1038/nrn2175/nrn2175
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972
Leu K, Pope WB, Cloughesy TF, Lai A, Nghiemphu PL, Chen W, Liau LM, Ellingson BM (2013) Imaging biomarkers for antiangiogenic therapy in malignant gliomas. CNS Oncol 2:33–47. doi:10.2217/cns.12.29
O’Connor JP, Jayson GC (2012) Do imaging biomarkers relate to outcome in patients treated with VEGF inhibitors? Clin Cancer Res 18:6588–6598. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1501
Lambrechts D, Lenz HJ, de Haas S, Carmeliet P, Scherer SJ (2013) Markers of response for the antiangiogenic agent bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 31:1219–1230. doi:10.1200/JCO.2012.46.2762
Tofts PS (2010) T1-weighted DCE imaging concepts: modelling, acquisition and analysis. MAGNETOM Flash 3:30–39
Cha S (2006) Update on brain tumor imaging: from anatomy to physiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:475–487
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E, Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozak KR, Cahill DP, Chen PJ, Zhu M, Ancukiewicz M, Mrugala MM, Plotkin S, Drappatz J, Louis DN, Ivy P, Scadden DT, Benner T, Loeffler JS, Wen PY, Jain RK (2007) AZD2171, a pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 11:83–95. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.021
Sorensen AG, Batchelor TT, Zhang WT, Chen PJ, Yeo P, Wang M, Jennings D, Wen PY, Lahdenranta J, Ancukiewicz M, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Jain RK (2009) A “vascular normalization index” as potential mechanistic biomarker to predict survival after a single dose of cediranib in recurrent glioblastoma patients. Cancer Res 69:5296–5300. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0814
Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, Larsson HB, Lee TY, Mayr NA, Parker GJ, Port RE, Taylor J, Weisskoff RM (1999) Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:223–232
Mouridsen K, Christensen S, Gyldensted L, Ostergaard L (2006) Automatic selection of arterial input function using cluster analysis. Magn Reson Med 55:524–531. doi:10.1002/mrm.20759
Murase K (2004) Efficient method for calculating kinetic parameters using T1-weighted dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 51:858–862. doi:10.1002/mrm.20022
Galban CJ, Chenevert TL, Meyer CR, Tsien C, Lawrence TS, Hamstra DA, Junck L, Sundgren PC, Johnson TD, Ross DJ, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2009) The parametric response map is an imaging biomarker for early cancer treatment outcome. Nat Med 15:572–576. doi:10.1038/nm.1919
Flaherty KT, Rosen MA, Heitjan DF, Gallagher ML, Schwartz B, Schnall MD, O’Dwyer PJ (2008) Pilot study of DCE-MRI to predict progression-free survival with sorafenib therapy in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther 7:496–501
Hahn OM, Yang C, Medved M, Karczmar G, Kistner E, Karrison T, Manchen E, Mitchell M, Ratain MJ, Stadler WM (2008) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging pharmacodynamic biomarker study of sorafenib in metastatic renal carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26:4572–4578. doi:10.1200/JCO.2007.15.5655
Hsu CY, Shen YC, Yu CW, Hsu C, Hu FC, Hsu CH, Chen BB, Wei SY, Cheng AL, Shih TT (2011) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers predict survival and response in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with sorafenib and metronomic tegafur/uracil. J Hepatol 55:858–865. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.01.032
Zhu AX, Sahani DV, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Catalano OA, Sindhwani V, Blaszkowsky LS, Yoon SS, Lahdenranta J, Bhargava P, Meyerhardt J, Clark JW, Kwak EL, Hezel AF, Miksad R, Abrams TA, Enzinger PC, Fuchs CS, Ryan DP, Jain RK (2009) Efficacy, safety, and potential biomarkers of sunitinib monotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 27:3027–3035. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.9908
Bjarnson GA, Williams R, Hudson JM, Bailey C, Lee CR, Lloyd BA, Kandel S, Ebos JM, Kiss A, Kerbel RS, Milot LM, Atri M, Stanisz GJ, Burns P (2011) Microbubble ultrasound (DCE-US) compared to DCE-MRI and DCE-CT for the assessment of vascular response to sunitinib in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). J Clin Oncol 29:4627
Zhang W, Kreisl T, Solomon J, Reynolds R, Glen D, Cox R, Fine H, Butman J (2009) Acute effects of bevacizumab on glioblastoma vascularity assessed with DCE-MRI and relation to patient survival. Proc Intl Soc Magn Reson Med 17:282
Verhoeff JJ, Lavini C, van Linde ME, Stalpers LJ, Majoie CB, Reijneveld JC, van Furth WR, Richel DJ (2010) Bevacizumab and dose-intense temozolomide in recurrent high-grade glioma. Ann Oncol 21:1723–1727. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp591
Cha S, Yang L, Johnson G, Lai A, Chen MH, Tihan T, Wendland M, Dillon WP (2006) Comparison of microvascular permeability measurements, K(trans), determined with conventional steady-state T1-weighted and first-pass T2*-weighted MR imaging methods in gliomas and meningiomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:409–417
Nguyen TB, Cron GO, Mercier JF, Foottit C, Torres CH, Chakraborty S, Woulfe J, Jansen GH, Caudrelier JM, Sinclair J, Hogan MJ, Thornhill RE, Cameron IG (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging using a phase-derived vascular input function in the preoperative grading of gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:1539–1545. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3012
Patankar TF, Haroon HA, Mills SJ, Baleriaux D, Buckley DL, Parker GJ, Jackson A (2005) Is volume transfer coefficient (K(trans)) related to histologic grade in human gliomas? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2455–2465
Zhou YH, Tan F, Hess KR, Yung WK (2003) The expression of PAX6, PTEN, vascular endothelial growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor in gliomas: relationship to tumor grade and survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:3369–3375
Abdulrauf SI, Edvardsen K, Ho KL, Yang XY, Rock JP, Rosenblum ML (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression and vascular density as prognostic markers of survival in patients with low-grade astrocytoma. J Neurosurg 88:513–520. doi:10.3171/jns.1998.88.3.0513
Carlson MR, Pope WB, Horvath S, Braunstein JG, Nghiemphu P, Tso CL, Mellinghoff I, Lai A, Liau LM, Mischel PS, Dong J, Nelson SF, Cloughesy TF (2007) Relationship between survival and edema in malignant gliomas: role of vascular endothelial growth factor and neuronal pentraxin 2. Clin Cancer Res 13:2592–2598. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-2772
Kickingereder P, Sahm F, Wiestler B, Roethke M, Heiland S, Schlemmer HP, Wick W, von Deimling A, Bendszus M, Radbruch A (2014) Evaluation of microvascular permeability with dynamic contrast-enhanced mri for the differentiation of primary cns lymphoma and glioblastoma: radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3915
Guo JY, Reddick WE, Rosen MA, Song HK (2009) Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging parameters independent of baseline T10 values. Magn Reson Imaging 27:1208–1215. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2009.05.015
Jung SC, Yeom JA, Kim JH, Ryoo I, Kim SC, Shin H, Lee AL, Yun TJ, Park CK, Sohn CH, Park SH, Choi SH (2014) Glioma: application of histogram analysis of pharmacokinetic parameters from T1-weighted dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging to tumor grading. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1103–1110. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3825
Heisen M, Fan X, Buurman J, van Riel NA, Karczmar GS, ter Haar Romeny BM (2010) The influence of temporal resolution in determining pharmacokinetic parameters from DCE-MRI data. Magn Reson Med 63:811–816. doi:10.1002/mrm.22171
Henderson E, Rutt BK, Lee TY (1998) Temporal sampling requirements for the tracer kinetics modeling of breast disease. Magn Reson Imaging 16:1057–1073
Bagher-Ebadian H, Jain R, Nejad-Davarani SP, Mikkelsen T, Lu M, Jiang Q, Scarpace L, Arbab AS, Narang J, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Paudyal R, Ewing JR (2012) Model selection for DCE-T1 studies in glioblastoma. Magn Reson Med 68:241–251. doi:10.1002/mrm.23211
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant of the DKFZ—German Cancer Research Center (“Intramurales Förderprogramm”).
Conflict of interest
Philipp Kickingereder: none; Benedikt Wiestler: none; Markus Graf: none; Sabine Heiland: none; Heinz-Peter Schlemmer—UNRELATED: Consultancy: Siemens, Grants/Grants Pending: Siemens, Payment for Lectures (including service on Speakers Bureaus): Siemens, Curagita, Covidien, Travel/Accommodations/Meeting Expenses Unrelated to Activities Listed: Siemens; Wolfgang Wick—UNRELATED: Consultancy: Roche, MSD, Payment for Lectures (including service on Speakers Bureaus): Roche, Prime Oncology, Research support: Apogenix, Boehringer Ingelheim, MSD and Roche. Member of the Steering Committee of the AVAglio trial. Patents (planned, pending or issued): IDH diagnostic antibody; Antje Wick: none Martin Bendszus—UNRELATED: Board Membership: Vascular Dynamics, Payment for Lectures (including service on Speakers Bureaus): Novartis, Roche, Codman, Guerbet; Alexander Radbruch: none.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11060_2014_1644_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1. Corresponding concentration–time curves of patients shown in Fig. 1 [x axis relative enhancement, y axis time (s)]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kickingereder, P., Wiestler, B., Graf, M. et al. Evaluation of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI derived microvascular permeability in recurrent glioblastoma treated with bevacizumab. J Neurooncol 121, 373–380 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1644-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1644-6