Abstract
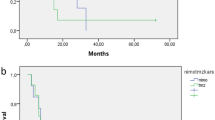
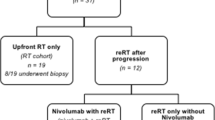
Radiotherapy is the only treatment definitely indicated for diffuse pontine gliomas (DIPG). Findings on the role of EGFR signaling in the onset of childhood DIPG prompted the use of nimotuzumab, an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody. Assuming a potential synergy with both radiotherapy and vinorelbine, a pilot phase 2 protocol was launched that combined nimotuzumab with concomitant radiation and vinorelbine. An amendment in July 2011 introduced re-irradiation at relapse. The primary endpoint for first-line treatment was objective response rate (CR + PR + SD) according to the RECIST. This report concerns the outcome of this strategy as a whole. Vinorelbine 20 mg/m2 was administered weekly, with nimotuzumab 150 mg/m2 in the first 12 weeks of treatment; radiotherapy was delivered from weeks 3 to 9, for a total dose of 54 Gy. Vinorelbine 25 mg/m2 and nimotuzumab were given every other week thereafter until the tumor progressed or for up to 2 years. Re-irradiation consisted of 19.8 Gy, fractionated over 11 days. Baseline and latest MRIs were assessed blindly by an outside neuroradiologist. Twenty five children (mean age 7.4 years) were enrolled as of August 2009 (median follow-up 29 months). A response was observed in 24/25 patients (96 %). The nimotuzumab/vinorelbine combination was very well tolerated, with no acute side-effects. Eleven of 16 locally-relapsing patients were re-irradiated. One-year PFS and OS rates were 30 ± 10 % and 76 ± 9 %, respectively; 2-year OS was 27 ± 9 %; the median PFS and OS were 8.5 and 15 months, respectively. This strategy generated interesting results and warrants further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fischbein NJ, Prados MD, Wara W, Russo C, Edwards MS, Barkovich AJ (1996) Radiologic classification of brain stem tumors: correlation of magnetic resonance imaging appearance with clinical outcome. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:9–23
Donaldson SS, Laningham F, Fisher PG (2006) Advances toward an understanding of brainstem gliomas. J Clin Oncol 24:1266–1272
Massimino M, Spreafico F, Biassoni V et al (2008) Diffuse pontine gliomas in children: changing strategies, changing results? A mono-institutional 20-year experience. J Neurooncol 87:355–361
Hargrave D, Bartels U, Bouffet E (2006) Diffuse brainstem glioma in children: critical review of clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 7:241–248
Jansen MH, van Vuurden DG, Vandertop WP, Kaspers GJ (2012) Diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas: a systematic update on clinical trials and biology. Cancer Treat Rev 38:27–35
Bode U, Massimino M, Bach F et al (2012) Nimotuzumab treatment of malignant gliomas. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 12:1649–1659
Poussaint TY, Kocak M, Vajapeyam S et al (2011) MRI as a central component of clinical trials analysis in brainstem glioma: a report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium (PBTC). Neuro Oncol 13:417–427
Gilbertson RJ, Hill DA, Hernan R et al (2003) ERBB1 is amplified and overexpressed in high-grade diffusely infiltrative pediatric brain stem glioma. Clin Cancer Res 9:3620–3624
Zarghooni M, Bartels U, Lee E et al (2010) Whole-genome profiling of pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas highlights platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase as potential therapeutic targets. J Clin Oncol 28:1337–1344
Warren KE, Killian K, Suuriniemi M, Wang Y, Quezado M, Meltzer PS (2012) Genomic aberrations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Neuro Oncol 14:326–332
Wu G, Broniscer A, McEachron TA et al (2012) Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nat Genet 44:251–253
Schwartzentruber J, Korshunov A, Liu XY et al (2012) Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 482:226–231
Sturm D, Witt H, Hovestadt V et al (2012) Hotspot mutations in H3F3A and IDH1 define distinct epigenetic and biological subgroups of glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 22:425–437
Ballester LY, Wang Z, Shandilya S et al (2013) Morphologic characteristics and immunohistochemical profile of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Am J Surg Pathol 37:1357–1364
Massimino M, Bode U, Biassoni V, Fleischhack G (2011) Nimotuzumab for pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Expert Opin Biol Ther 11:247–256
Dietil M. Scientifically based report on the blood–brain-barrier in malignant tumors. Expert Opinion—BBB—malignant brain tumors. BBB-09-11-16:1–9, Institute for Pathology, Charite´-University Medicine Berlin
Fichtner I, Nowak CH. Report: biodistribution of nimotuzumab in xenografetd mice. Experimental Pharmacology & Oncology, Berlin-Buch gmbh, 22 April 2010
Crombet Ramos T, Figueredo J, Catala S et al (2006) Treatment of high-grade glioma patients with the humanized anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody h-R3. Cancer Biol Ther 5:375–379
Hanley ML, Elion GB, Colvin OM et al (1998) Therapeutic efficacy of vinorelbine against pediatric and adult central nervous system tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42:479–482
Mouchard-Delmas C, Gourdier B, Vistelle R, Wiczewski M (1995) Modification of the blood-brain barrier permeability following intracarotid infusion of vinorelbine. Anticancer Res 15:2593–2596
Binet S, Fellous A, Lataste H, Krikorian A, Couzinier JP, Meininger V (1989) In situ analysis of the action of Navelbine on various types of microtubules using immunofluorescence. Semin Oncol 16(Suppl 4):5–8
Crinò L, Cappuzzo F, Zatloukal P et al (2008) Gefitinib versus vinorelbine in chemotherapy-naive elderly patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (INVITE): a randomized, phase II study. J Clin Oncol 26:4253–4260
Depenbrock H, Shirvani A, Rastetter J, Hanauske AR (1995) Effects of vinorelbine on epidermal growth factor-receptor binding of human breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Invest New Drugs 13:187–193
Tsai CM, Chiu CH, Chang KT et al (2012) Gefitinib enahances cytotoxicities of antimicrotubile agents in non-small cell lung cancer cells exhibiting no sensitizing epidermal growth factor mutation. J Thorac Oncol 7:1218–1227
Fontanilla HP, Pinnix CC, Ketonen LM et al (2012) Palliative reirradiation for progressive diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Am J Clin Oncol 35:51–57
Fleischhack G, Siegler N, Zimmermann M, et al (2010) Concomitant therapy of nimotuzumab and standard radiotherapy for the treatment of newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas in children and adolescents. 14th international symposium of pediatric neuro-oncology, Vienna, Austria 20–23 June 2010 [abstract]. Neurooncology 12:ii8
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Casanova M, Ferrari A, Spreafico F et al (2002) Vinorelbine in previously treated advanced childhood sarcomas: evidence of activity in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer 94:3263–3268
Geoerger B, Hargrave D, Thomas F et al (2011) Innovative Therapies for Children with Cancer pediatric phase I study of erlotinib in brainstem glioma and relapsing/refractory brain tumors. Neuro Oncol 13:109–118
Pollack IF, Stewart CF, Kocak M et al (2011) A phase II study of gefitinib and irradiation in children with newly diagnosed brainstem gliomas: a report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium. Neuro Oncol 13:290–297
Broniscer A, Baker JN, Tagen M et al (2010) Phase I study of vandetanib during and after radiotherapy in children with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Clin Oncol 28:4762–4768
Broniscer A, Baker SD, Wetmore C et al (2013) Phase I trial, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of vandetanib and dasatinib in children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Clin Cancer Res 19:3050–3058
Lewis J, Lucraft H, Gholkar A (1997) UKCCSG study of accelerated radiotherapy for paediatric brain stem gliomas. United Kingdom Childhood Cancer Study Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 38:925–929
Janssens GO, Jansen MH, Lauwers SJ et al (2009) The role of hypofractionation radiotherapy for diffuse intrinsic brainstem glioma in children: a pilot study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 73:722–726
Negretti L, Bouchireb K, Levy-Piedbois C et al (2011) Hypofractionated radiotherapy in the treatment of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma in children: a single institution’s experience. J Neurooncol 104:773–777
Sedlacik J, Winchell A, Kocak M, Loeffler RB, Broniscer A, Hillenbrand CM (2013) MR Imaging assessment of tumor perfusion and 3D segmented volume at baseline, during treatment, and at tumor progression in children with newly diagnosed diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. Am J Neuroradiol 34:1450–1455
Broniscer A, Laningham FH, Sanders RP, Kun LE, Ellison DW, Gajjar A (2008) Young age may predict a better outcome for children with diffuse pontine glioma. Cancer 113:566–572
Wolff JE, Rytting ME, Vats TS, Zage PE, Ater JL, Woo S et al (2012) Treatment of recurrent diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: the MD Anderson Cancer Center experience. J Neurooncol 106:391–397
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Associazione Bianca Garavaglia Onlus (Busto Arsizio Italy), the Fondo di Giò Onlus (Trieste, Italy), and the Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca Sul Cancro (AIRC); nimotuzumab was given on compassionate grounds by Oncoscience AG.
Conflict of interest
There are no other conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massimino, M., Biassoni, V., Miceli, R. et al. Results of nimotuzumab and vinorelbine, radiation and re-irradiation for diffuse pontine glioma in childhood. J Neurooncol 118, 305–312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1428-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-014-1428-z