Abstract
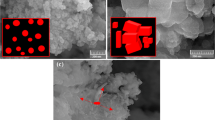
A simple and fast microwave-assisted hydrothermal method is proposed for the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. The addition of different surfactants (polyvinylpyrrolidone, oleic acid, or trisodium citrate) was studied to investigate the effect on size distribution, morphology, and functionalization of the magnetite nanoparticles. Microwave irradiation at 150 °C for 2 h of aqueous ferrous chloride and hydrazine without additives resulted in hexagonal magnetite nanoplatelets with a facet-to-facet distance of 116 nm and a thickness of 40 nm having a saturation magnetization of ~65 Am2 kg−1. The use of polyvinylpyrrolidone led to hexagonal nanoparticles with a facet-to-facet distance of 120 nm and a thickness of 53 nm with a saturation magnetization of ~54 Am2 kg−1. Additives such as oleic acid and trisodium citrate yielded quasi-spherical nanoparticles of 25 nm in size with a saturation magnetization of ~70 Am2 kg−1 and spheroidal nanoparticles of 60 nm in size with a saturation magnetization up to ~82 Am2 kg−1, respectively. A kinetic control of the crystal growth is believed to be responsible for the hexagonal habit of the nanoparticles obtained without additive. Conversely, a thermodynamic control of the crystal growth, leading to spheroidal nanoparticles, seems to occur when additives which strongly interact with the nanoparticle surface are used. A thorough characterization of the materials was performed. Magnetic properties were investigated by Superconducting Quantum Interference Device and Vibrating Sample magnetometers. Based on the observed magnetic properties, the magnetite obtained using citrate appears to be a promising support for magnetically transportable catalysts.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Reziq R, Alper H, Wang D, Post ML (2006) Metal supported on dendronized magnetic nanoparticles: highly selective hydroformylation catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 128:5279–5282. doi:10.1021/ja060140u
Altomare A, Cuocci C, Giacovazzo C et al (2008) QUALX: a computer program for qualitative analysis using powder diffraction data. J Appl Crystallogr 41:815–817. doi:10.1107/S0021889808016956
Arruebo M, Galán M, Navascués N et al (2006) Development of magnetic nanostructured silica-based materials as potential vectors for drug-delivery applications. Chem Mater 18:1911–1919. doi:10.1021/cm051646z
Caliandro R, Belviso DB (2014) RootProf: software for multivariate analysis of unidimensional profiles. J Appl Crystallogr 47:1087–1096. doi:10.1107/S1600576714005895
Cao S-W, Zhu Y-J, Ma M-Y et al (2008) Hierarchically nanostructured magnetic hollow spheres of Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3: preparation and potential application in drug delivery. J Phys Chem C 112:1851–1856. doi:10.1021/jp077468+
Chen M, Kim J, Liu JP et al (2006) Synthesis of FePt nanocubes and their oriented self-assembly. J Am Chem Soc 128:7132–7133. doi:10.1021/ja061704x
Cheon J, Kang N-J, Lee S-M et al (2004) Shape evolution of single-crystalline iron oxide nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 126:1950–1951. doi:10.1021/ja038722o
Daou TJ, Pourroy G, Bégin-Colin S et al (2006) Hydrothermal synthesis of monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Chem Mater 18:4399–4404. doi:10.1021/cm060805r
Daou TJ, Grenèche JM, Pourroy G et al (2008) Coupling agent effect on magnetic properties of functionalized magnetite-based nanoparticles. Chem Mater 20:5869–5875. doi:10.1021/cm801405n
De Vidales JLM, López-Delgado A, Vila E, López FA (1999) The effect of the starting solution on the physico-chemical properties of zinc ferrite synthesized at low temperature. J Alloys Compd 287:276–283. doi:10.1016/S0925-8388(99)00069-9
Fantechi E, Campo G, Carta D et al (2012) Exploring the effect of Co doping in fine maghemite nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 116:8261–8270. doi:10.1021/jp300806j
Gawande MB, Bonifácio VDB, Varma RS et al (2013) Magnetically recyclable magnetite–ceria (Nanocat-Fe-Ce) nanocatalyst—applications in multicomponent reactions under benign conditions. Green Chem 15:1226–1231. doi:10.1039/C3GC40375K
Gawande MB, Shelke SN, Zboril R, Varma RS (2014) Microwave-assisted chemistry: synthetic applications for rapid assembly of nanomaterials and organics. Acc Chem Res 47:1338–1348. doi:10.1021/ar400309b
Grosvenor AP, Kobe BA, Biesinger MC, McIntyre NS (2004) Investigation of multiplet splitting of Fe 2p XPS spectra and bonding in iron compounds. Surf Interface Anal 36:1564–1574. doi:10.1002/sia.1984
Gupta RP, Sen SK (1974) Calculation of multiplet structure of core p-vacancy levels. Phys Rev B 10:71–77. doi:10.1103/PhysRevB.10.71
Hong RY, Pan TT, Li HZ (2006) Microwave synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles used as a precursor of nanocomposites and ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater 303:60–68. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.10.230
Hu L, Percheron A, Chaumont D, Brachais C-H (2011) Microwave-assisted one-step hydrothermal synthesis of pure iron oxide nanoparticles: magnetite, maghemite and hematite. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 60:198–205. doi:10.1007/s10971-011-2579-4
Iglesias GR, Durán JDG, Delgado AV (2012) Dynamic characterization of extremely bidisperse magnetorheological fluids. J Colloid Interface Sci 377:153–159. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2012.03.077
Jia C-J, Sun L-D, Luo F et al (2008) Large-scale synthesis of single-crystalline iron oxide magnetic nanorings. J Am Chem Soc 130:16968–16977. doi:10.1021/ja805152t
Kim D, Lee N, Park M et al (2009) Synthesis of uniform ferrimagnetic magnetite nanocubes. J Am Chem Soc 131:454–455. doi:10.1021/ja8086906
Kiss LB, Söderlund J, Niklasson GA, Granqvist CG (1999) New approach to the origin of lognormal size distributions of nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 10:25–28. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/10/1/006
Kolhatkar AG, Jamison AC, Litvinov D et al (2013) Tuning the magnetic properties of nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci 14:15977–16009. doi:10.3390/ijms140815977
Kubickova S, Vejpravova J, Holec P, Niznansky D (2013) Correlation of crystal structure and magnetic properties of Co(1−x)NixFe2O4/SiO2 nanocomposites. J Magn Magn Mater 334:102–106. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.01.005
Kus M, Ozel F, Varal NM, Ersoz M (2013) Luminescence enhancement of OLED performance by doping Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Prog Electromagn Res 134:509–524. doi:10.2528/PIER12103106
Laureti S, Varvaro G, Testa AM et al (2010) Magnetic interactions in silica coated nanoporous assemblies of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with cubic magnetic anisotropy. Nanotechnology 21:315701. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/31/315701
Leonelli C, Lojkowski W (2007) Main development directions in the application of microwave irradiation to the synthesis of nanopowders. Chem Today 25:34–38
Li S, Qin T, Gaowu W, Pei W et al (2009) Capping groups induced size and shape evolution of magnetite particles under hydrothermal condition and their magnetic properties. J Am Ceram Soc 92:631–635. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2009.02928.x
Li L, Yang Y, Ding J, Xue J (2010a) Synthesis of magnetite nanooctahedra and their magnetic field-induced two-/three-dimensional superstructure. Chem Mater 22:3183–3191. doi:10.1021/cm100289d
Li Z, Godsell JF, O’Byrne JP et al (2010b) Supercritical fluid synthesis of magnetic hexagonal nanoplatelets of magnetite. J Am Chem Soc 132:12540–12541. doi:10.1021/ja105079y
Li C, Wei R, Xu Y et al (2014) Synthesis of hexagonal and triangular Fe3O4 nanosheets via seed-mediated solvothermal growth. Nano Res 7:536–543. doi:10.1007/s12274-014-0421-3
Liu G, Wang D, Zhou F, Liu W (2015) Electrostatic self-assembly of Au nanoparticles onto thermosensitive magnetic core-shell microgels for thermally tunable and magnetically recyclable catalysis. Small 11:2807–2816. doi:10.1002/smll.201403305
Lu X, Niu M, Qiao R, Gao M (2008) Superdispersible PVP-coated Fe3O4 nanocrystals prepared by a “One-Pot” reaction. J Phys Chem B 112:14390–14394. doi:10.1021/jp8025072
Ma M, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Gu N (2013) Facile synthesis of ultrathin magnetic iron oxide nanoplates by Schikorr reaction. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:16. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-8-16
Muscas G, Concas G, Cannas C et al (2013) Magnetic properties of small magnetite nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C 117:23378–23384. doi:10.1021/jp407863s
Noh S, Na W, Jang J et al (2012) Nanoscale magnetism control via surface and exchange anisotropy for optimized ferrimagnetic hysteresis. Nano Lett 12:3716–3721. doi:10.1021/nl301499u
Norgren BS, Somers MAJ, De Wit JHW (1994) Application of tougaard background subtraction to XPS spectra of passivated Fe–17 Cr. Surf Interface Anal 21:378–381. doi:10.1002/sia.740210609
Nyirő-Kósa I, Rečnik A, Pósfai M (2012) Novel methods for the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles with special morphologies and textured assemblages. J Nanoparticle Res 14:1–10. doi:10.1007/s11051-012-1150-8
Ooi F, DuChene JS, Qiu J et al (2015) A facile solvothermal synthesis of octahedral Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Small 11:2649–2653. doi:10.1002/smll.201401954
Peddis D, Cannas C, Piccaluga G et al (2010) Spin-glass-like freezing and enhanced magnetization in ultra-small CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 21:125705. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/21/12/125705
Peddis D, Cannas C, Musinu A et al (2013) Beyond the effect of particle size: influence of CoFe2O4 nanoparticle arrangements on magnetic properties. Chem Mater 25:2005–2013. doi:10.1021/cm303352r
Pinna N, Grancharov S, Beato P et al (2005) Magnetite nanocrystals: nonaqueous synthesis, characterization, and solubility. Chem Mater 17:3044–3049. doi:10.1021/cm050060+
Prete F, Rizzuti A, Esposito L et al (2011) Highly homogeneous Al2O3–ZrO2 nanopowder via microwave-assisted hydro- and solvo- thermal synthesis. J Am Ceram Soc 94:3587–3590. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2011.04594.x
Richards V (2010) Nucleation control in size and dispersity in metallic nanoparticles: the prominent role of particle aggregation. All Theses and Dissertations (ETDs), paper 294, Washington University
Rizzuti A, Leonelli C (2008) Crystallization of aragonite particles from solution under microwave irradiation. Powder Technol 186:255–262. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2007.12.012
Rizzuti A, Viviani M, Corradi A et al (2007) Microwave-assisted hydrothermal synthesis as a rapid route towards manganite preparation. Solid State Phenom 128:21–24. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.128.21
Rizzuti A, Corradi A, Leonelli C et al (2010) Microwave technique applied to the hydrothermal synthesis and sintering of calcia stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. J Nanoparticle Res 12:327–335. doi:10.1007/s11051-009-9619-9
Russo P, Acierno D, Palomba M et al (2012) Ultrafine magnetite nanopowder: synthesis, characterization, and preliminary use as filler of polymethylmethacrylate nanocomposites. J Nanotechnol 2012:e728326. doi:10.1155/2012/728326
Salafranca J, Gazquez J, Pérez N et al (2012) Surfactant organic molecules restore magnetism in metal-oxide nanoparticle surfaces. Nano Lett 12:2499–2503. doi:10.1021/nl300665z
Salazar-Alvarez G, Qin J, Šepelák V et al (2008) Cubic versus spherical magnetic nanoparticles: the role of surface anisotropy. J Am Chem Soc 130:13234–13239. doi:10.1021/ja0768744
Scherrer P (1918) Bestimmung der Größe und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels. Röntgenstrahlen. 1918:98–100
Shavel A, Rodríguez-González B, Pacifico J et al (2009) Shape control in iron oxide nanocrystal synthesis, induced by trioctylammonium ions. Chem Mater 21:1326–1332. doi:10.1021/cm803201p
Shimizu K, Sasaki F, Watanabe Y, Yazawa M (2013) Magnetic pigments US2013257035 (A1)
Sun H, Chen B, Jiao X et al (2012) Solvothermal synthesis of tunable electroactive magnetite nanorods by controlling the side reaction. J Phys Chem C 116:5476–5481. doi:10.1021/jp211986a
Wang J, Sun J, Sun Q, Chen Q (2003) One-step hydrothermal process to prepare highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles with improved magnetic properties. Mater Res Bull 38:1113–1118. doi:10.1016/S0025-5408(03)00129-6
Wang W-W, Zhu Y-J, Ruan M-L (2007) Microwave-assisted synthesis and magnetic property of magnetite and hematite nanoparticles. J Nanoparticle Res 9:419–426. doi:10.1007/s11051-005-9051-8
Wang B, Wei Q, Qu S (2013) Synthesis and characterization of uniform and crystalline magnetite nanoparticles via oxidation-precipitation and modified co-precipitation methods. Int J Electrochem Sci 8:3786–3793
Yin L, Adler I, Tsang T et al (1974) Paramagnetism and shake-up satellites in X-ray photoelectron spectra. Chem Phys Lett 24:81–84. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(74)80219-8
Yu D, Sun X, Zou J et al (2006) Oriented Assembly of Fe3O4 nanoparticles into monodisperse hollow single-crystal microspheres. J Phys Chem B 110:21667–21671. doi:10.1021/jp0646933
Zhang L, He R, Gu H-C (2006) Oleic acid coating on the monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles. Appl Surf Sci 253:2611–2617. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2006.05.023
Zhen G, Muir BW, Moffat BA et al (2011) Comparative study of the magnetic behavior of spherical and cubic superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115:327–334. doi:10.1021/jp104953z
Zheng Y, Cheng Y, Bao F, Wang Y (2006) Synthesis and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater Res Bull 41:525–529. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2005.09.015
Zhou H, Yi R, Li J et al (2010) Microwave-assisted synthesis and characterization of hexagonal Fe3O4 nanoplates. Solid State Sci 12:99–104. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2009.10.012
Acknowledgments
Part of this work has been carried out within the activities fostering sustainable manufacturing of “SOSTENERE” interest group—AITEM association. Regione Puglia is gratefully acknowledged for financial support (X-Ray Lab Project–Reti di Laboratori Pubblici di Ricerca, cod. n. 45 and 56). We thank Dr. D. Peddis for the useful discussion on magnetic properties, Mr E. Patrizi for technical assistance in magnetic measurements, and Giuseppe Chita (IC-CNR, Bari, Italy) for his contribution in XRD data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizzuti, A., Dassisti, M., Mastrorilli, P. et al. Shape-control by microwave-assisted hydrothermal method for the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles using organic additives. J Nanopart Res 17, 408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-3213-0