Abstract
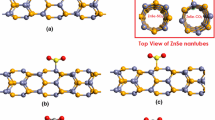
The electron transport properties of CO adsorbed SiC nanotubes as a function of concentration density and structural deformation have been characterized for the single-walled (7,0) zigzag model using a combined formalism of density-functional theory and nonequilibrium Green’s function. It is found that CO adsorption can significantly suppress the transmission spectrum of SiC nanotube for a wide range of energies. As the concentration increases, a density-dependent superimposed transport gap exists and widens the initial electronic band gap of SiC nanotube. Under the same applied bias voltage, the current through SiC nanotube decreases with the increasing CO concentrations. The local torsional deformation has no effect on this essential motif. However, the current in the locally twisted system is larger than that of the undeformed one. The transmission suppression and the current differences can be attributed to the response of the localized impurity state induced by CO adsorption to density and deformation. Our results show that SiC nanotube can be a promising gas sensor for CO detection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson M, Pearce R, Spetz AL (2013) New generation SiC based field effect transistor gas sensors. Sens Actuators B 179:95–106
Baierle RJ, Miwa RH (2007) Hydrogen interaction with native defects in SiC nanotubes. Phys Rev B 76:205410
Baumeier B, Krüger P, Pollma J (2007) Structural, elastic, and electronic properties of SiC, BN, and BeO nanotubes. Phys Rev B 76:085407
Brandbyge M, Mozos J-L, Ordejón P, Taylor J, Stokbro K (2002) Density-functional method for nonequilibrium electron transport. Phys Rev B 65:165401
Collins PG, Bradley K, Ishigami M, Zettl A (2000) Extreme oxygen sensitivity of electronic properties of carbon nanotubes. Science 287:1801–1804
da Silva LB, Fagan SB, Mota R (2004) Ab initio study of deformed carbon nanotube sensors for carbon monoxide molecules. Nano Lett 4:65–67
Delley B (1990) An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J Chem Phys 92:508–517
Delley B (2000) From molecules to solids with the DMol3 approach. J Chem Phys 113:7756–7764
Gali A (2006) Ab initio study of nitrogen and boron substitutional impurities in single-wall SiC nanotubes. Phys Rev B 73:245415
Gali A (2007) Ab initio theoretical study of hydrogen and its interaction with boron acceptors and nitrogen donors in single-wall silicon carbide nanotubes. Phys Rev B 75:085416
Harris GL (1995) Properties of silicon carbide. INSPEC: Institution of Electrical Engineers, London
He T, Zhao MW, Xia YY, Li WF, Song C, Lin XH, Liu XD, Mei LM (2006) Tuning the electronic structures of semiconducting SiC nanotubes by N and NHx (x = 1,2) groups. J Chem Phys 125:194710
Jhi SH, Louie SG, Cohen ML (2000) Electronic properties of oxidized carbon nanotubes. Phys Rev Lett 85:1710–1713
Jia JM, Ju SP, Shi DN, Lin KF (2011) Electromechanical response of a SiC nanotube under local torsional deformation. J Phys Chem C 115:24347–24352
Kong J, Franklin NR, Zhou CW, Chapline MG, Peng S, Cho K, Dai HJ (2000) Nanotube molecular wires as chemical sensors. Science 287:622–625
Kong J, Chapline MG, Dai HJ (2001) Functionalized carbon nanotubes for molecular hydrogen sensors. Adv Mater 13:1384–1386
Li F, Xia YY, Zhao MW, Liu XD, Huang BD, Yang ZH, Ji YJ, Song C (2005) Density-functional theory calculations of XH3-decorated SiC nanotubes (X = {C, Si}): structures, energetics, and electronic structures. J Appl Phys 97:104311
Li KJ, Wang WC, Cao DP (2011) Metal (Pd, Pt)-decorated carbon nanotubes for CO and NO sensing. Sens Actuators B 159:171–177
Mavrandonakis A, Froudakis GE, Schnell M, Muhlhauser M (2003) From pure carbon to silicon−carbon nanotubes: an ab initio study. Nano Lett 3:1481–1484
Meng TZ, Wang CY, Wang SY (2007) First-principles study of a single Ti atom adsorbed on silicon carbide nanotubes and the corresponding adsorption of hydrogen molecules to the Ti atom. Chem Phys Lett 437:224–228
Menon M, Richter E, Mavrandonakis A, Froudakis G, Andriotis AN (2004) Structure and stability of SiC nanotubes. Phys Rev B 69:115322
Miyamoto Y, Yu BD (2002) Computational designing of graphitic silicon carbide and its tubular forms. Appl Phys Lett 80:586–588
Monkhorst HJ, Pack JK (1976) Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys Rev B 13:5188–5192
Park H, Zhao JJ, Lu JP (2006) Effects of sidewall functionalization on conducting properties of single wall carbon nanotubes. Nano Lett 6:916–919
Peng S, Cho K (2000) Chemical control of nanotube electronics. Nanotechnology 11:57–60
Peng S, Cho K (2003) Ab initio study of doped carbon nanotube sensors. Nano Lett 3:513–517
Perdew JP, Zunger A (1981) Self-interaction correction to density-functional approximations for many-electron systems. Phys Rev B 23:5048–5079
Soler JM, Artacho E, Gale JD, García A, Junquera J, Ordejón P, Sánchez-Portal D (2002) The SIESTA method for ab initio order-N materials simulation. J Phys 14:2745–2779
Sun XH, Li CP, Wong WK, Wong NB, Lee CS, Lee ST, Teo BK (2002) Formation of silicon carbide nanotubes and nanowires via reaction of silicon (from disproportionation of silicon monoxide) with carbon nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 124:14464–14471
Szabó Á, Gali A (2009) Effect of oxygen on single-wall silicon carbide nanotubes studied by first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B 80:075425
Taylor J, Guo H, Wang J (2001) Ab initio modeling of quantum transport properties of molecular electronic devices. Phys Rev B 63:245407
Teo BK, Sun XH (2007) Silicon-based low-dimensional nanomaterials and nanodevices. Chem Rev 107:1454–1532
Tombler TW, Zhou CW, Alexseyev L, Kong J, Dai HJ, Liu L, Jayanthi CS, Tang MJ, Wu SY (2000) Reversible electromechanical characteristics of carbon nanotubes underlocal-probe manipulation. Nature 405:769–772
Troullier N, Martins JL (1991) Efficient pseudopotentials for plane-wave calculations. Phys Rev B 43:1993–2006
Wang XQ, Wang BL, Zhao JJ, Wang GH (2008) Structural transitions and electronic properties of the ultrathin SiC nanotubes under uniaxial compression. Chem Phys Lett 461:280–284
Wong EW, Sheehan PE, Lieber CM (1997) Nanobeam mechanics: elasticity, strength, and toughness of nanorods and nanotubes. Science 277:1971–1975
Wu RQ, Yang M, Lu YH, Feng YP, Huang ZG, Wu QY (2008) Silicon carbide nanotubes as potential gas sensors for CO and HCN detection. J Phys Chem C 112:15985–15988
Zhao JX, Ding YH (2009) Can silicon carbide nanotubes sense carbon dioxide? J Chem Theory Comput 5:1099–1105
Zhao JJ, Buldum A, Han J, Lu JP (2002) Gas molecule adsorption in carbon nanotubes and nanotube bundles. Nanotechnology 13:195–200
Zhao JJ, Chen ZF, Zhou Z, Park H, Schleyer PVR, Lu JP (2005a) Engineering the electronic structure of single-walled carbon nanotubes by chemical functionalization. ChemPhysChem 6:598–601
Zhao MW, Xia YY, Li F, Zhang RQ, Lee S-T (2005b) Strain energy and electronic structures of silicon carbide nanotubes: density functional calculations. Phys Rev B 71:085312
Zhao MW, Xia YY, Zhang RQ, Lee S-T (2005c) Manipulating the electronic structures of silicon carbide nanotubes by selected hydrogenation. J Chem Phys 122:214707
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by program for Excellent Talents in Huaiyin Teachers College (ETHYTC, No. 06QNZC023), Universities Natural Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (No. JSKC08054), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (NSFJS, Nos. BK2010499, BK2011411, and HAG2011006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, Nos. 11174101 and 11374159). Shin-Pon Ju thanks the (1) National Science Council of Taiwan (under Grant Nos. NSC98-2221-E-110-022-MY3, NSC99-2628-E-110-004, NSC99-2811-E-110-016, and NSC99-2911-I-110-512), (2) National Center for High-performance Computing, Taiwan, (3) National Center for Theoretical Sciences, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Jm., Ju, Sp., Shi, Dn. et al. CO adsorption on a zigzag SiC nanotube: effects of concentration density and local torsion on transport. J Nanopart Res 15, 1977 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1977-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1977-7