Abstract
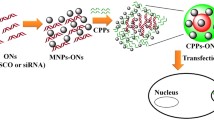
Gene delivery using magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) is known as magnetofection and is an efficient non-viral gene delivery system. γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles (primary diameter = 29 nm) and Fe3O4 nanoparticles (primary diameter = 20–30 nm) coated with deacylated linear polyethylenimine (PEI max) were prepared and conjugated with DNA. The dependency of transfection efficiency on the weight of MNPs, viability of HeLa cells, and size of DNA/PEI max/MNP complexes was evaluated. Transfection efficiency initially increased with the weight of the complexes; however, it decreased with further increase in weight. In contrast, cell viability increased with further increase in weight. Cytotoxicity assay showed that the decline in transfection efficiency at higher weights was not attributable to cytotoxicity of DNA/PEI max/MNP complexes. The DNA/PEI max/MNP complexes aggregated because of DNA binding and pH interaction with the medium. Aggregation depending on the weight of MNPs was confirmed. The number of complexes was estimated from the size distribution. In addition, the dependency of the transfection efficiency on aggregation was assessed with respect to cellular endocytic pathways using the complexes. The complexes were internalized through clathrin-dependent endocytosis, which was a size-dependent pathway. This study reveals that decreased transfection efficiency was associated with the extent of aggregation, which was induced by high weight of MNPs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akincl A, Thomas M, Klibanov AM, Langer R (2005) Exploring polyethylenimine-mediated DNA transfection and the proton sponge hypothesis. J Gene Med 7:657–663
Akiyama H, Ito A, Kawabe Y, Kamihira M (2010) Genetically engineered angiogenic cell sheets using magnetic force-based gene delivery and tissue fabrication techniques. Biomaterials 31:1251–1259
Arsianti M, Lim M, Marquis CP, Amal R (2010a) Assembly of polyethylenimine-based magnetic iron oxide vectors: insight into gene delivery. Langmuir 26:7314–7326
Arsianti M, Lim M, Marquis CO, Amal R (2010b) Polyethylenimine based magnetic iron-oxide vector: the effect of vector component assembly on cellular entry mechanism, intracellular localization, and cellular viability. Biomacromolecules 11:2521–2531
Banerjee P, Weissleder R, Bogdanov A Jr (2006) Linear polyethylenimine grafted to a hyperbranched poly(ethylene glycol)-like core: a copolymer for gene delivery. Bioconjug Chem 17:125–131
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta MA, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B, Behr J (1995) A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7297–7301
De Smedt SC, Demeester J, Hennink WE (2000) Cationic polymer based gene delivery systems. Pharm Res 17:113–126
Decuzzi P, Ferrari M (2007) The role of specific and non-specific interactions in receptor-mediated endocytosis of nanoparticles. Biomaterials 28:2915–2922
Furlani EP, Xue X (2012) Field, force and transport analysis for magnetic particle-based gene delivery. Microfluid Nanofluidics 13:589–602
Gao H, Shi W, Freund LB (2005) Mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9469–9474
Ghosh PS, Kim C, Han G, Forbes NS, Rotello VM (2008) Efficient gene delivery vectors by tuning the surface charge density of amino acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2:2213–2218
Godbey WT, Wu KK, Mikos AG (1999) Poly(ethylenimine) and its role in gene delivery. J Control Release 60:149–160
Gruenstein E, Rich A, Weihing RR (1975) Actin associated with membranes from 3T3 mouse fibroblast and HeLa cells. J Cell Biol 64:223–234
Guo X, Kim KS, Liu D (2007) Nonviral gene delivery: what we know and what is next. AAPS J 9:E92–E104
Huth S, Lausier J, Gersting SW, Rudolph C, Plank C, Welsch U, Rosenecker J (2004) Insight into the mechanism of magnetofection using PEI-based magnetofection for gene transfer. J Gene Med 6:923–936
Jeong JH, Song DH, Lim DW, Lee H, Park TG (2001) DNA transfection using poly(ethylenimine) prepared by controlled acid hydrolysis of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline). J Control Release 73:391–399
Johnson HP, Lowrie W, Kent DV (1975) Stability of anhysteretic remanent magnetization in fine and coarse magnetite and maghemite particles. Geophys J R Astr Soc 41:1–10
Kami D, Takeda S, Makino H, Toyoda M, Gojo S, Kyo S, Umezawa A, Watanabe M (2011a) Efficient transfection method using deacylated polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J Artif Organs 14:215–222
Kami D, Takeda S, Toyoda M, Watanabe M (2011b) Application of magnetic nanoparticles to biomedicine. Int J Mol Sci 11:3705–3722
Kichler A, Leborgne C, Coeytaux E, Danos O (2001) Polyethylenimine-mediated gene delivery: a mechanistic study. J Gene Med 3:135–144
Kievit FM, Veiseh O, Bhattarai N, Fang C, Gunn JW, Lee D, Ellenbogen RG, Olson JM, Zhang M (2009) PEI–PEG–chitosan copolymer coated iron oxide nanoparticles for safe gene delivery: synthesis, complexation, and transfection. Adv Funct Mater 19:2244–2251
Kircheis R, Wightman L, Wagner E (2001) Design and gene delivery activity of modified polyethylenimines. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:341–358
Lee KJ, An JH, Shin JS, Kim DH, Yoo HS, Cho CK (2011) Biostability of γ-Fe2O3 nano particles evaluated using an in vitro cytotoxicity assays on various tumor cell lines. Curr Appl Phys 11:467–471
Lunov O, Zablotskii V, Syrovets T, Röcker C, Tron K, Nienhaus GU, Simmet T (2011) Modeling receptor-mediated endocytosis of polymer-functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles by human macrophage. Biomaterials 32:547–555
McCord JM (1998) Iron free radicals, and oxidative injury. Semin Hematol 35:5–12
Miao L, Zhang K, Oiao C, Jin X, Zhang C, Yang B, Sun H (2013) Antitumor effect of human TRAIL on adenoid cystic carcinoma using magnetic nanoparticle–mediated gene expression. Nano-medicine 9:141–150
Mislick KA, Baldeschwieler JD (1996) Evidence for the role of proteoglycans in cation-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12349–12354
Oku N, Yamazaki Y, Matsuura M, Sugiyama M, Hasegawa M, Nango M (2001) A novel non-viral gene transfer system, polycation liposomes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 52:209–218
Pan B, Cui D, Sheng Y, Ozkan C, Gao F, He R, Li Q, Xu P, Huang T (2007) Dendrimer-modified magnetic nanoparticles enhance efficiency of gene delivery system. Cancer Res 67:8156–8163
Pankfurst QA, Connolly J, Jones SK, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D 36:R167–R181
Payne CK, Jones SA, Chen CC, Zhuang X (2007) Internalization and trafficking of cell surface proteoglycans and proteoglycan-binding ligand. Traffic 8:389–401
Plank C, Schillinger U, Scherer F, Bergemann C, Rémy JS, Kröetz F, Anton M, Lausier J, Rosenecker J (2003) The magnetofection method: using magnetic force to enhance gene delivery. Biol Chem 384:737–747
Prabha S, Zhou WZ, Panyam J, Labhastwar V (2002) Size-dependent of nanoparticle-mediated gene transfection: studies with fractionated nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 244:105–115
Prijic S, Prosen L, Cemazar M, Scancar J, Romih R, Lavrencakv J, Bregar VB, Coer A, Krzan M, Znidarsic A, Sersa G (2012) Surface modified magnetic nanoparticles for immuno-gene therapy of murine mammary adenocarcinoma. Biomaterials 233:4379–4391
Rejman J, Oberle V, Zuhorn IS, Hoekstr D (2004) Size-dependent internalization of particles via the pathways of clathrin-and caveolae-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J 377:159–169
Rejman J, Bragonzi A, Conese M (2005) Role of clathrin- and caveolae-mediated endocytosis in gene transfer mediated by lipo- and polyplexes. Mol Ther 12:468–474
Roy I, Ohulchanskyy TY, Bharali DJ, Pudavar HE, Mistretta RA, Kaur N, Prasad PN (2005) Optical tracking of organically modified silica nanoparticles as DNA carriers: a nonviral, nanomedicine approach for gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad 102:279–284
Sahay G, Alakhova DY, Kabanov AV (2010) Endocytosis of nanomedicines. J Control Release 145:182–195
Scherer F, Anton M, Schillinger U, Henke J, Bergemann C, Krüger A, Gänsbacher B, Plank C (2002) Magnetofection: enhancing and targeting gene delivery by magnetic force in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther 9:102–109
Seino S, Matsuoka Y, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa T, Yamamoto TA (2009) Dispersibility improvement of gold/iron-oxide composite nanoparticles by polyethylenimine modification. J Magn Magn Mater 321:1404–1407
Steitz B, Hofmann H, Kamau SW, Hassa PO, Hottiger MO, Rechenberg B, Hofmann-Amtenbrink M, Petri-Fink A (2007) Characterization of PEI-coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for transfection: size distribution, colloidal properties and DNA interaction. J Magn Magn Mater 311:300–305
Thomas M, Lu JJ, Ge Q, Zhang C, Chen J, Klibanov AM (2005) Full deacylation of polyethylenimine dramatically boosts its gene delivery efficiency and specificity to mouse lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5679–5684
van den Bos EJ, Wagner A, Mahrholdt H, Thompson RB, Morimoto Y, Sutton BS, Judd RM, Taylor DA (2003) Improved efficacy of stem cell labeling for magnetic resonance imaging studies by the use of cationic liposomes. Cell Transplant 12:743–756
Vercauteren D, Piest M, van der Aa LJ, Al Soraj M, Jones AT, Engbersen JF, De Smedt SC, Braeckmans K (2011) Flotillin-dependent endocytosis and a phagocytosis-like mechanism for cellular internalization of disulfide-based poly(amido amine)/DNA polyplexes. Biomaterials 32:3072–3084
Wang X, Zhou L, Ma Y, Li X, Gu H (2009) Control of aggregation size of polyethylenimine-coated magnetic nanoparticles for magnetofection. Nano Res 2:365–372
Wang S, Lee C, Chiou A, Wei P (2010) Size-dependent endocytosis of gold nanoparticles studied by three-dimensional mapping of plasmonic scattering images. J Nanobiotech 8:33
Wigo HTR, Lim M, Bulmus V, Gutiérrez L, Woodward RC, Amal R (2012) Insight into serum protein interactions with functionalized magnetic nanoparticles in biological media. Langmuir 28:4346–4356
Win KY, Feng S (2005) Effects of particle size and surface coating on cellular uptake of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 26:2713–2722
Zanta M, Boussif O, Adib A, Behr J (1997) In vitro gene delivery to hepatocytes with galactosylated polyethylenimine. Bioconjug Chem 8:839–844
Zou S, Erbacher P, Remy JS, Behr J (2000) Systemic linear polyethylenimine (l-PEI)-mediated gene delivery in the mouse. J Gene Med 2:128–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ota, S., Takahashi, Y., Tomitaka, A. et al. Transfection efficiency influenced by aggregation of DNA/polyethylenimine max/magnetic nanoparticle complexes. J Nanopart Res 15, 1653 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1653-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1653-y