Abstract
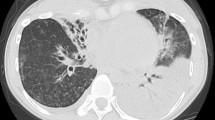
A 16-year-old boy with chronic granulomatous disease presented with pneumonia and rib osteomyelitis. Emericella nidulans var. echinulata was isolated from his sputum. After starting voriconazole, Rasamsonia piperina was isolated from the rib swelling. A combination therapy of voriconazole and micafungin effectively eradicated this invasive mixed-mold infection. In immunocompromised patients, a precise pathogenic diagnosis is clinically useful for administration of an appropriate treatment regimen.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Segal BH, Leto TL, Gallin JI, Malech HL, Holland SM. Genetic, biochemical, and clinical features of chronic granulomatous disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2000;79:170–200.
Kobayashi S, Murayama S, Takanashi S, Takahashi K, Miyatsuka S, Fujita T, Ichinohe S, Koike Y, Kohagizawa T, Mori H, Deguchi Y, Higuchi K, Wakasugi H, Sato T, Wada Y, Nagata M, Okabe N, Tatsuzawa O. Clinical features and prognoses of 23 patients with chronic granulomatous disease followed for 21 years by a single hospital in Japan. Eur J Pediatr. 2008;167:1389–94.
Shukla AK. Biodiversity in Aspergillus nidulans group on the basis of lipases profile. IJSR. 2012;3:1391–4.
Houbraken J, Giraud S, Meijer M, Bertout S, Frisvad JC, Meis JF, Bouchara JP, Samsona RA. Taxonomy and antifungal susceptibility of clinical important Rasamsonia species. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:22–30.
Mizuki M, Chikuba K, Tanaka K. A case of chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis due to Aspergillus nidulans. Mycopathologia. 1994;128:75–9.
Cunha C, Kurzai O, Löffler J, Aversa F, Romani L, Carvalho A. Neutrophil responses to aspergillosis: new roles for old players. Mycopathologia. 2014;178:387–93.
Verweij PE, Varga J, Houbaraken J, Rijs AJMM, VerduynLunel FM, Blijlevens NMA, Shea YR, Holland SM, Warris A, Melchers WJG, Samson RA. Emericella quadrilineata as cause of invasive aspergillosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:566–72.
White CJ, Kwon-Chung KJ, Gallin JI. Chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. An unusual case of infection with Aspergillus nidulans var. echinulatus. Am J Clin Pathol. 1988;90:312–6.
Yu J, Mu X, Li R. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis due to Emericella nidulans var. echinulata, successfully cured by voriconazole and micafungin. J Clin Microbiol. 2013;51:1327–9.
Blumental S, Mouy R, Mahlaoui N, Bougnoux M, Debré M, Beauté J, Lortholary O, Blanche S, Fischer A. Invasive mold infections in chronic granulomatous disease: a 25-year retrospective survey. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:e159–69.
Dotis J, Roilides E. Osteomyelitis due to Aspergillus species in chronic granulomatous disease: an update of the literature. Mycoses. 2011;54:e686–96.
Henriet SSV, Verweij PE, Warris A. Aspergillus nidulans and chronic granulomatous disease: a unique host-pathogen interaction. J Infect Dis. 2012;206:1128–37.
Segal BH, Decarlo ES, Kwon-Chung KJ, Malech HL, Gallin JI, Holland SM. Aspergillus nidulans infection in chronic granulomatous disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 1998;77:345–54.
Houbraken J, Spierenburg H, Frisvead JC. Rasamsonia, a new genus comprising thermotolerant and thermophilic Talaromyces and Geosmithia species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2012;101:403–21.
Ravin SSD, Challipalli M, Anderson V, Shea YR, Marciano B, Hilligoss D, Marquesen M, DeCastro R, Liu Y, Sutton DA, Wickes BL, Kammeyer PL, Sigler L, Sullivan K, Kang EM, Malech HL, Holland SM, Zelazny AM. Geosmithia argillacea: an emerging cause of invasive mycosis in human chronic granulomatous disease. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;52:e136–43.
Heyn K, Tredup A, Salvenmoser S, Müller FC. Effect of voriconazole combined with micafungin against Candida, Aspergillus, and Scedosporium spp. and Fusarium solani. Antimoicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:5157–9.
Matsuda T, Koreeda Y, Mataki H, Taira T, Noma S, Higashimoto I. A case of Aspergillus empyema successfully treated with combination therapy of voriconazole and micafungin: excellent penetration of voriconazole and micafungin into pleural fluid. Intern Med. 2010;49:1163–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly appreciate the assistance of Kyoko Yarita for analyzing the fungal isolates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors report no potential conflicts.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiwada, N., Takeshita, K., Yaguchi, T. et al. The First Case of Invasive Mixed-Mold Infections Due to Emericella nidulans var. echinulata and Rasamsonia piperina in a Patient with Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Mycopathologia 181, 305–309 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-015-9963-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-015-9963-5