Abstract
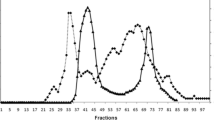
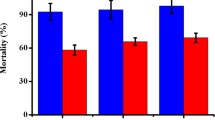
Serine protease plays an important role in fungal infection to invertebrate hosts. An extracellular protease (Hnsp) was detected in liquid culture of Hirsutella rhossiliensis OWVT-1 with nematodes (Panagrellus redivivus) as the unique nitrogen source and purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulphate precipitation, anion exchange chromatography and gel filtration. Its molecular mass was about 32 kDa, and the optimal reaction pH value and temperature were pH 7 and 40°C, respectively. The Hnsp activity was stable at pH 6–8 and decreased radically at 50°C for 10 min. Hnsp was highly sensitive to inhibitor of PMSF and well decomposed the substrate N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe-p-nitroanilide, suggesting that it belonged to the chymotrypsin/subtilisin of serine proteases. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of Hnsp was SVTDQQGADCGLARISHRE, which showed high homology with other serine proteases from nematophagous fungi. Ability to kill nematode and degrade its cuticle in vitro indicated that Hnsp could be involved in the infection of nematode.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cox GN, Kusch M and Edgar RS (1981). Cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans: Its isolation and partial characterization. J Cell Biol 90: 7–17
Wharton DA (1980). Nematode egg-shells. Parasitology 81: 447–463
Morton CO, Hirsch PR and Kerry BR (2004). Infection of plant-parasitic nematodes by nematophagous fungi – a review of the application of molecular biology to understand infection processes and to improve biological control. Nematology 6: 161–170
Lopez-Llorca LV (1990). Purification and properties of extracellular protease produced by the nematophagous fungus Verticillium suchlasporium Can J Microbiol 36: 530–537
Lopez-Llorca LV and Robertson WM (1992). Immunocytochemical localization of a 32-kDa protease from the nematophagous fungus Verticillium suchlasporium in infected nematode eggs. Exp Mycol 16: 261–267
Lopez-Llorca LV, Olivares-Bernabeu C, Salinas J, Jansson HB and Kolattukudy PE (2002). Prepenetration events in fungal parasitism of nematode eggs. Mycol Res 106: 499–506
Seger R, Butt TM, Kerry BR and Peberdy JF (1994). The nematophagous fungus Verticillium chlamydosporium produces a chymoeslastase-like protease which hydrolyses host nematode proteins. in situ Microbiology-(UK) 140: 2715–2723
Tunlid A and Jansson S (1991). Protease and their involvement in the infection and immobilization of nematodes by the nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Appl Environ Microb 57: 2868–2872
Tunlid A, Rosen S, Ek B and Rask R (1994). Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology-(UK) 140: 1687–1695
Zhao ML, Mo MH and Zhang KQ (2004). Characterization of a neutral serine protease and its full-length cDNA from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Mycologia 96: 16–22
Wang M, Yang JK and Zhang KQ (2006). Characterization of an extracellular protease and its cDNA from the nematode-trapping fungus Monacrosporium microscaphoides. Can J Microbiol 52: 130–139
Li J, Yang JK, Huang XW and Zhang KQ (2006). Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from Clonostachys rosea and its potential as a pathogenic factor. Process Biochem 41: 925–929
Ahman J, Johansson T, Olsson M, Punt PJ, Tunlid A and Hondel C (2002). Improving the pathogenicity of a nematode-trapping fungus by genetic engineering of a subtilisin with nematotoxic activity. Appl Environ Microb 68: 3408–3415
Jaffee BA and Zehir EI (1985). Parasitic and saprophytic abilities of the nematode-attacking fungus Hirsutella rhossiliensis. J Nematol 17: 341–345
Liu XZ and Chen SY (2000). Parasitism of Heterodera glycines by Hirsutella spp. in Minnesota soybean fields. Biol Control 19: 161–166
Timper P and Brodie BB (1993). Infection of Pratylenchus penetrans by pathogenic fungi. J Nematol 25: 297–302
Liu XZ and Chen SY (2001). Screening isolates of Hirsutella species for biocontrol of Heterodera glycines. Biocontrol Sci Technol 11: 151–160
Sun MH and Liu XZ (2006). Carbon requirements of some nematophagous, entomopathogenic and mycoparasitic hyphomycetes as fungal biocontrol agents. Mycopathologia 161: 295–305
Laemmli UK (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Bonants PJM, Fitters PFL, Thijs H, Waalwijk C, Henfling JWDM and Belder B (1995). A basic serine protease from Paecilomyces lilacinus with biological activity against Meloidogyne hapla eggs. Microbiology-(UK) 141: 775–784
Morton CO, Hirsch PR, Peberdy PR and Kerry BR (2003). Cloning of and genetic variation in protease VCP1 from the nematophagous fungus Pochonia chlamydosporia. Mycol Res 107: 38–46
Ahman J, Ek B, Rask L and Tunlid A (1996). Sequence analysis and regulation of a gene encoding a cuticle-degrading serine protease from the nematophagous fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology-(UK) 142: 1605–1616
Gunkel FA and Gassen HG (1989). Proteinase K from Tritirachium album Limber, characterization of the chromosomal gene and expression of the cDNA in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem 179: 185–194
Zhao ML, Huang JS, Mo MH and Zhang KQ (2005). A potential virulence factor involved in fungal pathogenicity: Serine-like protease activity of nematophagous fungus Clonostachys rosea. Fungal Divers 19: 217–234
Yang JK, Huang XW, Tian BY, Wang M, Niu QH and Zhang KQ (2005). Isolation and characterization of a serine protease from the nematophagous fungus, Lecanicillium psalliotae, displaying nematicidal activity. Biotechnol Lett 27: 1123–1128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Wu, W. & Liu, X. Purification and characterization of a neutral serine protease with nematicidal activity from Hirsutella rhossiliensis . Mycopathologia 163, 169–176 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-007-0100-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-007-0100-y