Abstract
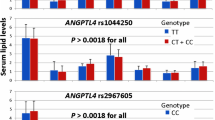
Although the role of matrix Gla protein (MGP) is not completely known but, its expression within subendothelial macrophages and vascular smooth muscle cells is suggested to be involved in vascular calcification. In this study, we investigated the associations between the serum MGP levels and the MGP promoter high minor allele frequency (MAF) variants with the development of stenosis in coronary arteries. Moreover, we evaluated the allele changes within predicted transcription factor elements with bioinformatics tools. 182 subjects were recruited from who underwent coronary angiography. The MGP promoter rs1800801, rs1800802 and rs1800799 genotypes and haplotypes were detected by ARMS-RFLP PCR techniques. The serum MGP concentration was measured using ELISA method. Jaspar profiles were used for scoring the polymorphic variations within the transcription factor elements. The genotype and two-allelic haplotype distributions were not significant between the patient and control groups (P > 0.05). The serum MGP levels had not significant differences between the genotypes (P > 0.1) and haplotypes (P > 0.4). Based on the prediction studies, we did not observe significant differences between the polymorphic scores in the predicted elements (P > 0.05). We concluded that the genotype and haplotype distributions of the MGP promoter high-MAF polymorphisms, as confirmed in the prediction studies and the serum MGP level are not significantly associated with the coronary artery disease. Based on the study results, the MGP protein did not play an important role in the development of stenosis of coronary arteries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Erbel R, Budoff M (2012) Improvement of cardiovascular risk prediction using coronary imaging: subclinical atherosclerosis: the memory of lifetime risk factor exposure. Eur Heart J 33:1201–1213
Lee KB, Budoff MJ, Zavodni A, Polak JF, Jeffrey Carr J, Burke GL, Herrington DM (2012) Coronary artery calcium is associated with degree of stenosis and surface irregularity of carotid artery. Atherosclerosis 223:160–165
Takeda Y, Hoshiga M, Tatsugami F, Morinaga I, Takehara K, Hotchi J, Yuki T, Ishihara T, Hanafusa T (2009) Clinical significance of calcification in ascending aorta as a marker for the requirement of coronary revascularization. J Atheroscler Thromb 16:346–354
Brancaccio D, Biondi ML, Gallieni M, Turri O, Galassi A, Cecchini F, Russo D, Andreucci V, Cozzolino M (2005) Matrix GLA protein gene polymorphisms: clinical correlates and cardiovascular mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Am J Nephrol 25:548–552
Proudfoot D, Shanahan CM (2001) Biology of calcification in vascular cells: intima versus media. Herz 26:245–251
Agatston AS, Janowitz WR, Hildner FJ, Zusmer NR, Viamonte MJ, Detrano R (1990) Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast computed tomography. J Am Coll Cardiol 15:827–832
Schinke T, McKee MD, Krsenty G (1999) Extracellular matrix calcification: where is the action? Nat Genet 21:150–151
Hackeng TM, Rosing J, Spronk HM, Vermeer C (2001) Total chemical synthesis of human matrix Gla protein. Protein Sci 10:864–870
Doherty TM, Fitzpatrick LA, Inoue D, Qiao JH, Fishbein MC, Detrano RC, Shah PK, Rajavashisth TB (2004) Molecular, endocrine, and genetic mechanisms of arterial calcification. Endocr Rev 25:629–672
Proudfoot D, Shanahan CM (2006) Molecular mechanisms mediating vascular calcification: role of matrix Gla protein. Nephrology (Carlton) 11:455–461
Luo G, Ducy P, McKee MD, Pinero GJ, Loyer E, Behringer RR, Karsenty G (1997) Spontaneous calcification of arteries and cartilage in mice lacking matrix GLA protein. Nature 386:78–81
Shanahan CM, Cary NR, Salisbury JR, Proudfoot D, Weissberg PL, Edmonds ME (1999) Medial localization of mineralization-regulating proteins in association with Monckeberg’s sclerosis: evidence for smooth muscle cell-mediated vascular calcification. Circulation 100:2168–2176
Farzaneh-Far A, Davies JD, Braam LA, Spronk HM, Proudfoot D, Chan SW, O’Shaughnessy KM, Weissberg PL, Vermeer C, Shanahan CM (2001) A polymorphism of the human matrix gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein promoter alters binding of an activating protein-1 complex and is associated with altered transcription and serum levels. J Biol Chem 276:32466–32473
Herrmann SM, Whatling C, Brand E, Nicaud V, Gariepy J, Simon A, Evans A, Ruidavets JB, Arveiler D, Luc G, Tiret L, Henney A, Cambien F (2000) Polymorphisms of the human matrix gla protein (MGP) gene, vascular calcification, and myocardial infarction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 20:2386–2393
Munroe PB, Olgunturk RO, Fryns JP, Van Maldergem L, Ziereisen F, Yuksel B, Gardiner RM, Chung E (1999) Mutations in the gene encoding the human matrix Gla protein cause Keutel syndrome. Nat Genet 21:142–144
Kobayashi N, Kitazawa R, Maeda S, Schurgers L, Kitazawa S (2004) T-138C polymorphism of matrix gla protein promoter alters its expression but is not directly associated with atherosclerotic vascular calcification. Kobe J Med Sci 50:69–81
Crosier MD, Booth SL, Peter I, Dawson-Hughes B, Price PA, O’Donnell CJ, Hoffmann U, Williamson MK, Ordovas JM (2009) Matrix Gla protein polymorphisms are associated with coronary artery calcification in men. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 55:59–65
Adkins RM (2004) Comparison of the accuracy of methods of computational haplotype inference using a large empirical dataset. BMC Genet 3(5):22
Roustazadeh A, Najafi M, Amirfarhangi A, Nourmohammadi I (2013) No association between MGP rs1800802 polymorphism and stenosis of the coronary artery. Ann Saudi Med 33:149–154
Frieldewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low -density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Najafi M, Gohari LH, Firoozrai M (2009) Paraoxonase 1 gene promoter polymorphisms are associated with the extent of stenosis in coronary arteries. Thromb Res 123:503–510
Ataman AV, Garbusova VY, Ataman YA, Matlaj OI, Obuchova OA (2012) Investigation of the MGP promoter and exon 4 polymorphisms in patients with ischemic stroke in the Ukrainian population. J Cell Mol Biol 10:19–26
Harbuzova VIu, Hur’ianova VL, Parkhomenko OM, Dosenko VIe, Ataman OV (2011) The frequency of allelic polymorphism of matrix Gla-protein gene in acute coronary syndrome patients. Fiziol Zh 57:16–24
Jia G, Stormont RM, Gangahar DM, Agrawal DK (2012) Role of matrix Gla protein in angiotensin II-induced exacerbation of vascular stiffness. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 303:H523–H532
Matsumoto K, Maniwa T, Tanaka T, Satoh K, Okunishi H, Oda T (2012) Proteomic analysis of calcified abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms. Int J Mol Med 30:417–429
Shea MK, O’Donnell CJ, Vermeer C, Magdeleyns EJ, Crosier MD, Gundberg CM, Ordovas JM, Kritchevsky SB, Booth SL (2011) Circulating uncarboxylated matrix gla protein is associated with vitamin K nutritional status, but not coronary artery calcium, in older adults. J Nutr 141:1529–1534
Price PA, Faus SA, Williamson MK (1998) Warfarin causes rapid calcification of the elastic lamellae in rat arteries and heart valves. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:1400–1407
Murshed M, Schinke T, McKee MD, Karsenty G (2004) Extracellular matrix mineralization is regulated locally; different roles of two gla-containing proteins. J Cell Biol 165:625–630
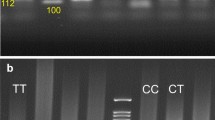
Najafi M, Firoozrai M, Gohari HL, Zavarehie A, Basiri G (2007) Direct haplotyping of bi-allelic SNPs using Arms and RFLP analysis techniques. Biomol Eng 24:609–612
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Najafi, M., Roustazadeh, A., Amirfarhangi, A. et al. Matrix Gla protein (MGP) promoter polymorphic variants and its serum level in stenosis of coronary artery. Mol Biol Rep 41, 1779–1786 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3027-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3027-7