Abstract
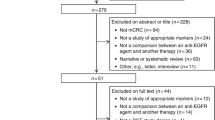
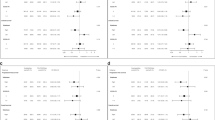
Anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (anti-EGFR MoAbs) in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) treatment are still not effective in all patients. This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between BRAF V600E mutation and the tumor response of anti-EGFR MoAbs for first-line treatment in mCRC patients. We searched the MEDLINE and EMBASE databases, using the key words that included colorectal cancer, cetuximab, panitumumab, and BRAF mutation and retrieved 445 articles. Among them four were included in the systematic review. Relative risks (RRs) with 95 % confidence intervals (CI) for response rate were calculated. BRAF mutation carriers had worse ORR than non-carriers in mCRC patients with KRAS wild-type in first-line treatment whether adding anti-EGFR MoAb to chemotherapy or not (RR = 0.43, [95 % CI 0.16–0.75]; RR = 0.38, [95 % CI 0.20–0.73]). But in the unselected patients whose KRAS mutation were unknown, BRAF mutation carriers had similar ORR whether adding cetuximab to chemotherapy or not (RR = 0.45, [95 % CI 0.18–1.09]; RR = 0.57, [95 % CI 0.15–2.23]). In BRAF mutation carriers adding anti-EGFR MoAb to chemotherapy was similar to chemotherapy alone whether in patients with wild-type KRAS or unselected patients (RR = 1.61, [95 % CI 0.57–4.47]; RR = 0.71, [95 % CI 0.18–2.77]). But in the BRAF mutation non-carriers, adding anti-EGFR MoAb produced a clear benefit in response rate than chemotherapy alone and this advantage was restricted to KRAS wild-type patients (RR = 1.48, [95 % CI 1.28–1.71]). BRAF mutation decreases tumor response in first-line treatment whether cetuximab was given or not in patients with KRAS wild-type, and anti-EGFR MoAb produces a clear benefit in response rate in patients with BRAF and KRAS wild-type.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saltz LB, Cox JV, Blanke C, Rosen LS, Fehrenbacher L, Moore MJ, Maroun JA, Ackland SP, Locker PK, Pirotta N (2000) Irinotecan plus fluorouracil and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 343(13):905–914
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G, Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G (2004) FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol 22(2):229–237
Colucci G, Gebbia V, Paoletti G, Giuliani F, Caruso M, Gebbia N, Cartenì G, Agostara B, Pezzella G, Manzione L (2005) Phase III randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: a multicenter study of the Gruppo Oncologico Dell’Italia Meridionale. J Clin Oncol 23(22):4866–4875
Sargent DJ, Wieand HS, Haller DG, Gray R, Benedetti JK, Buyse M, Labianca R, Seitz JF, O’Callaghan CJ, Francini G (2005) Disease-free survival versus overall survival as a primary end point for adjuvant colon cancer studies: individual patient data from 20,898 patients on 18 randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 23(34):8664–8670
Peeters M, Price TJ, Cervantes A, Sobrero AF, Ducreux M, Hotko Y, André T, Chan E, Lordick F, Punt CJA (2010) Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan (FOLFIRI) compared with FOLFIRI alone as second-line treatment in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(31):4706–4713
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D’Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G (2009) Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360(14):1408–1417
Di Fiore F, Blanchard F, Charbonnier F, Le Pessot F, Lamy A, Galais M, Bastit L, Killian A, Sesboüé R, Tuech J (2007) Clinical relevance of KRAS mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer treated by Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. Br J Cancer 96(8):1166–1169
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, Juan T, Sikorski R, Suggs S, Radinsky R (2008) Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(10):1626–1634
Di Nicolantonio F, Martini M, Molinari F, Sartore-Bianchi A, Arena S, Saletti P, De Dosso S, Mazzucchelli L, Frattini M, Siena S, Bardelli A (2008) Wild-type BRAF is required for response to panitumumab or cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26(35):5705–5712
Loupakis F, Ruzzo A, Cremolini C, Vincenzi B, Salvatore L, Santini D, Masi G, Stasi I, Canestrari E, Rulli E, Floriani I, Bencardino K, Galluccio N, Catalano V, Tonini G, Magnani M, Fontanini G, Basolo F, Falcone A, Graziano F (2009) KRAS codon 61, 146 and BRAF mutations predict resistance to cetuximab plus irinotecan in KRAS codon 12 and 13 wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 101(4):715–721
Van Cutsem E, Kohne CH, Lang I, Folprecht G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D, Tejpar S, Schlichting M, Zubel A, Celik I, Rougier P, Ciardiello F (2011) Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol 29(15):2011–2019
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, Celik I, Schlichting M, Koralewski P (2011) Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: the OPUS study. Ann Oncol 22(7):1535–1546
Rebersek M, Boc M, Cerkovnik P, Benedik J, Hlebanja Z, Volk N, Novakovic S, Ocvirk J (2011) Efficacy of first-line systemic treatment in correlation with BRAF V600E and different KRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer-a single institution retrospective analysis. Radiol Oncol 45(4):285–291
Tol J, Dijkstra JR, Vink-Borger ME, Koopman M, Vincent AD, Van Krieken JHJM, Ligtenberg MJL, Nagtegaal ID, Punt CJA (2009) BRAF mutation is associated with a decreased outcome in patients (pts) with advanced colorectal cancer (ACC) treated with chemotherapy and bevacizumab with or without cetuximab. Eur J Cancer Suppl 7(2–3):321
Tol J, Koopman M, Cats A, Rodenburg CJ, Creemers GJM, Schrama JG, Erdkamp FLG, Vos AH, van Groeningen CJ, Sinnige HAM (2009) Chemotherapy, bevacizumab, and cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 360(6):563–572
Tol J, Dijkstra JR, Klomp M, Teerenstra S, Dommerholt M, Vink-Borger ME, van Cleef PH, van Krieken JH, Punt CJA, Nagtegaal ID (2010) Markers for EGFR pathway activation as predictor of outcome in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with or without cetuximab. Eur J Cancer 46(11):1997–2009
Saridaki Z, Tzardi M, Papadatos-Patsos D, Kampouraki E, Zois E, Stathopoulos E, Georgoulias V, Mavroudis D, Souglakos J (2009) Prognostic and predictive significance of BRAF mutation in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer treated with 5-fluorouracil-based 1st line chemotherapy. Eur J Cancer Suppl 7(2–3):91–92
Bokemeyer C, Cutsem EV, Rougier P, Ciardiello F, Heeger S, Schlichting M, Celik I, Kohne CH (2012) Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: Pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer 48(10):1466–1475
Maughan TS, Adams RA, Smith CG, Meade AM, Seymour MT, Wilson RH, Idziaszczyk S, Harris R, Fisher D, Kenny SL, Kay E, Mitchell JK, Madi A, Jasani B, James MD, Bridgewater J, Kennedy MJ, Claes B, Lambrechts D, Kaplan R, Cheadle JP (2011) Addition of cetuximab to oxaliplatin-based first-line combination chemotherapy for treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial. Lancet 377(9783):2103–2114
Tveit KM, Guren T, Glimelius B, Pfeiffer P, Sorbye H, Pyrhonen S, Sigurdsson F, Kure E, Ikdahl T, Skovlund E, Fokstuen T, Hansen F, Hofsli E, Birkemeyer E, Johnsson A, Starkhammar H, Yilmaz MK, Keldsen N, Erdal AB, Dajani O, Dahl O, Christoffersen T (2012) Phase III Trial of cetuximab with continuous or intermittent fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (Nordic FLOX) versus FLOX alone in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: the NORDIC-VII study. J Clin Oncol 30(15):1755–1762
Modest DP, Jung A, Moosmann N, Laubender RP, Giessen C, Schulz C, Haas M, Neumann J, Boeck S, Kirchner T, Heinemann V, Stintzing S (2012) The influence of KRAS and BRAF mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab-based first-line therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer: an analysis of the AIO KRK-0104-trial. Int J Cancer 131(4):980–986. doi:10.1002/ijc.26467
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C (2004) Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 351(4):337–345
Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Salvatore L, Schirripa M, Lonardi S, Vaccaro V, Cuppone F, Giannarelli D, Zagonel V, Cognetti F, Tortora G, Falcone A, Bria E (2012) Clinical impact of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 118(6):1523–1532. doi:10.1002/cncr.26460
Mao C, Liao R-Y, Qiu L-X, Wang X-W, Ding H, Chen Q (2011) BRAF V600E mutation and resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep 38(4):2219–2223
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Taixing Wu for the guide on methodology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, D., Cao, D., Yang, Y. et al. Effect of BRAF V600E mutation on tumor response of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer treatment: a meta-analysis of randomized studies. Mol Biol Rep 41, 1291–1298 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2974-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-013-2974-8