Abstract
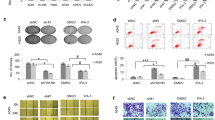
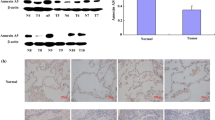
The purposes of this study were to elucidate the effects of ARHI (aplysia ras homolog I) on several biological features of lung cancer cells, including growth, proliferation and invasion, to collect experimental evidence for the future biological treatment of human lung cancer. The eukaryotic expression vector, pcDNA3.1–ARHI, was constructed and transfected into the human lung cancer cell line SK-MES-1. The biological properties of the resulting ARHI-expressing lung cancer cell line were evaluated using methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assay, flow cytometry, and a Transwell invasion assay. Additionally, the influence of ARHI on the gene expression levels of cyclin D1, p27KIP1, death-associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK1), and matrix metalloproteinases1/2 (MMP-1/2) was determined. Compared to the non-transfected SK-MES-1 cells and the cells transfected with the empty pcDNA3.1 plasmid, the ARHI-transfected cells displayed significantly reduced growth rates and decreased viability (P < 0.05). The ARHI-transfected cells also displayed a significantly higher percentage of cells in G1 phase (P < 0.05) and a lower percentage of cells in S phase (P < 0.05); a higher percentage of apoptosis (P < 0.05); and finally, a notable reduction in the basement membrane-penetration rate in the Transwell invasion assay (P < 0.05). Furthermore, it was determined that ARHI is capable of inhibiting the expression of cyclin D1, MMP-1, and MMP-2; however, ARHI promotes the expression of both p27KIP1 and DAPK1 in SK-MES-1 cells. In conclusion, overexpression of ARHI gene might be associated with the inhibition of lung cancer cell growth, proliferation and invasion, and the promotion of apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badgwell DB, Lu Z, Le K, Gao F, Yang M, Suh GK, Bao JJ, Das P, Andreeff M, Chen W, Yu Y, Ahmed AA, SLL W, Bast RC Jr (2012) The tumor-suppressor gene ARHI (DIRAS3) suppresses ovarian cancer cell migration through inhibition of the Stat3 and FAK/Rho signaling pathways. Oncogene 31:68–79
Prager GW, Poettler M, Unseld M, Zielinski CC (2012) Angiogenesis in cancer: anti-VEGF escape mechanisms. Transl Lung Cancer Res 1:14–25
Zou CF, Jia L, Jin H, Yao M, Zhao N, Huan J, Lu Z, Bast RC Jr, Feng Y, Yu Y (2011) Re-expression of ARHI (DIRAS3) induces autophagy in breast cancer cells and enhances the inhibitory effect of paclitaxel. BMC Cancer 11:22
Shadfan M, Lopez-Pajares V, Yuan ZM (2012) MDM2 and MDMX: alone and together in regulation of p53. Transl Cancer Res 1:88–99
Luo RZ, Fang X, Marquez R, Liu SY, Mills GB, Liao WS, Yu Y, Bast RC (2003) ARHI is a Ras-related small G-protein with a novel N-terminal extension that inhibits growth of ovarian and breast cancers. Oncogene 22:2897–2909
Méndez M, Custodio A, Provencio M (2011) New molecular targeted therapies for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis 3:30–56
Rosen DG, Wang L, Jain AN, Lu KH, Luo RZ, Yu Y, Liu J, Bast RC Jr (2004) Expression of the tumor suppressor gene ARHI in epithelial ovarian cancer is associated with increased expression of p21WAF1/CIP1 and prolonged progression-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 10:6559–6566
Li Y, Shi L, Han C, Wang Y, Yang J, Cao C, Jiao S (2012) Effects of ARHI on cell cycle progression and apoptosis levels of breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol 33:1403–1410
Nurunnabi M, Khatun Z, Moon WC, Lee G, Lee YK (2012) Heparin based nanoparticles for cancer targeting and noninvasive imaging. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2:219–226
Field JK, Liloglou T, Warrak S, Burger M, Becker E, Berlin K, Nimmrich I, Maier S (2005) Methylation discriminators in NSCLC identified by a microarray based approach. Int J Oncol 27:105–111
Yang H, Lu X, Qian J, Xu F, Hu Y, Yu Y, Bast RC, Li J (2010) Imprinted tumor suppressor gene ARHI induces apoptosis correlated with changes in DNA methylation in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 3:581–587
Waltering KK, Helenius MA, Sahu B, Manni V, Linja MJ, Janne OA, Visakorpi T (2009) Increased expression of androgen receptor sensitizes prostate cancer cells to low levels of androgens. Cancer Res 69:8141–8149
Lu X, Qian J, Yu Y, Yang H, Li J (2009) Expression of the tumor suppressor ARHI inhibits the growth of pancreatic cancer cells by inducing G1 cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep 22:635–640
Lin D, Cui F, Bu Q, Yan C (2011) The expression and clinical significance of GTP-binding RAS-like 3 (ARHI) and microRNA 221 and 222 in prostate Cancer. J Int Med Res 39:1870–1875
Chen MY, Liao WS, Lu Z, Bornmann WG, Hennessey V, Washington MN, Rosner GL, Yu Y, Ahmed AA, Bast RC Jr (2011) Decitabine and suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) inhibit growth of ovarian cancer cell lines and xenografts while inducing expression of imprinted tumor suppressor genes, apoptosis, G2/M arrest, and autophagy. Cancer 117:4424–4438
Zhao X, Li J, Zhuo J, Cai L (2010) Reexpression of ARHI inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis and impairs the mTOR/VEGF pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 403:417–421
Peng H, Xu F, Pershad R, Hunt KK, Frazier ML, Berchuck A, Gray JW, Hogg D, Bast RC Jr, Yu Y (2000) ARHI is the center of allelic deletion on chromosome 1p31 in ovarian and breast cancers. Int J Cancer 86:690–694
Lu Z, Luo RZ, Lu Y, Zhang X, Yu Q, Khare S, Kondo S, Kondo Y, Yu Y, Mills GB, Liao WS, Bast RC Jr (2008) The tumor suppressor gene ARHI regulates autophagy and tumor dormancy in human ovarian cancer cells. J Clin Investig 118:3917–3929
Xu C, Hao Y, Wei B, Ma J, Li J, Huang Q, Zhang F (2011) Apoptotic gene expression by human periodontal ligament cells following cyclic stretch. J Periodontal Res 46:742–748
Aberg M, Johnell M, Wickstrom M, Siegbahn A (2011) Tissue Factor/FVIIa prevents the extrinsic pathway of apoptosis by regulation of the tumor suppressor Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 (DAPK1). Thromb Res 127:141–148
Carter CJ (2008) Interactions between the products of the Herpes simplex genome and Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility genes: relevance to pathological-signalling cascades. Neurochem Int 52:920–934
Wong JC, Chan SK, Schaeffer DF, Sagaert X, Lim HJ, Kennecke H, Owen DA, Suh KW, Kim YB, Tai IT (2011) Absence of MMP2 expression correlates with poor clinical outcomes in rectal cancer, and is distinct from MMP1-related outcomes in colon cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:4167–4176
Jeffery N, McLean MH, El-Omar EM, Murray GI (2009) The matrix metalloproteinase/tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase profile in colorectal polyp cancers. Histopathology 54:820–828
Pritchard SC, Nicolson MC, Lloret C, McKay JA, Ross VG, Kerr KM, Murray GI, McLeod HL (2001) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 2, 9 and their tissue inhibitors in stage II non-small cell lung cancer: implications for MMP inhibition therapy. Oncol Rep 8:421–424
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Liang, L., Dong, L. et al. Effect of ARHI on lung cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis and invasion in vitro. Mol Biol Rep 40, 2671–2678 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2353-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-2353-x