Abstract
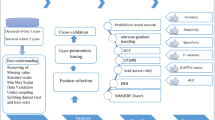
Drug-induced myelotoxicity usually leads to decrease the production of platelets, red cells, and white cells. Thus, early identification and characterization of myelotoxicity hazard in drug development is very necessary. The purpose of this investigation was to develop a prediction model of drug-induced myelotoxicity by using a Naïve Bayes classifier. For comparison, other prediction models based on support vector machine and single-hidden-layer feed-forward neural network methods were also established. Among all the prediction models, the Naïve Bayes classification model showed the best prediction performance, which offered an average overall prediction accuracy of \(94 \pm 0.9~\%\) for the training set and \(82 \pm 2.5~\%\) for the external test set. The significant contributions of this study are that we first developed a Naïve Bayes classification model of drug-induced myelotoxicity adverse effect using a larger scale dataset, which could be employed for the prediction of drug-induced myelotoxicity. In addition, several important molecular descriptors and substructures of myelotoxic compounds have been identified, which should be taken into consideration in the design of new candidate compounds to produce safer and more effective drugs, ultimately reducing the attrition rate in later stages of drug development.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parent-Massin D, Hymery N, Sibiril Y (2010) Stem cells in myelotoxicity. Toxicology 267:112–117. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2009.10.031
Gribaldo L, Casati S, Figliuzzi L, Marafante E (1998) In vitro myelotoxicity of environmental contaminants. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 6:135–141. doi:10.1016/S1382-6689(98)00029-5
De Jager R, Cheverton P, Tamanoi K, Coyle J, Ducharme M, Sakamoto N, Satomi M, Suzuki M (2000) DX-8951f: summary of phase I clinical trials. Ann N Y Acad Sci 922:260–273. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb07044.x
Gribaldo L, Malerba I, Collotta A, Casati S, Pessina A (2000) Inhibition of CFU-E/BFU-E by 3-azido-3-deoxythymidine, chlorpropamide, and protoporphirin IX zinc (II): a comparison between direct exposure of progenitor cells and long-term exposure of bone marrow cultures. Toxicol Sci 58:96–101. doi:10.1093/toxsci/58.1.96
Gisbert JP, Gomollón F (2008) Thiopurine-induced myelotoxicity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Am J Gastroenterol 103:1783–1800. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.01848.x
Masubuchi N, May RD, Atsumi R (2004) A predictive model of human myelotoxicity using five camptothecin derivatives and the in vitro colony forming unit granulocyte/macrophage assay. Clin Cancer Res 10:6722–6731. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0721
Holt DE, Andrews CM, Payne JP, Williams TC, Turton JA (1998) The myelotoxicity of chloramphenicol: in vitro and in vivo studies: II: in vivo myelotoxicity in the B6C3F1 mouse. Hum Exp Toxicol 17:8–17. doi:10.1177/096032719801700102
Sanpera N, Masot N, Janer M, Romeo C, De Pedro R (2002) Oestrogen-induced bone marrow aplasia in a dog with a Sertoli cell tumour. J Small Anim Pract 43:365–369. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.2002.tb00087.x
Parchment RE, Huang M, Erickson-Miller CL (1993) Roles for in vitro myelotoxicity tests in preclinical drug development and clinical trial planning. Toxicol Pathol 21:241–250. doi:10.1177/019262339302100217
Le Dréan G, Auffret M, Batina P, Arnold F, Sibiril Y, Arzur D, Parent-Massin D (2005) Myelotoxicity of trichothecenes and apoptosis: an in vitro study on human cord blood CD34\(^+\) hematopoietic progenitor. Toxicol In Vitro 19:1015–1024. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2005.03.017
Pessina A, Albella B, Bayo M, Bueren J, Brantom P, Casati S, Croera C, Gagliardi G, Foti P, Parchment R, Parent-Massin D, Schoeters G, Sibiril Y, Van Den Heuvel R, Gribaldo L (2003) Application of the CFU-GM assay to predict acute drug-induced neutropenia: an international blind trial to validate a prediction model for the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of myelosuppressive xenobiotics. Toxicol Sci 75:355–367. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg188
Rio B, Lautraite S, Parent-Massin D (1997) In vitro toxicity of trichothecenes on human erythroblastic progenitors. Hum Exp Toxicol 16:673–679. doi:10.1177/096032719701601108
Stephenson J, Axelrad AA, Mc Leod DL, Shreeve MM (1971) Induction of colonies of hemoglobin-synthesizing cells by erythropoietin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:1542–1546. doi:10.1073/pnas.68.7.1542
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Laliykina KS (1970) The development of fibroblasts colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea pig bone marrow and spleen. Cell Tissue Kinet 3:393–403. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.1970.tb00347.x
Naughton BA, Sibanda D, Azar L, San Roman J (1992) Differential effects of drugs upon hematopoiesis can be assessed in long-term bone marrow culture established on nylon screens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 199:481–490. doi:10.3181/00379727-199-43384
Dickins M, Modi S (2002) Importance of predictive ADME simulations. Drug Discov Today 7:755–756. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.022
Grime KH, Barton P, McGinnity DF (2013) Application of in silico, in vitro and preclinical pharmacokinetic data for the effective and efficient prediction of human pharmacokinetics. Mol Pharm 10:1191–1206. doi:10.1021/mp300476z
Kimber I, Humphris C, Westmoreland C, Alepee N, Dal Negro G, Manou I (2011) Computational chemistry, systems biology and toxicology. Harnessing the chemistry of life: revolutionizing toxicology. A commentary. J Appl Toxicol 31:206–209. doi:10.1002/jat.1666
Modi S, Hughes M, Garrow A, White A (2012) The value of in silico chemistry in the safety assessment of chemicals in the consumer goods and pharmaceutical industries. Drug Discov Today 17:135–142. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2011.10.022
Modi S (2004) Positioning ADMET in silico tools in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 9:14–15. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(04)02956-3
Vedani A, Smiesko M (2009) In silico toxicology in drug discovery—concepts based on three-dimensional models. Altern Lab Anim 37:477–496. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.08.022
Ekins S, Williams AJ, Xu JJ (2010) A predictive ligand-based bayesian model for human drug-induced liver injury. Drug Metab Dispos 38:2302–2308. doi:10.1124/dmd.110.035113
Ekins S (2014) Progress in computational toxicology. J Pharm Toxicol Methods 69:115–140. doi:10.1016/j.vascn.2013.12.003
Hu X, Yan A (2012) In silico models to discriminate compounds inducing and noninducing toxic myopathy. Mol Inf 31:27–39. doi:10.1002/minf.201100067
Zhang H, Li W, Xie Y, Wang WJ, Li LL, Yang SY (2011) Rapid and accurate assessment of seizure liability of drugs by using an optimal support vector machine method. Toxicol In vitro 25:1848–1854. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2011.05.015
Zhang H, Chen QY, Xiang ML, Ma CY, Huang Q, Yang SY (2009) In silico prediction of mitochondrial toxicity by using GA-CG-SVM approach. Toxicol In Vitro 23:134–140. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.001
Box GEP, Tiao CC (1973) Bayesian inference in statistical analysis. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Berger JO (1985) Statistical decision theory and bayesian analysis. Springer, New York
Langdon SR, Mulgrew J, Paolini GV, van Hoorn WP (2010) Pre-dicting cytotoxicity from heterogeneous data sources with Bayesian learning. J Cheminform 2:11–29. doi:10.1186/1758-2946-2-11
Di-wu L, Li LL, Wang WJ, Xie HZ, Yang J, Zhang CH, Huang Q, Zhong L, Feng S, Yang SY (2012) Identification of CK2 inhibitors with new scaffolds by a hybrid virtual screening approach based on Bayesian model; pharmacophore hypothesis and molecular docking. J Mol Graph Model 36:42–47. doi:10.1016/j.jmgm.2012.03.004
Yang Y, Zhang W, Cheng JG, Tang Y, Peng YQ, Li Z (2013) Pharmacophore, 3D-QSAR, and bayesian model analysis for ligands binding at the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptors: the key roles of amino group and hydrophobic sites. Chem Biol Drug Des 81:583–590. doi:10.1111/cbdd.12100
Zientek M, Stoner C, Ayscue R, Klug-McLeod J, Jiang Y, West M, Collins C, Ekins S (2010) Integrated in silico-in vitro strategy for addressing cytochrome P450 3A4 time-dependent inhibition. Chem Res Toxicol 23:664–676. doi:10.1021/tx900417f
Rogers D, Brown RD, Hahn M (2005) Using extended-connectivity fingerprints with Laplacian-modified Bayesian analysis in high-throughput screening follow-up. J Biomol Screen 10:682–686. doi:10.1021/tx900417f
Yang SY, Huang Q, Li LL, Ma CY, Zhang H, Bai R, Teng QZ, Xiang ML, Wei YQ (2009) An integrated scheme for feature selection and parameter setting in the support vector machine modeling and its application to the prediction of pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. Artif Intell Med 46:155–163. doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.001
Li LK, Shao S, Yiu KFC (2013) A new optimization algorithm for single hidden layer feedforward neural networks. Appl Soft Comput 13:2857–2862. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2012.04.034
Crivori E, Pennella G, Magistrelli M, Grossi P, Giusti AM (2011) Predicting myelosuppression of drugs from in silico models. J Chem Inf Model 51:434–445. doi:10.1021/ci1003834
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project for Enhancing the Research Capability of Young Teachers in Northwest Normal University (NWNU-LKQN-12-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Yu, P., Zhang, TG. et al. In silico prediction of drug-induced myelotoxicity by using Naïve Bayes method. Mol Divers 19, 945–953 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-015-9613-3