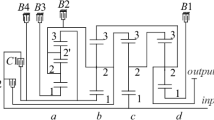
Abstract
Transmission efficiency is a principal index for estimating the performance of 2K-H closed epicyclical gear trains. To calculate transmission efficiency, it must confirm the power flow direction in transformation gear train and verify if there is power circulation in closed epicyclical gear train firstly. In this paper, a simple algorithm is proposed to confirm the power flow direction and estimate if there exist the power circulation based on transmission ratio of basic links in differential gear train and transformation gear train. The simplified equations are deduced to calculate the transmission efficiency and some examples are given finally.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cervantes-Sánchez JJ, Rico-Martínez JM, Panduro-Calvario C (2012) A general and systematic framework for the kinematic analysis of complex gear systems. Meccanica 47(1):3–21
Uyguroğlu M, Tokad Y (1998) Kinematic analysis of robotic bevel-gear trains: an application of network model approach. Meccanica 33(2):177–194
Uyguroğlu M, Demirel H (2005) TSAI–TOKAD (T–T) graph: the combination of non-oriented and oriented graphs for the kinematics of articulated gear mechanisms. Meccanica 40(3):223–232
Höhn BR (2010) Improvements on noise reduction and efficiency of gears. Meccanica 45:425–437
Macmillan RH (1949) Epicyclic gear efficiencies. Engineer 23:727–728
Macmillan RH (1961) Power flow and loss in differential mechanisms. J Mech Eng Sci 3(1):37–41
Radzimovsky EI (1956) A simplified approach for determining power losses and efficiency of planetary gear drives. Mach Des 28(3):101–110
Glover JH (1965) Efficiency and speed ratio expression for planetary gear systems. Prod Eng 27:72–79
Lei T, Lu LQ (1997) Matrix system for the analysis of planetary transmissions. ASME J Mech Des 119:333–337
Mathis R, Remond Y (1999) A new approach to solving the inverse problem for compound gears. ASME J Mech Des 12:98–106
del Castillo JM (2000) Symbolic computation of planetary gear efficiency. In: European congress on computational methods in applied sciences and engineering, CIMNE, Barcelona
Hedman A (1993) Transmission analysis: automatic derivation of relationships. ASME J Mech Des 115:1031–1037
del Castillo JM (2002) The analytical expression of the efficiency of planetary gear train. Mech Mach Theory 37(2):197–214
Salgado DR, Castillo D (2005) Selection and design of planetary gear train based on power flow maps. ASME J Mech Des 127(1):120–134
Pennestri E, Freudenstein F (1993) The mechanical efficiency of epicyclic gear train. ASME J Mech Des 115(3):645–651
Pennestrì E, Valentini PP (2003) A review of formulas for the mechanical efficiency analysis of two degrees-of-freedom epicyclic gear train. ASME J Mech Des 125(3):602–608
Kahraman A, Ligata HK, Zini DM (2004) A kinematics and power flow analysis methodology for automatic transmission planetary gear train. ASME J Mech Des 126(6):1071–1081
Nelson CA, Cipra RJ (2005) Simplified kinematic analysis of bevel epicyclic gear train with application to power-flow and efficiency analyses. ASME J Mech Des 127(2):278–286
Freudenstein F, Yang AT (1972) Kinematics and statics of a coupled epicyclic spur-gear train. Mech Mach Theory 7(2):263–275
Litvin FL, Fuentes A, Vecchiato D et al. (2004) New design and improvement of planetary gear train. NASA Glenn Research Center Technical Reports
Chen C, Liang TT (2011) Theoretic study of efficiency of two-DOF of epicyclic gear transmission via virtual power. ASME J Mech Des 133(3):031007
Chen C, Angeles J (2007) Virtual-power flow and mechanical gear-mesh power losses of epicyclic gear train. ASME J Mech Des 129(1):107–113
Fu ZS, Lu Zx (1998) Design of mechanism (pp 305–311). China University of Petroleum Press, Dongying, China
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of the Shangdong Province Young and Middle-Aged Scientists Research Awards Fund (BS2011ZZ002). The authors would also like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their suggestions for improving the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Cui, Hy. The analysis of power circulation and the simplified expression of the transmission efficiency of 2K-H closed epicyclic gear trains. Meccanica 48, 1071–1080 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-012-9652-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-012-9652-0