Abstract
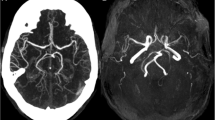
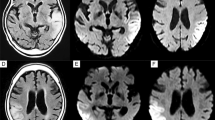
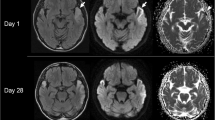
We reported a 53-year-old with late-onset mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) accompanied by aneurysm and large vessel dilations. Most studies have focused on microangiopathy causing stroke-like episodes. We report a case to describe large vessel involvement in clinical considerations, and possible mechanisms of aneurysm formation. We recommended regular angiographic examination for patients with MELAS.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MELAS:
-
mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke like episodes
- NAA:
-
N-acetyl aspartate
- NO:
-
nitric oxide
- eNOS:
-
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- UIA:
-
unruptured intracranial aneurysm
- DSA:
-
digital subtraction angiography
- IA:
-
intracranial aneurysm
- IL:
-
interleukin
- DAMPs:
-
damage associated molecular patterns
- COX:
-
cytochrome c oxidase
References
Bown MJ, Lloyd GM, Sandford RM, Thompson JR, London NJ, Samani NJ, Sayers RD (2007) The interleukin-10-1082 'A' allele and abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Vasc Surg 46:687–693. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2007.06.025
Brunetti-Pierri N et al (2011) Dilation of the aortic root in mitochondrial disease patients. Mol Genet Metab 103:167–170. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2011.02.007
El-Hattab AW, Emrick LT, Craigen WJ, Scaglia F (2012a) Citrulline and arginine utility in treating nitric oxide deficiency in mitochondrial disorders. Mol Genet Metab 107:247–252. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.06.018
El-Hattab AW, Hsu JW, Emrick LT, Wong LJ, Craigen WJ, Jahoor F, Scaglia F (2012b) Restoration of impaired nitric oxide production in MELAS syndrome with citrulline and arginine supplementation. Mol Genet Metab 105:607–614. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2012.01.016
El-Hattab AW, Adesina AM, Jones J, Scaglia F (2015) MELAS syndrome: clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, and treatment options. Mol Genet Metab 116:4–12. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2015.06.004
El-Hattab AW et al (2016) Impaired nitric oxide production in children with MELAS syndrome and the effect of arginine and citrulline supplementation. Mol Genet Metab 117:407–412. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2016.01.010
Finsterer J, Zarrouk-Mahjoub S (2016) Mitochondrial vasculopathy. World J Cardiol 8:333–339. doi:10.4330/wjc.v8.i5.333
Fukuyama K, Ishikawa Y, Ogino T, Inoue H, Yamaoka R, Hirose T, Nishihira T (2012) Mucosal necrosis of the small intestine in myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 18:5986–5989. doi:10.3748/wjg.v18.i41.5986
Gabrielson M et al (2016) Altered PPARgamma Coactivator-1 alpha expression in abdominal aortic aneurysm: possible effects on mitochondrial biogenesis. J Vasc Res 53:17–26. doi:10.1159/000446653
Lindeman JH, Abdul-Hussien H, Schaapherder AF, Van Bockel JH, Von der Thusen JH, Roelen DL, Kleemann R (2008) Enhanced expression and activation of pro-inflammatory transcription factors distinguish aneurysmal from atherosclerotic aorta: IL-6- and IL-8-dominated inflammatory responses prevail in the human aneurysm. Clin Sci (Lond) 114:687–697. doi:10.1042/CS20070352
Pavlakis SG, Phillips PC, DiMauro S, De Vivo DC, Rowland LP (1984) Mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes: a distinctive clinical syndrome. Ann Neurol 16:481–488. doi:10.1002/ana.410160409
Ping P et al (2015) Harnessing the power of integrated mitochondrial biology and physiology: a special report on the NHLBI mitochondria in heart diseases initiative. Circ Res 117:234–238. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.306693
Raju R et al (2016) Dermal γδ T-cells can Be activated by mitochondrial damage-associated molecular patterns. PLoS One 11:e0158993. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0158993
Schaefer AM, Phoenix C, Elson JL, McFarland R, Chinnery PF, Turnbull DM (2006) Mitochondrial disease in adults: a scale to monitor progression and treatment. Neurology 66:1932–1934. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000219759.72195.41
Schüll S et al (2015) Cytochrome c oxidase deficiency accelerates mitochondrial apoptosis by activating ceramide synthase 6. Cell Death and Disease 6:e1691. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.62
Sinha I, Sinha-Hikim AP, Hannawa KK, Henke PK, Eagleton MJ, Stanley JC, Upchurch GR Jr (2005) Mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in experimental rodent abdominal aortic aneurysms. Surgery 138:806–811. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2005.07.011
Srinivasan S, Avadhani NG (2012) Cytochrome c oxidase dysfunction in oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 53:1252–1263. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.07.021
Srinivasan S, Spear J, Chandran K, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B, Avadhani NG (2013) Oxidative stress induced mitochondrial protein kinase a mediates cytochrome c oxidase dysfunction. PLoS One 8:e77129. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077129
Takahashi N et al (2005) Vascular involvement in a patient with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. The American journal of the medical sciences 329:265–266
Tamura T, Jamous MA, Kitazato KT, Yagi K, Tada Y, Uno M, Nagahiro S (2009) Endothelial damage due to impaired nitric oxide bioavailability triggers cerebral aneurysm formation in female rats. J Hypertens 27:1284–1292. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328329d1a7
Tay SH, Nordli DR Jr, Bonilla E, Null E, Monaco S, Hirano M, DiMauro S (2006) Aortic rupture in mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes. Arch Neurol 63:281–283. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.2.281
Vattemi G et al (2011) Increased protein nitration in mitochondrial diseases: evidence for vessel wall involvement. Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP 10:M110.002964. doi:10.1074/mcp.M110.002964
Wang S, Wu S, Zheng T, Yang Z, Ma X, Jia W, Xiang K (2013) Mitochondrial DNA mutations in diabetes mellitus patients in Chinese Han population. Gene 531:472–475. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.019
Wang F, Quan QQ, Zhang CL, Li YB, Jiang TB (2015) Association between polymorphisms in the interleukin-10 gene and risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Genet Mol Res 14:17599–17604. doi:10.4238/2015.December.21.32
Wiebers DO et al. (2003) Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet (London, England) 362:103–110
Yang C, Qi ZY, Shao C, Xing WK, Wang Z (2015) Association between three eNOS polymorphisms and intracranial aneurysms risk: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e452. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000000452
Yatsuga S et al (2012) MELAS: a nationwide prospective cohort study of 96 patients in Japan. Biochim Biophys Acta 1820:619–624. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.03.015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, K., Li, S., Chen, H. et al. Late onset MELAS with m.3243A > G mutation and its association with aneurysm formation. Metab Brain Dis 32, 1069–1072 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9989-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9989-0