Abstract
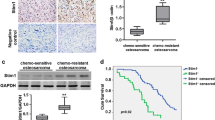
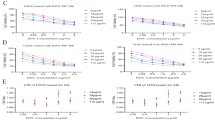
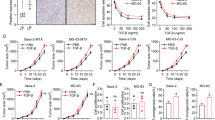
In vitro evidence of hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin (CDDP)-mediated apoptosis exists in human osteosarcoma (OS). Gambogic acid (GA) is a promising chemotherapeutic compound that could increase the chemotherapeutic effectiveness of CDDP in human OS cells by inducing cell cycle arrest and promoting apoptosis. This study examined whether GA could overcome OS cell resistance to CDDP. Hypoxia significantly reduced levels of CDDP-induced apoptosis in the OS cell lines MG63 and HOS. However, combined treatment with GA and CDDP revealed a strong synergistic action between these drugs, and higher protein levels of the apoptosis-related factor Fas, cleaved caspase-8 and cleaved caspase-3 and lower expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α are detected in both cell lines. Meanwhile, drug resistance was not reversed by exposure to the HIF-1α inhibitor 2-methoxyestradiol. These findings strongly suggest that hypoxia-induced resistance to CDDP is reversed by GA in OS cells independently of HIF-1α. Furthermore, in vivo studies using xenograft mouse models revealed that combination therapy with CDDP and GA exerted increased antitumor effects by inducing apoptosis. Taken together, our results demonstrate that GA may be a new potent therapeutic agent useful for targeting human OS cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
Gambogic acid
- CDDP:
-
Cisplatin
- 2ME2:
-
2-Methoxyestradiol
- OS:
-
Osteosarcoma
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1a
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
References
Bertout JA, Patel SA, Simon MC (2008) The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:967–975
Saikumar P, Dong Z, Patel Y et al (1998) Role of hypoxia-induced Bax translocation and cytochrome c release in reoxygenation injury. Oncogene 17:3401–3415
Aragones J, Jones DR, Martin S et al (2001) Evidence for the involvement of diacylglycerol kinase in the activation of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 by low oxygen tension. J Biol Chem 276:10548–10555
Santore MT, McClintock DS, Lee VY et al (2002) Anoxia-induced apoptosis occurs through a mitochondria-dependent pathway in lung epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L727–L734
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG et al (2003) The hypoxia-inducible factor-1a is a negative factor for tumor therapy. Oncogene 22:3213–3220
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM et al (1998) Role of HIF-1 alpha or in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 394:485–490
Moritz W, Meier F, Stroka DM et al (2002) Apoptosis in hypoxic human pancreatic islets correlates with HIF-1alpha expression. FASEB J 16(7):745–747
Akakura N, Kobayashi M, Horiuchi I et al (2001) Constitutive expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha renders pancreatic cancer cells resistant to apoptosis induced by hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res 61(17):6548–6554
Gatta G, Corazziari I, Magnani C et al (2003) Childhood cancer survival in Europe. Ann Oncol 5:v119–v127
Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW et al (1986) The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J Med 314:1600–1606
Zhao W, You CC, Zhuang JP et al (2013) Viability inhibition effect of gambogic acid combined with cisplatin on osteosarcoma cells via mitochondria-independent apoptotic pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 382:243–252
Zhao W, Zhou SF, Zhang ZP et al (2011) Gambogic acid inhibits the growth of osteosarcoma cells in vitro by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Oncol Rep 25(5):1289–1295
Berenbaum MC (1989) What is synergy? Pharmacol Rev 41:93–141
Greco WR, Bravo G, Parsons JC (1995) The search for synergy: a critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol Rev 47:331–385
Zhang JL, Wang Z, Hu W et al (2013) DHA regulates angiogenesis and improves the efficiency of CDDP for the treatment of lung carcinoma. Microvasc Res 87:14–24
Wang LH, Li Y, Yang SN et al (2014) Gambogic acid synergistically potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer through suppressing NF-κB and MAPK/HO-1 signalling. Br J Cancer 110:341–352
Wang F, Zhang W, Guo L et al (2014) Gambogic acid suppresses hypoxia-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α/vascular endothelial growth factor expression via inhibiting phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target protein of rapamycin pathway in multiple myeloma cells. Cancer Sci 105:1063–1070
Hussein D, Estlin EJ, Dive C et al (2006) Chronic hypoxia promotes hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-dependent resistance to etoposide and vincristine in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2241–2250
Kilic M, Kasperczyk H, Fulda S et al (2007) Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha in modulation of apoptosis resistance. Oncogene 26:2027–2038
Adamski J, Price A, Dive C, Makin G (2013) Hypoxia-induced cytotoxic drug resistance in osteosarcoma is independent of HIF-1Alpha. PLoS One 8:e65304. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0065304
Liu L, Ning X, Sun L et al (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha contributes to hypoxia-induced chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 99(1):121–128
Sermeus A, Cosse JP, Crespin M et al (2008) Hypoxia induces protection against etoposide-induced apoptosis: molecular profiling of changes in gene expression and transcription factor activity. Mol Cancer 7:27
Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM et al (2003) 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell 3:363–375
Lockshin RA, Zakeri Z (2007) Cell death in health and disease. J Cell Mol Med 11:1214–1224
Siddik ZH (2003) Cisplatin: mode of cytotoxic action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene 22:65–79
Unruh A, Ressel A, Mohamed HG et al (2003) The hypoxia-inducible factor-1a is a negative factor for tumor therapy. Oncogene 22:3213–3220
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81441081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Zhao Wei and Xia Shi-Qi have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Xia, SQ., Zhuang, JP. et al. Hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells is reversed by gambogic acid independently of HIF-1α. Mol Cell Biochem 420, 1–8 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2759-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2759-1