Abstract
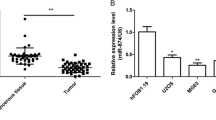
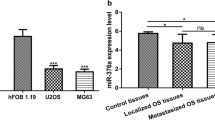
Recent data strongly suggest the important role of miRNAs in various cancer-related processes. Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common primary cancer of the bone and usually leads to deaths due to its rapid proliferation and metastasis. Here, we demonstrated that compared with noncancerous bone tissues, miR-135b expression is frequently upregulated in OS specimens, inversely correlated with potential target-FOXO1 expression pattern. Bioinformatics analysis combined with experimental confirmation revealed FOXO1 is a direct target of miR-135b in OS. Functionally, miR-135b inhibitor significantly inhibited OS cells proliferation and invasion. Forced expression of FOXO1 showed the opposite effect, and FOXO1 knockdown abolished the effect of miR-135b inhibitor. Taken together, our data provide compelling evidence that miR-135b functions as an onco-miRNA in OS to promote OS cells proliferation and invasion, and its oncogenic effects are mediated chiefly through targeting FOXO1.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
He H, Ni J, Huang J (2014) Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in osteosarcoma. Oncol Lett 7:1352–1362
Yang J, Zhang W (2013) New molecular insights into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol 25:398–406
Sakamoto A, Iwamoto Y (2008) Current status and perspectives regarding the treatment of osteo-sarcoma: chemotherapy. Rev Recent Clin Trials 3:228–231
Croce CM, Calin GA (2005) miRNAs, cancer and stem cell division. Cell 122:6–7
Croce CM (2009) Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 10:704–714
Di Leva G, Garofalo M, Croce CM (2014) MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol 9:287–314
Wu X, Zhong D, Gao Q, Zhai W, Ding Z, Wu J (2013) MicroRNA-34a inhibits human osteosarcoma proliferation by downregulating ether a go-go 1 expression. Int J Med Sci 10:676–682
Zhao H, Guo M, Zhao G, Ma Q, Ma B, Qiu X, Fan Q (2012) miR-183 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma via downregulation of the expression of Ezrin in F5M2 cells. Int J Mol Med 30:1013–1020
Yang J, Gao T, Tang J, Cai H, Lin L, Fu S (2013) Loss of microRNA-132 predicts poor prognosis in patients with primary osteosarcoma. Mol Cell Biochem 381:9–15
Xu Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Song Y, Luo Y, Zhang X, Jiang L, Sun Z, Miao Z, Xu H (2012) MicroRNA-335 acts as a metastasis suppressor in gastric cancer by targeting Bcl-w and specificity protein 1. Oncogene 31:1398–1407
Wu W, Wang Z, Yang P, Yang J, Liang J, Chen Y, Wang H, Wei G, Ye S, Zhou Y (2014) MicroRNA-135b regulates metastasis suppressor 1 expression and promotes migration and invasion in colorectal cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 388:249–259
Arigoni M, Barutello G, Riccardo F, Ercole E, Cantarella D, Orso F, Conti L, Lanzardo S, Taverna D, Merighi I, Calogero RA, Cavallo F, Quaglino E (2013) miR-135b coordinates progression of ErbB2-driven mammary carcinomas through suppression of MID1 and MTCH2. Am J Pathol 182:2058–2070
Lin CW, Chang YL, Chang YC, Lin JC, Chen CC, Pan SH, Wu CT, Chen HY, Yang SC, Hong TM, Yang PC (2013) MicroRNA-135b promotes lung cancer metastasis by regulating multiple targets in the Hippo pathway and LZTS1. Nat Commun 4:1877
Zhang L, Sun ZJ, Bian Y, Kulkarni AB (2013) MicroRNA-135b acts as a tumor promoter by targeting the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway in genetically defined mouse model of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett 331:230–238
Munding JB, Adai AT, Maghnouj A, Urbanik A, Zöllner H, Liffers ST, Chromik AM, Uhl W, Szafranska-Schwarzbach AE, Tannapfel A, Hahn SA (2012) Global microRNA expression profiling of microdissected tissues identifies miR-135b as a novel biomarker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer 131:E86–E95
Matsuyama H, Suzuki HI, Nishimori H, Noguchi M, Yao T, Komatsu N, Mano H, Sugimoto K, Miyazono K (2011) miR-135b mediates NPM-ALK-driven oncogenicity and renders IL-17-producing immunophenotype to anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood 118:6881–6892
Bhinge A, Poschmann J, Namboori SC, Tian X, Jia Hui Loh S, Traczyk A, Prabhakar S, Stanton LW (2014) MiR-135b is a direct PAX6 target and specifies human neuroectoderm by inhibiting TGF-β/BMP signaling. EMBO J 33:1271–1283
Xu S, Cecilia Santini G, De Veirman K, Vande Broek I, Leleu X, De Becker A, Van Camp B, Vanderkerken K, Van Riet I (2013) Upregulation of miR-135b is involved in the impaired osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells derived from multiple myeloma patients. PLoS One 8:e79752
Huang H, Tindall DJ (2007) Dynamic FoxO transcription factors. J Cell Sci 120:2479–2487
Huang H, Regan KM, Lou Z, Chen J, Tindall DJ (2006) CDK2-dependent phosphorylation of FOXO1 as an apoptotic response to DNA damage. Science 314:294–297
Greer EL, Brunet A (2005) FOXO transcription factors at the interface between longevity and tumor suppression. Oncogene 24:7410–7425
Li F, Liu B, Gao Y, Liu Y, Xu Y, Tong W, Zhang A (2014) Upregulation of microRNA-107 induces proliferation in human gastric cancer cells by targeting the transcription factor FOXO1. FEBS Lett 588:538–544
Dong XY, Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Vessella RL, Wang RX, Chung LW, Zhou W, Dong JT (2006) FOXO1A is a candidate for the 13q14 tumor suppressor gene inhibiting androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 66:6998–7006
Fendler A, Jung M, Stephan C, Erbersdobler A, Jung K, Yousef GM (2013) The antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in prostate cancer by inhibition of FOXO1. PLoS One 8:e80807
Sangodkar J, Dhawan NS, Melville H, Singh VJ, Yuan E, Rana H, Izadmehr S, Farrington C, Mazhar S, Katz S, Albano T, Arnovitz P, Okrent R, Ohlmeyer M, Galsky M, Burstein D, Zhang D, Politi K, Difeo A, Narla G (2012) Targeting the FOXO1/KLF6 axis regulates EGFR signaling and treatment response. J Clin Invest 122:2637–2651
Li ZC, Zhang LM, Wang HB, Ma JX, Sun JZ (2014) Curcumin inhibits lung cancer progression and metastasis through induction of FOXO1. Tumour Biol 35:111–116
Chang YW, Zhao YF, Cao YL, Gu XF, Li ZQ, Wang SQ, Miao JH, Zhan HS (2013) Liver X receptor α inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of FoxO1. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:180–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hong Pei and Zhiliang Jin have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, H., Jin, Z., Chen, S. et al. MiR-135b promotes proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells via targeting FOXO1. Mol Cell Biochem 400, 245–252 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2281-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2281-2