Abstract
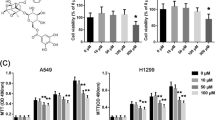
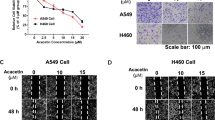
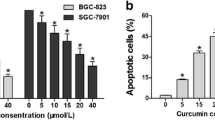
Oleanolic acid (OA) is a natural compound from plants with anti-tumor activities. However, the mechanism of the inhibitory effect of OA on cell cycle progression has not been completely explored. We employed several lung carcinoma cell lines to investigate the cell cycle-related molecular pathway affected by OA. The data revealed that OA suppressed the proliferation of lung cancer cells in both dose- and time-dependent manners, along with an increase in miR-122 abundance. The suppression of miR-122 abolished the effect of OA on lung cancer cells. CCNG1 and MEF2D, two putative miR-122 targets, were found to be downregulated by OA treatment. Restoring their expression counteracted the effect of OA on lung carcinoma cells. OA was further shown to induce the expression of miR-122-regulating transcriptional factors in lung cancer cells. Collectively, OA induced cell cycle arrest in lung cancer cells through miR-122/Cyclin G1/MEF2D pathway. This finding may contribute to the understanding of the molecular mechanism of OA’s anti-tumor activity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu J (2005) Oleanolic acid and ursolic acid: research perspectives. J Ethnopharmacol 100:92–94. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2005.05.024
Guo G, Yao W, Zhang Q, Bo Y (2013) Oleanolic acid suppresses migration and invasion of malignant glioma cells by inactivating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. PLoS One 8:e72079. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0072079
Liu J, Wu N, Ma L, Liu M, Liu G, Zhang Y, Lin X (2014) Oleanolic acid suppresses aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells by switching pyruvate kinase type m isoforms. PLoS One 9:e91606. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091606
Zhou R, Zhang Z, Zhao L, Jia C, Xu S, Mai Q, Lu M, Huang M, Wang L, Wang X, Jin D, Bai X (2011) Inhibition of mTOR signaling by oleanolic acid contributes to its anti-tumor activity in osteosarcoma cells. J Orthop Res 29:846–852. doi:10.1002/jor.21311
Wang X, Bai H, Zhang X, Liu J, Cao P, Liao N, Zhang W, Wang Z, Hai C (2013) Inhibitory effect of oleanolic acid on hepatocellular carcinoma via ERK-p53-mediated cell cycle arrest and mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 34:1323–1330. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgt058
Way TD, Tsai SJ, Wang CM, Ho CT, Chou CH (2014) Chemical constituents of rhododendron formosanum show pronounced growth inhibitory effect on non-small-cell lung carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem 62:875–884. doi:10.1021/jf404243p
Shah MY, Calin GA (2014) MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in human cancers. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. doi:10.1002/wrna.1229
Ma L, Liu J, Shen J, Liu L, Wu J, Li W, Luo J, Chen Q, Qian C (2010) Expression of miR-122 mediated by adenoviral vector induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 9:554–561
Fornari F, Gramantieri L, Giovannini C, Veronese A, Ferracin M, Sabbioni S, Calin GA, Grazi GL, Croce CM, Tavolari S, Chieco P, Negrini M, Bolondi L (2009) MiR-122/cyclin G1 interaction modulates p53 activity and affects doxorubicin sensitivity of human hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Res 69:5761–5767. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4797
Coulouarn C, Factor VM, Andersen JB, Durkin ME, Thorgeirsson SS (2009) Loss of miR-122 expression in liver cancer correlates with suppression of the hepatic phenotype and gain of metastatic properties. Oncogene 28:3526–3536. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.211
Xu Y, Xia F, Ma L, Shan J, Shen J, Yang Z, Liu J, Cui Y, Bian X, Bie P, Qian C (2011) MicroRNA-122 sensitizes HCC cancer cells to adriamycin and vincristine through modulating expression of MDR and inducing cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett 310:160–169. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2011.06.027
Ma L, Liu J, Liu L, Duan G, Wang Q, Xu Y, Xia F, Shan J, Shen J, Yang Z, Bie P, Cui Y, Bian XW, Prieto J, Avila MA, Qian C (2014) Overexpression of the transcription factor MEF2D in hepatocellular carcinoma sustains malignant character by suppressing G2-M transition genes. Cancer Res 74:1452–1462. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2171
Kang J, Kim E, Kim W, Seong KM, Youn H, Kim JW, Kim J, Youn B (2013) Rhamnetin and cirsiliol induce radiosensitization and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by miR-34a-mediated suppression of Notch-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem 288:27343–27357. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.490482
Zhang Y, Zhang GB, Xu XM, Zhang M, Qu D, Niu HY, Bai X, Kan L, He P (2012) Suppression of growth of A549 lung cancer cells by waltonitone and its mechanisms of action. Oncol Rep 28:1029–1035. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1869
Hu J, Xu Y, Hao J, Wang S, Li C, Meng S (2012) MiR-122 in hepatic function and liver diseases. Protein Cell 3:364–371. doi:10.1007/s13238-012-2036-3
Thomas M, Deiters A (2013) MicroRNA miR-122 as a therapeutic target for oligonucleotides and small molecules. Curr Med Chem 20:3629–3640
Kim MK, Kim SC, Kang JI, Hyun JH, Boo HJ, Eun SY, Park DB, Yoo ES, Kang HK, Kang JH (2011) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced PC12 cell death is mediated by MEF2D down-regulation. Neurochem Res 36:223–231. doi:10.1007/s11064-010-0309-x
Liu AM, Xu Z, Shek FH, Wong KF, Lee NP, Poon RT, Chen J, Luk JM (2014) miR-122 targets pyruvate kinase M2 and affects metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One 9:e86872. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086872
Liu J, Zheng L, Ma L, Wang B, Zhao Y, Wu N, Liu G, Lin X (2014) Oleanolic acid inhibits proliferation and invasiveness of Kras-transformed cells via autophagy. J Nutr Biochem. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2014.06.006
Liu J, Zheng L, Zhong J, Wu N, Liu G, Lin X (2014) Oleanolic acid induces protective autophagy in cancer cells through the JNK and mTOR pathways. Oncol Rep 32:567–572. doi:10.3892/or.2014.3239
Liu J, Zheng L, Wu N, Ma L, Zhong J, Liu G, Lin X (2014) Oleanolic acid induces metabolic adaptation in cancer cells by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase pathway. J Agric Food Chem 62:5528–5537. doi:10.1021/jf500622p
Liu J, Wu N, Ma LN, Zhong JT, Liu G, Zheng LH, Lin XK (2014) p38 MAPK signaling mediates mitochondrial apoptosis in cancer cells induced by oleanolic acid. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 15:4519–4525
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Liu, M. & Li, D. Oleanolic acid suppresses the proliferation of lung carcinoma cells by miR-122/Cyclin G1/MEF2D axis. Mol Cell Biochem 400, 1–7 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2228-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2228-7