Abstract
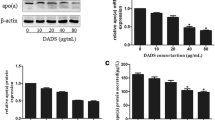
Lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] is a highly atherogenic lipoprotein, whose metabolism is poorly understood. Efficient and secure drugs that can lower elevated plasma Lp(a) concentrations are currently lacking. Fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF-21), a member of the FGFS super family, regulates glucose and lipid metabolism in hepatocytes and adipocytes via FGFR-ERK1/2 signaling. In this study, we investigated the molecular mechanisms that influence apolipoprotein(a) [apo(a)] biosynthesis. We also determined the effects of FGF21 on HepG2 cell apo(a) expression and secretion, as well as the mechanism of FGF21 in these effects. Results showed that FGF21 inhibited apo(a) expression at both mRNA and protein levels in a dose- and time--dependent manner and then suppressed the secretion of apo(a). These effects were attenuated by PD98059 (ERK1/2 inhibitor) and Elk-1 siRNA. PD166866 (FGFR1 inhibitor) also attenuated the FGF21-mediated inhibition of apo(a) expression and inhibited ERK1/2 and Elk-1 activation. These results demonstrate that FGF21 suppresses apo(a) expression via the FGFR1-ERK1/2-Elk-1 pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berg K (1963) A new serum type system in man-the Lp system. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 59:369–382
Zlatohlávek L, Zídková K, Vrablík M, Haas T, Prusíková M, Svobodová H, Ceska R (2008) Lipoprotein(a) and its position among other risk factors of atherosclerosis. Physiol Res 57:777–783
Nielsen LB, Juul K, Nordestgaard BG (1998) Increased degradation of lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic compared with nonlesioned aortic intima-inner media of rabbits: in vivo evidence that lipoprotein(a) may contribute to foam cell formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:641–649
Sotiriou SN, Orlova VV, Al-Fakhri N, Ihanus E, Economopoulou M, Isermann B, Bdeir K, Nawroth PP, Preissner KT, Gahmberg CG, Koschinsky ML, Chavakis T (2006) Lipoprotein(a) in atherosclerotic plaques recruits inflammatory cells through interaction with Mac-1 integrin. FASEB J 20:559–561
Pedersen TX, McCormick SP, Tsimikas S, Bro S, Nielsen LB (2010) Lipoprotein(a) accelerates atherosclerosis in uremic mice. J Lipid Res 51:2967–2975
Brunner C, Kraft HG, Utermann G, Muller HJ (1993) Cys4057 of apolipoprotein(a) is essential for lipoprotein(a) assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:11643–11647
Becker L, McLeod RS, Marcovina SM, Yao Z, Koschinsky ML (2001) Identification of a critical lysine residue in apolipoprotein B-100 that mediates noncovalent interaction with apolipoprotein(a). J Biol Chem 276:36155–36162
McLean JW, Tomlinson JE, Kuang WJ, Eaton DL, Chen EY, Fless GM, Scanu AM, Lawn RM (1987) cDNA sequence of human apolipoprotein(a) is homologous to plasminogen. Nature 330:132–137
Utermann G, Duba C, Menzel HJ (1988) Genetics of the quantitative Lp(a) lipoprotein trait. II. Inheritance of Lp(a) glycoprotein phenotypes. Hum Genet 78:47–50
Norata GD, Ballantyne CM, Catapano AL (2013) New therapeutic principles in dyslipidaemia: focus on LDL and Lp(a) lowering drugs. Eur Heart J 34:1783–1789
Dieplinger H, Utermann G (1999) The seventh myth of lipoprotein (a): where and how is it assembled. Curr Opin Lipidol 10:275–283
Bonen DK, Hausman AM, Hadjiagapiou C, Skarosi SF, Davidson NO (1997) Expression of a recombinant apolipoprotein(a) in HepG2 cells. Evidence for intracellular assembly of lipoprotein(a). J Biol Chem 272:5659–5667
White AL, Rainwater DL, Hixson JE, Estlack LE, Lanford RE (1994) Intracellular processing of apo(a) in primary baboon hepatocytes. Chem Phys Lipids 67–68(123–133):114
Li H, Zhang J, Jia W (2013) Fibroblast growth factor 21: a novel metabolic regulator from pharmacology to physiology. Front Med 7:25–30
Murata Y, Konishi M, Itoh N (2011) FGF21 as an endocrine regulator in lipid metabolism: from molecular evolution to physiology and pathophysiology. J Nutr Metab 2011:981315
Kharitonenkov A, Larsen P (2011) FGF21 reloaded: challenges of a rapidly growing field. Trends Endocrinol Metab 22:81–86
Shen Y, Ma X, Zhou J, Pan X, Hao Y, Zhou M, Lu Z, Gao M, Bao Y, Jia W (2013) Additive relationship between serum fibroblast growth factor 21 level and coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 12:124
Cong WT, Ling J, Tian HS, Ling R, Wang Y, Huang BB, Zhao T, Duan YM, Jin LT, Li XK (2013) Proteomic study on the protective mechanism of fibroblast growth factor 21 to ischemia-reperfusion injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 91:973–984
Reitman ML (2013) FGF21 mimetic shows therapeutic promise. Cell Metab 18:307–309
Ming AY, Yoo E, Vorontsov EN, Altamentova SM, Kilkenny DM, Rocheleau JV (2012) Dynamics and distribution of Klothoβ (KLB) and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 (FGFR1) in living cells reveal the fibroblast growth factor-21 (FGF21)-induced receptor complex. J Biol Chem 287:19997–20006
Bookout AL, de Groot MH, Owen BM, Lee S, Gautron L, Lawrence HL, Ding X, Elmquist JK, Takahashi JS, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2013) FGF21 regulates metabolism and circadian behavior by acting on the nervous system. Nat Med 19:1147–1152
Cuevas-Ramos D, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Gómez-Pérez FJ (2012) Metabolic actions of fibroblast growth factor 21. Curr Opin Pediatr 24:523–529
Fisher FM, Estall JL, Adams AC, Antonellis PJ, Bina HA, Flier JS, Kharitonenkov A, Spiegelman BM, Maratos-Flier E (2011) Integrated regulation of hepatic metabolism by fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in vivo. Endocrinology 152:2996–3004
Chennamsetty I, Claudel T, Kostner KM, Trauner M, Kostner GM (2012) Gene expression APOA FGF19 signaling cascade suppresses. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:1220–1227
Wei DH, Zhang XL, Wang R, Zeng JF, Zhang K, Yang J, Li S, Lin XL, Jiang ZS, Wang GX, Wang Z (2013) Oxidized lipoprotein(a) increases endothelial cell monolayer permeability via ROS generation. Lipids 48:579–586
Panek RL, Lu GH, Dahring TK, Batley BL, Connolly C, Hamby JM, Brown KJ (1998) In vitro biological characterization and antiangiogenic effects of PD 166866, a selective inhibitor of the FGF-1 receptor tyrosine kinase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:569–577
Nygaard EB, Vienberg SG, Ørskov C, Hansen HS, Andersen B (2012) Metformin stimulates FGF21 expression in primary hepatocytes. Exp Diabetes Res 2012:465282
Adams AC, Kharitonenkov A (2013) FGF21 drives a shift in adipokine tone to restore metabolic health. Aging (Albany NY) 5:386–387
Chennamsetty I, Claudel T, Kostner KM, Baghdasaryan A, Kratky D, Levak-Frank S, Frank S, Gonzalez FJ, Trauner M, Kostner GM (2011) Farnesoid X receptor represses hepatic human APOA gene expression. J Clin Invest 121:3724–3734
Yie J, Hecht R, Patel J, Stevens J, Wang W, Hawkins N, Steavenson S, Smith S, Winters D, Fisher S, Cai L, Belouski E, Chen C, Michaels ML, Li YS, Lindberg R, Wang M, Véniant M, Xu J (2009) FGF21N- and C-termini play different roles in receptor interaction and activation. FEBS Lett 583:19–24
Gaich G, Chien JY, Fu H, Glass1 LC, Deeg MA, Holland WL, Kharitonenkov A, Bumol T, Schilske HE, David E (2013) Moller the effects of LY2405319, an FGF21 analog, in obese human subjects with type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabolism 18:333–340
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Innovative Research Team for Science and Technology in Higher Educational Institutions of Hunan Province and Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81070221) and Visiting Scholar Foundation of Key Laboratory for Biorheological Science, and Technology (Chongqing University) of Ministry of Education (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guohua Li: co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Li, G., He, X. et al. FGF21 inhibits apolipoprotein(a) expression in HepG2 cells via the FGFR1-ERK1/2-Elk-1 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 393, 33–42 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2044-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2044-0