Abstract
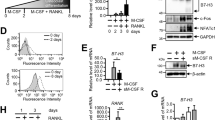
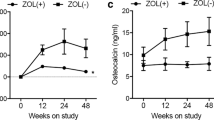
Hepatitis C combination therapy comprising ribavirin and interferon-α causes dramatic improvement with the sustained virological response; however, this treatment may result in the loss of bone mineral density. To investigate the effects of ribavirin on bone cells, we examined osteoblast differentiation as well as the formation of osteoclasts from their precursors. Ribavirin enhances osteoclast formation through osteoblasts by up-regulation of TRANCE/RANKL gene expression, whereas it has no significant effect on either osteoblast differentiation or on bone formation. Understanding ribavirin’s underlying mechanism of action on bone cells will enable the improved management of bone loss in chronic hepatitis C patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoofnagle JH, Mullen KD, Jones DB, Rustgi V, Di Bisceglie A, Peters M, Waggoner JG, Park Y, Jones EA (1986) Treatment of chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis with recombinant human alpha interferon. A preliminary report. N Engl J Med 315:1575–1578
McHutchison JG, Poynard T (1999) Combination therapy with interferon plus ribavirin for the initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Semin Liver Dis 19 Suppl(1):57–65
Zeuzem S, Feinman SV, Rasenack J, Heathcote EJ, Lai MY, Gane E, O’Grady J, Reichen J, Diago M, Lin A, Hoffman J, Brunda MJ (2000) Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med 343:1666–1672
Tsuneoka K, Tameda Y, Takase K, Nakano T (1996) Osteodystrophy in patients with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. J Gastroenterol 31:669–678
Crosbie OM, Freaney R, McKenna MJ, Hegarty JE (1999) Bone density, vitamin D status, and disordered bone remodeling in end-stage chronic liver disease. Calcif Tissue Int 64:295–300
Gallego-Rojo FJ, Gonzalez-Calvin JL, Munoz-Torres M, Mundi JL, Fernandez-Perez R, Rodrigo-Moreno D (1998) Bone mineral density, serum insulin-like growth factor I, and bone turnover markers in viral cirrhosis. Hepatology 28:695–699
Gonzalez-Amaro R, Garcia-Monzon C, Garcia-Buey L, Moreno-Otero R, Alonso JL, Yague E, Pivel JP, Lopez-Cabrera M, Fernandez-Ruiz E, Sanchez-Madrid F (1994) Induction of tumor necrosis factor alpha production by human hepatocytes in chronic viral hepatitis. J Exp Med 179:841–848
Van der Merwe SW, van den Bogaerde JB, Goosen C, Maree FF, Milner RJ, Schnitzler CM, Biscardi A, Mesquita JM, Engelbrecht G, Kahn D, Fevery J (2003) Hepatic osteodystrophy in rats results mainly from portasystemic shunting. Gut 52:580–585
Coelho LF, de Freitas Almeida GM, Mennechet FJ, Blangy A, Uze G (2005) Interferon-{alpha} and -{beta} differentially regulate osteoclastogenesis: role of differential induction of chemokine CXCL11 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11917–11922
Weide R, Ehlenz K, Lorenz W, Walthers E, Klausmann M, Pfluger KH (1996) Successful treatment of osteoporosis in systemic mastocytosis with interferon alpha-2b. Ann Hematol 72:41–43
Solis-Herruzo JA, Castellano G, Fernandez I, Munoz R, Hawkins F (2000) Decreased bone mineral density after therapy with alpha interferon in combination with ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 33:812–817
Trombetti A, Giostra E, Mentha G, Negro F, Rizzoli R (2002) Lack of evidence for ribavirin-induced bone loss. Hepatology 36:255–257
Kim K, Kim JH, Lee J, Jin HM, Lee SH, Fisher DE, Kook H, Kim KK, Choi Y, Kim N (2005) Nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 induces osteoclast-associated receptor gene expression during tumor necrosis factor-related activation-induced cytokine-mediated osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem 280:35209–35216
So H, Rho J, Jeong D, Park R, Fisher DE, Ostrowski MC, Choi Y, Kim N (2003) Microphthalmia transcription factor and PU.1 synergistically induce the leukocyte receptor osteoclast-associated receptor gene expression. J Biol Chem 278:24209–24216
Suda T, Jimi E, Nakamura I, Takahashi N (1997) Role of 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in osteoclast differentiation, function. Methods Enzymol 282:223–235
Moreira RO, Balduino A, Martins HS, Reis JS, Duarte ME, Farias ML, Borojevic R (2004) Ribavirin, but not interferon alpha-2b, is associated with impaired osteoblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro. Calcif Tissue Int 75:160–168
Hsu H, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Solovyev I, Colombero A, Timms E, Tan HL, Elliott G, Kelley MJ, Sarosi I, Wang L, Xia XZ, Elliott R, Chiu L, Black T, Scully S, Capparelli C, Morony S, Shimamoto G, Bass MB, Boyle WJ (1999) Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3540–3545
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20:345–357
Glue P (1999) The clinical pharmacology of ribavirin. Semin Liver Dis 19 Suppl 19 Suppl(1):17–24
Acknowledgments
We thank A. Ko and K. Kim for assistance. We also thank C. Perchonock for critical reading and providing helpful comments on this manuscript. This work was supported in part by Chonnam National University (to J. Lee) and Grant R13-2002-013-03001-0 (to N. Kim) from the Korea Science & Engineering Foundation through the Medical Research Center for Gene Regulation at Chonnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Kim, J.H., Kim, K. et al. Ribavirin enhances osteoclast formation through osteoblasts via up-regulation of TRANCE/RANKL. Mol Cell Biochem 296, 17–24 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9293-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-006-9293-5