Abstract
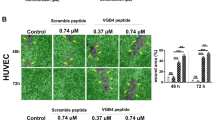
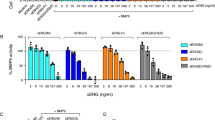
Many diseases are associated with angiogenesis. Therefore, inhibition of angiogenesis is deemed as a treatment for those diseases. To date, many angiogenesis inhibitors are from large plasma proteins. In this study we identified a 21-aa peptide (named peptide ZY1) from human placenta growth factor-1 and it may serve as a potent angiogenesis inhibitor. Our study demonstrated ZY1 inhibited angiogenesis in vitro by suppressing proliferation, migration and tube formation of HUVECs. The in vivo inhibition activity of ZY1 was observed in chicken chorioallantoic membrane assays and tumor-bearing mouse models. Moreover, we found ZY1 inhibited angiogenesis by decreasing the expression of HIF-1β and subsequently reducing its downstream molecule VEGF. In conclusion, peptide ZY1 can inhibit angiogenesis and may serve as an anti-angiogenesis drug candidate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassino E, Antoniotti S, Gasparri F, Munaron L (2016) Effects of flavonoid derivatives on human microvascular endothelial cells. Nat Prod Res 2:1–4
Cao RH, Wu HL, Veitonmāki N et al (1999) Suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth by the inhibitor K1-5 generated by plasmin-mediated proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5728–5733
Chen JF, Ye L, Zhang LJ, Jiang WG (2008) Placenta growth factor, PLGF, influenes the motility of lung cancer cells, the role of Rho associated kinase, Rock1. J Cell Biochem 105:313–320
Christinger HW, Fuh G, de Vos AM, Wiesmann C (2004) The crystal structure of placental growth facotr in complex with domain 2 of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1. J Biol Chem 279:10382–10388
Drevs J, Zirrgiebel U, Schmidt-Gersbach CIM et al (2005) Soluble markers for the assessment of biological activity with PTK787/ZK 222584 (PTK/ZK), a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced colorectal cancer from two phase I trials. Ann Oncol 16:558–565
Eelen G, de Zeeuw P, Simons M, Carmeliet P (2015) Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased vasculature. Circ Res 116:1231–1244
Errico M, Riccioni T, Iyer S et al (2004) Identification of placenta growth factor determinants for binding and activation of Flt-1 receptor. J Biol Chem 279:43929–43939
Ettayapuram Ramaprasad AS, Singh S, Gajendra PSR, Venkatesan S (2015) AntiAngioPred: a server for prediction of anti-angiogenic peptides. PLos One 9:e0136990
Falcon BL, Chintharlapalli S, Uhlik MT, Pytowski B (2016) Antagonist antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) as anti-angiogenic agents. Pharmacol Ther 164:204–225
Gacche RN, Meshram RJ (2014) Angiogenic factors as potential drug target: efficacy and limitations of anti-angiogenic therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1846:161–179
Hao Z, Sadek L (2016) Sunitinib: the antiangiogenic effects and beyond. Onco Targets Ther 9:5495–5505
Iyer S, Leonidas DD, Swaminathan J et al (2001) The crystal structure of human placenta growth factor-1 (PlGF-1) an angiogenic protein at 2.0 Å resolution. J Biol Chem 276:12153–12161
Jayson GC, Kerbel R, Ellis LM, Harris AL (2016) Antiangiogenic therapy in oncology: current status and future directions. The Lancet 10043:518–529
Kasai A, Shintani N, Oda M et al (2004) Apelin is a novel angiogenic factor in retinal endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:395–400
Lin Z, Zhang Q, Luo W (2016) Angiogenesis inhibitors as therapeutic agents in cancer: challenges and future directions. Eur J Pharmacol 793:76–81
Luttun A, Autiero M, Tjwa M, Carmeliet P (2004) Genetic dissection of tumor angiogenesis: are PlGF and VEGFR-1 novel anti-cancer targets?. Biochim Biophys Acta 1654:79–94
Maltepe E, Schmidt JV, Baunoch D et al (1997) Abnormal angiogenesis and responses to glucose and oxygen deprivation in mice lacking the protein ARNT. Nature 386:403–407
Masoud GN, Li W (2015) HIF-1 α pathway: role, regulation and intervention for cancer therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 5:378–389
Ribatti D (2008) The discovery of the placental growth factor and its role in angiogenesis: a historical review. Angiogenesis 11:215–221
Rosca EV, Koskimaki JE et al (2011) Anti-angiogenic peptides for cancer therapeutics. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12:1101–1116
Shahneh FZ, Baradaran B, Zamani F, Aghebati-Maleki L (2013) Tumor aniogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapies. Hum Antib 22:15–19
Sulochana KN, Fan HP, Jois S et al (2005) Peptides derived from human decorin leucine-rich repeat 5 inhibit angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 280:27935–27948
Takeshita S, Zheng LP, Brogi E et al (1994) Therapeutic angiogenesis: a single intraarterial bolus of vascular endothelial growth factor augments revascularization in a rabbit ischemic hind limb model. J Clin Invest 93:662–670
Terashima J, Sampei S, Iidzuka M et al (2016) VEGF expression is regulated by HIF-1α and ARNT in 3D KYSE-70, esophageal cancer cell spheroids. Cell Biol Int 11:1187–1194
Tjwa M, Luttun A, Autiero M, Carmeliet P (2003) VEGF and PlGF, two pleiotropic growth factors with distinct roles in development and homeostasis. Cell Tissue Res 314:5–14
Vandewynckel YP, Laukens D, Devisscher L et al (2016) Placental growth factor inhibition modulates the interplay between hypoxia and unfolded protein response in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 16:9
Warfel NA, El-Deiry WS (2014) HIF-1 signaling in drug resistance to chemotherapy. Curr Med Chem 26:3021–3028
Welti J, Loges S, Dimmeler S, Carmeliet P (2013) Recent molecular discoveries in angiogenesis and antiangiogenic therapies in cancer. J Clin Invest 123:3190–3200
Xu Y, Zhao H, Zheng Y et al (2010) A novel antiangiogenic peptide derived from hepatocyte growth factor inhibits neovascularization in vitro and in vivo. Mol Vis 16:1982–1995
Yi ZF, Cho SG, Zhao H et al (2009) A novel peptide from human apolipoprotein (a) inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth by targeting c-Scr phosphorylation in VEGF-induced human umbilical endothelial cell. Int J Cancer 124:843–852
Ying Z, Qing G, Xun X (2012) Inhibition of ocular neovascularization by a novel peptide derived from human placenta growth factor-1. Acta Ophthalmol 90:512–523
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants from the Research Fund for the National Nature Science Funding of China (No. 81402233). Weijun Wang and Qing Gu performed the research. Ying Zheng and Weijun Wang analyzed the data. Ying Zheng and Xun Xu designed the research study and wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Gu, Q., Xu, X. et al. A PlGF-1 Derived Peptide Inhibits Angiogenesis via HIF-1β/VEGF Pathway. Int J Pept Res Ther 23, 343–355 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9567-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9567-z