Abstract
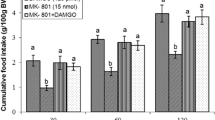
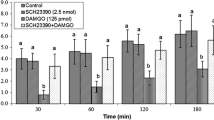
Endocannabinoids and opiates have regulatory role in some physiological functions in mammals but their interaction(s) have not been studied in avian. This survey is designed to investigate interaction of these systems on feeding behavior in neonatal chickens. In experiment 1, chicken intracerebroventricular (ICV) injected with saline, DAMGO (µ-opioid receptors agonist, 125 pmol), SR141716A (CB1 receptors antagonist, 6.25 µg) and SR141716A + DAMGO. In experiment 2, saline, DAMGO, AM630 (CB2 receptors antagonist, 1.25 µg) and DAMGO + AM630. Experiments 3–6 followed the procedure similar to experiments 1 and 2, except DPDPE (δ-opioid receptors agonist, 40 pmol) and U-50488H (κ-opioid receptors agonist, 30 nmol) instead of DAMGO were used. In experiment 7, saline, Naloxone (opioid receptors antagonist, 5 µg), 2-AG (CB1 receptors agonist, 2 µg), Naloxone + 2-AG were used. Experiment 8 was similar to experiment 7, except CB65 (CB2 receptors agonist, 1.25 µg) used instead of 2-AG. Cumulative food intake was recorded until 120 min post injection. Data provided that, ICV injection of DAMGO decreased food intake and its effect amplified by CB1 and CB2 receptors antagonist (P < 0.001). DPDPE increased food intake and CB2 receptors antagonist blocked DPDPE-induced hyperphagia (P < 0.001). U-50488H-induced feeding but its effect did not alter via CB1 and CB2 receptors antagonist (P > 0.05). Hyperphagia-induced by CB1 and CB2 receptors agonist amplified by naloxone (P < 0.001). Perhaps there is interaction between endocannabinoid and opioidergic systems on appetite regulation in chicken.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes MJ, Holmes G, Primeaux SD, York DA, Bray GA (2006) Increased expression of mu opioid receptors in animals susceptible to diet-induced obesity. Peptides 27:3292–3298
Bodnar RJ (2012) Endogenous opiates and behavior: 2011. Peptides 38:463–522
Braida D, Pozzi M, Parolaro D, Sala M (2001) Intracerebral self-administration of the cannabinoid receptor agonist CP 55,940 in the rat: interaction with the opioid system. Eur J Pharmacol 413:227–234
Browning KN, Zheng Z, Gettys TW, Travagli RA (2006) Vagal afferent control of opioidergic effects in rat brainstem circuits. J Physiol 575:761–776
Bungo T, Kawamura K, Izumi T, Dodo K, Ueda H (2004) Feeding responses to µ-, δ- and κ-opioid receptor agonists in the meat-type chick. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 78:707–710
Bungo T, Kawamura K, Izumi T, Dodo K, Ueda H (2005) Effects of various µ-, δ- and κ-opioid ligands on food intake in the meat-type chick. Physiol Behav 85:519–523
Chen RZ, Frassetto A, Fong TM (2006) Effects of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor inverse agonist AM251 on food intake and body weight in mice lacking μ-opioid receptors. Brain Res 1108:176–178
D’Addario C, Micioni Di Bonaventura MV, Puccia M, Romano A, Gaetani S, Ciccocioppo R, Cifani C, Maccarrone M (2014) Endocannabinoid signaling and food addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 47:203–224
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin A (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of l-proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695
Denbow DM (1994) Peripheral regulation of food intake in poultry. J Nutr 124:1349S–1354S
Di Marzo VGS, Wang L, Liu J, Batkai S, Jarai Z, Fezza F, Miura GI, Palmiter RD, Sugiura T, Kunos G (2001) Leptin regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature 410:822–825
Dodo K, Izumi TH, Ueda H, Bungo T (2005) Response of neuropeptide Y-induced feeding to µ-, δ- and κ-opioid receptor antagonists in the neonatal chick. Neurosci Lett 373:85–88
Emadi L, Jonaidi H, Hosseini Amir Abad E (2011) The role of central CB2 cannabinoid receptors on food intake in neonatal chicks. J Comp Physiol A 197:1143–1147
Fichna J, Janecka A, Costentin J, Do Rego J (2007) The endomorphin system and its evolving neurophysiological role. Pharmacol Rev 59:88–123
Fowler CJ, Nilsson O, Andersson M, Disney G, Jacobsson SO, Tiger G (2001) Pharmacological properties of cannabinoid receptors in the avian brain: similarity of rat and chicken cannabinoid1 receptor recognition sites and expression of cannabinoid2 receptor-like immunoreactivity in the embryonic chick brain. Pharmacol Toxicol 88:213–222
Furuse M, Matsumoto M, Saito N, Sugahara K, Hasegawa S (1997) The central corticotropin-releasing factor and glucagon-like peptide-1 in food intake of the neonatal chick. Eur J Pharmacol 339:211–214
Ghozland S, Matthes HW, Simonin F, Filliol D, Kieffer BL, Maldonado R (2002) Motivational effects of cannabinoids are mediated by μ-opioid and 6-opioid receptors. J Neurosci 22(3):1146–1154
Ibegbu AO, Mullaney I, Fyfe L, MacBean D (2011) The roles of opioid receptors and agonists in health and disease conditions. Br J Pharmacol Toxicol 2(2):84–91
Irwin N, Hunter K, Frizzell N, Flatt PR (2008) Antidiabetic effects of sub-chronic administration of the cannabinoid receptor (CB1) antagonist, AM251, in obese diabetic (ob/ob) mice. Eur J Pharmacol 581:226–233
Kaneko K, Yoshikawa M, Ohinata K (2012) Novel orexigenic pathway prostaglandin D2-NPY system-involvement in orally active orexigenic δ opioid peptide. Neuropeptides 46:353–357
Khan MSI, Ohkubo T, Masuda N, Tachibana T, Ueda H (2009) Central administration of metastin increases food intake through opioid neurons in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol Part A 153:209–212
Kirkham TC, Williams CM (2001) Synergistic effects of opioid and cannabinoid antagonists on food intake. Psychopharmacol 153:267–270
Kozlov AP, Nizhnikov M, Kramskaya TA, Varlinskaya EI, Spear NE (2013) Mu-opioid blockade reduces ethanol effects on intake and behavior of the infant rat during short-term but not long-term social isolation. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:773–782
Le Merrer J, Becker JAJ, Befort K, Kieffer BL (2009) Reward processing by the opioid system in the brain. Physiol Rev 89:1379–1412
Levine AS (2006) The animal model in food intake regulation: examples from the opioid literature. Physiol Behav 89:92–96
López HH (2010) Cannabinoid–hormone interactions in the regulation of motivational processes. Hormones Behav 58:100–110
Manzanares J, Ortiz S, Oliva JM, Perez-Rial S, Palomo T (2005) Interactions between cannabinoid and opioid receptor systems in the mediation of ethanol effects. Alcohol Alcohol 40(1):25–34
McCormack JF, Denbow DM (1990) Central versus peripheral opioid regulation of ingestive behavior in the domestic fowl. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 96(1):211–216
Meade S, Denbow M (2001) Feeding, drinking, and temperature response of chickens to intracerebroventricular histamine. Physiol Behav 73:65–73
Novoseletsky N, Nussinovitch A, Friedman-Einat M (2011) Attenuation of food intake in chicks by an inverse agonist of cannabinoid receptor 1 administered by either injection or ingestion in hydrocolloid carriers. Gen Comp Endocrinol 170:522–527
Olanrewaju HA, Thaxton JP, Dozier WA, Purswell J, Roush WB, Branton SL (2006) A review of lighting programs for broiler production. Int J poultry Sci 5(4):301–308
Onaivi ES, Carpio O, Ishiguro H, Schanz N, Uhl GR, Benno R (2008) Behavioral effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptor activation and its influence on food and alcohol consumption. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1139:426–433
Onaivi ES, Ishiguro H, Gu S, Liu QR (2012) CNS effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptors: beyond neuro-immuno-cannabinoid activity. J Psychopharmacol 26:92–103
Pickel V, Chan J, Kash T, Rodriguez J, MacKie K (2004) Compartment-specific localization of cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and μ-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens. Neuroscience 127(1):101–112
Pritchett CE, Pardee AL, McGuirk SR, Will MJ (2010) The role of nucleus accumbens adenosine–opioid interaction in mediating palatable food intake. Brain Res 1306:85–92
Saito ES, Kaiya H, Tachibana T, Tomonaga S, Denbow DM, Kangawa K, Furuse M (2005) Inhibitory effect of ghrelin on food intake is mediated by the corticotropin-releasing factor system in neonatal chicks. Regul Pept 125:201–208
Sharkey KA, Darmani NA, Parker LA (2014) Regulation of nausea and vomiting by cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Eur J Pharmacol 722:134–146
Skelly MJ, Guy EG, Howlett AC, Pratt WE (2010) CB1 receptors modulate the intake of a sweetened-fat diet in response to mu-opioid receptor stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:144–151
Solinas M, Goldberg SR (2005) Motivational effects of cannabinoids and opioids on food reinforcement depend on simultaneous activation of cannabinoid and opioid systems. Neuropsychopharmacol 30:2035–2045
Soria-Gomez E, Matias I, Rueda-Orozco PE, Cisneros M, Petrosino S, Navarro L, Di Marzo V, Prospero-Garcia O (2007) Pharmacological enhancement of the endocannabinoid system in the nucleus accumbens shell stimulates food intake and increases c-Fos expression in the hypothalamus. Br J Pharmacol 151:1109–1116
Taha SA (2010) Preference or fat? Revisiting opioid effects on food intake. Physiol Behav 100:429–437
Tambaro S, Tomasi ML, Bortolato M (2013) Long-term CB1 receptor blockade enhances vulnerability to anxiogenic-like effects of cannabinoids. Neuropharmacol 70:268–277
Van Tienhoven A, Juhasz LP (1962) The chicken telencephalon, diencephalon and mesencephalon in sterotaxic coordinates. J Comp Neurol 118:185–197
Wiley JL, Marusich JA, Zhang Y, Fulp A, Maitra R, Thomas BF, Mahadevan A (2012) Structural analogs of pyrazole and sulfonamide cannabinoids: effects on acute food intake in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 695:62–70
Williams CM, Kirkham TC (2002) Reversal of ∆9-THC hyperphagia by SR141716 and naloxone but not dexfenfluramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:333–340
Steinman JL, Fujikawa DG, Wasterlain CG, Cherkin A, Morley JE (1987) The effects of adrenergic, opioid and pancreatic polypeptidergic compounds on feeding and other behaviors in neonatal leghorn chicks. Peptides 8:585–592
Yanagita K, Shiraishi J, Fujita M, Bungo T (2008) Effects of N-terminal fragments of β-endorphin on feeding in chicks. Neurosci Lett 442:140–142
Yao L, McFarland K, Fan P, Jiang Z, Ueda T, Diamond I (2006) Adenosine A2a blockade prevents synergy between mu-opiate and cannabinoid CB1 receptors and eliminates heroin-seeking behavior in addicted rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:7877–7882
Zendehdel M, Hassanpour S (2014) Ghrelin-induced hypophagia is mediated by the β2 adrenergic receptor in chicken. J Physiol Sci 64:383–391
Zendehdel M, Mokhtarpouriani K, Babapour V, Baghbanzadeh A, Pourrahimi M, Hassanpour S (2013a) The effect of serotonergic system on nociceptin/orphanin FQ induced food intake in chicken. J Physiol Sci 63:271–277
Zendehdel M, Mokhtarpouriani K, Hamidi F, Montazeri R (2013b) Intracerebroventricular injection of ghrelin produces hypophagia through central serotonergic mechanisms in chicken. Vet Res Commun 37(1):37–41
Zendehdel M, Hamidi F, Hassanpour S (2014a) The effect of histaminergic system on nociceptin/orphanin FQ induced food intake in chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther. doi:10.1007/s10989-014-9445-5
Zendehdel M, Hasani K, Babapour V, Seyedali Mortezaei S, Khoshbakht Y, Hassanpour S (2014b) Dopamine-induced hypophagia is mediated by D1 and 5HT-2c receptors in chicken. Vet Res Commun 38:11–19
Zheng H, Patterson LM, Berthoud HR (2007) Orexin signaling in the ventral tegmental area is required for high-fat appetite induced by opioid stimulation of the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 27:11075–11082
Conflict of interest
Morteza Zendehdel, Shahin Hassanpour, Vahab Babapour, Saeed Charkhkar and Mahshid Mahdavi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
All experiments executed in according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the institutional animal ethical committee.
Informed Consent
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zendehdel, M., Hassanpour, S., Babapour, V. et al. Interaction Between Endocannabinoid and Opioidergic Systems Regulates Food Intake in Neonatal Chicken. Int J Pept Res Ther 21, 289–297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-015-9457-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-015-9457-9