Abstract
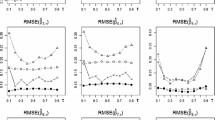
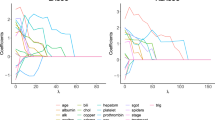
Regarding survival data analysis in regression modeling, multiple conditional quantiles are useful summary statistics to assess covariate effects on survival times. In this study, we consider an estimation problem of multiple nonlinear quantile functions with right censored survival data. To account for censoring in estimating a nonlinear quantile function, weighted kernel quantile regression (WKQR) has been developed by using the kernel trick and inverse-censoring-probability weights. However, the individually estimated quantile functions based on the WKQR often cross each other and consequently violate the basic properties of quantiles. To avoid this problem of quantile crossing, we propose the non-crossing weighted kernel quantile regression (NWKQR), which estimates multiple nonlinear conditional quantile functions simultaneously by enforcing the non-crossing constraints on kernel coefficients. The numerical results are presented to demonstrate the competitive performance of the proposed NWKQR over the WKQR.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen ED, Roos C, Terlaky T (2003) On implementing a primal-dual interior-point method for conic quadratic optimization. Math Programm 95:2
Bang H, Tsiatis AA (2002) Median regression with censored cost data. Biometrics 55:643–649
Cai T, Huang J, Tian L (2009) Regularized estimation for the accelerated failure time model. Biometrics 65:394–404
Cheong CW (2010) Estimating the Hurst parameter in financial time series via heuristic approaches. J Appl Stat 37:201–214
Cristianini N, Shawe-Taylor J (2000) An introduction to support vector machines (and other kernel-based learning methods). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Friberg HA (2013) Rmosek: the R-to-MOSEK optimization interface. R package version 7.0.1. http://rmosek.r-forge.r-project.org/, http://www.mosek.com/
Gelius-Dietrich G (2013) cplexAPI: R interfact to C API of IBM ILOG CPLEX. R package version 1.2.9. http://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/cplexAPI
Hendricks W, Koenker R (1992) Hierarchical spline models for conditional quantiles and the demand for electricity. J Am Stat Assoc 87:58–68
Huang H, Haaland P, Lu X, Liu Y, Marron JS (2013) DWD: DWD implementation based on A IPM SOCP solver. R package version 0.11. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=DWD
Huang J, Ma S, Xie H (2007) Least absolute deviations estimation for the accelerated failure time model. Stat Sin 17:1533–1548
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Karatzoglou A, Smola A, Hornik K, Zeileis A (2004) kernlab—an S4 Package for Kernel Methods in R. J Stat Softw 11(9):1–20. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v11/i09/
Kimeldorf G, Wahba G (1971) Some results on Tchebycheffian spline functions. J Math Anal Appl 33:82–95
Koenker R, Bassett G (1978) Regression quantiles. Econometrica 4:33–50
Koenker R, Geling R (2001) Reappraising medfly longevity: a quantile regression survival analysis. J Am Stat Assoc 96:458–468
Koenker R, Hallock K (2001) Quantile regression. J Econ Perspect 15:143–156
Koenker R, Ng P, Portnoy S (1994) Quantile smoothing splines. Biometrika 81:673–680
Koul H, Susarla V, Van Ryzin J (1981) Regression analysis with randomly right censored data. Ann Stat 9:1276–1288
León LF, Cai T, Wei LJ (2009) Robust inferences for covariate effects on survival time with censored linear regression models. Stat Biosci 1:50–64
Li Y, Liu Y, Zhu J (2007) Quantile regression in reproducing kernel hilbert spaces. J Am Stat Assoc 102:255–268
Liu Y, Wu Y (2011) Simultaneous multiple non-crossing quantile regression estimation using kernel constraints. J Nonparametr Stat 23:415–437
Miller R, Halpern J (1982) Regression with censored data. Biometrika 69(3):521–531
Park JY, Lee J-L, Baek S, Eo S-H, Ro JY, Cho YM (2014) Sarcomatoid features, necrosis, and grade are prognostic factors in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Hum Pathol 45(7):1437–1444
Portnoy S (2003) Censored regression quantiles. J Am Stat Assoc 98:1001–1012
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org/
Reich BJ, Fuentes M, Dunson DB (2011) Bayesian spatial quantile regression. J Am Stat Assoc 106:6–20
Scholkopf B, Smola A (2002) Learning with kernels support vector machines, regularization, optimization and beyond. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Shim J, Hwang C (2009) Support vector censored quantile regression under random censoring. Comput Stat Data Anal 53:912–919
Sousa SK, Pires JCM, Martins FG, Pereira MC, Alvim-Ferraz MCM (2008) Potentialities of quantile regression to predict ozone concentrations. Environmetrics 20:147–158
Stute W (1993) Consistent estimation under random censorship when covariables are present. J Multivar Anal 45:89–103
Takeuchi I, Le QV, Sears TD, Smola AJ (2006) Nonparametric quantile estimation. J Mach Learn Res 7:1231–1264
Therneau TM, Grambsch PM (2000) Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. Springer, New York
Turlach B, Weingessel A (2013) quadprog: Functions to solve quadratic programming problems. R package version 1.5-5. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=quadprog
Wang H, He X (2007) Detecting differential expressions in genechip microarray studies: a quantile approach. J Am Stat Assoc 102:104–112
Wang H, Wang L (2009) Locally weighted censored quantile regression. J Am Stat Assoc 104:1117–1128
Wu Y, Liu Y (2009) Stepwise multiple quantile regression estimation using non-crossing constraints. Stat Interface 2:299–310
Yang S (1999) Censored median regression using weighted empirical survival and hazard functions. J Am Stat Assoc 94:137–145
Ying Z, Jung SH, Wei LJ (1995) Survival analysis with median regression models. J Am Stat Assoc 90:178–184
Yuan M (2006) GACV for quantile smoothing splines. Comput Stat Data An 50:813–829
Zhou L (2006) A simple censored median regression estimator. Stat Sin 16:1043–1058
Zhou M (1992) M-estimation in censored linear models. Biometrika 79:837–841
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the editor, the associate editor, and the reviewers for their constructive and insightful comments and suggestions, which helped to dramatically improve the quality of this paper. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by (1) the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (NRF-2013R1A1A1007536) for S. Bang, (2) the Ministry of Education (NRF-2013R1A1A2A10007545) for M. Jhun, and (3) the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0007936) for H. Cho.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bang, S., Eo, SH., Cho, Y.M. et al. Non-crossing weighted kernel quantile regression with right censored data. Lifetime Data Anal 22, 100–121 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-014-9314-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10985-014-9314-8