Abstract
Context
Habitat heterogeneity is often assumed to benefit farmland biodiversity. Increasing heterogeneity of non-crop habitats is often too costly in terms of agricultural production. It has been suggested that increased crop heterogeneity could mitigate the negative effects of intensification on biodiversity while still maintaining high production levels.
Objectives
We investigated if habitat-specific species pools of two groups of farmland birds, field-nesting and non-crop-nesting species, were related to landscape-level heterogeneity of crop and non-crop cover. We analysed total number of species (gamma diversity) and average local species richness (alpha diversity) in landscapes and related these two biodiversity measures to four components of landscape heterogeneity (compositional and configurational heterogeneity of crop and non-crop cover).
Methods
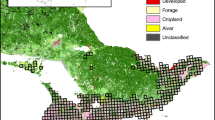
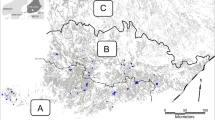
We selected 30 farmland landscapes (each 25 km2) in Sweden that largely broke up correlated relationships between crop and non-crop heterogeneity and between compositional and configurational heterogeneity. Estimates of species richness (alpha and gamma diversity) were calculated with bird survey data from specific habitats within landscapes (farmsteads and arable fields) and then related to measures of landscape heterogeneity.
Results
No measure of landscape species richness was associated with landscape-scale crop cover heterogeneities. However, gamma diversity of both bird groups was negatively related to the compositional and configurational heterogeneity of non-crop land-use in the landscapes, respectively.
Conclusions
Our results suggest that: (i) crop heterogeneities are not related to habitat-specific richness of farmland birds, (ii) heterogeneity effects of habitat complementarity in general are weak and (iii) relationships between diversity and heterogeneity in landscapes are dependent on the biodiversity measure used.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Báldi A, Batáry P (2011) Spatial heterogeneity and farmland birds: different perspectives in Western and Eastern Europe. Ibis 153:875–876. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.2011.01169.x
Barton K (2011) MuMIn: multi-model inference. R package version 1.6.1. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=MuMIn
Benton TG, Vickery JA, Wilson JD (2003) Farmland biodiversity: is habitat heterogeneity the key? Trends Ecol Evol 18:182–188. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(03)00011-9
Berg Å, Pärt T (1994) Abundance of breeding farmland birds on arable and set-aside fields at forest edges. Ecography 17:147–152. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.1994.tb00087.x
Billeter R, Liira J, Bailey D, Bugter R, Arens P, Augenstein I, Aviron S, Baudry J, Bukacek R, Burel F, Cerny M, De Blust G, De Cock R, Diekötter T, Dietz H, Dirksen J, Dormann C, Durka W, Frenzel M, Hamersky R, Hendrickx F, Herzog F, Klotz S, Koolstra B, Lausch A, Le Coeur D, Maelfait JP, Opdam P, Roubalova M, Schermann A, Schermann N, Schmidt T, Schweiger O, Smulders MJM, Speelmans M, Simova P, Verboom J, Van Wingerden WKRE, Zobel M, Edwards PJ (2008) Indicators for biodiversity in agricultural landscapes: a pan-European study. J Appl Ecol 45:141–150. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01393.x
Bonthoux S, Barnagaud J-Y, Goulard M, Balent G (2013) Contrasting spatial and temporal responses of bird communities to landscape changes. Oecologia 172:563–574. doi:10.1007/s00442-012-2498-2
Bruun M, Smith HG (2003) Landscape composition affects habitat use and foraging flight distances in breeding European starlings. Biol Conserv 114:179–187. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(03)00021-1
Chiron F, Filippi-Codaccioni O, Jiguet F, Devictor V (2010) Effects of non-cropped landscape diversity on spatial dynamics of farmland birds in intensive farming systems. Biol Conserv 143:2609–2616. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2010.07.003
Clough Y, Holzschuh A, Gabriel D, Purtauf T, Kleijn D, Kruess A, Steffan‐Dewenter I, Tscharntke T (2007) Alpha and beta diversity of arthropods and plants in organically and conventionally managed wheat fields. J Appl Ecol 44:804–812. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01294.x
Donald PF, Evans AD, Buckingham DL, Muirhead LB, Wilson JDD (2001) Factors affecting the territory distribution of Skylarks Alauda arvensis breeding on lowland farmland. Bird Study 48:271–278. doi:10.1080/00063650109461227
Duelli P, Obrist MK (2003) Regional biodiversity in an agricultural landscape: the contribution of seminatural habitat islands. Basic Appl Ecol 4:129–138
Erdős S, Báldi A, Batáry P (2009) Nest-site selection and breeding ecology of Sky Larks Alauda arvensis in Hungarian farmland. Bird Study 56:259–263. doi:10.1080/00063650902791983
Fahrig L, Baudry J, Brotons L, Burel FG, Crist TO, Fuller RJ, Sirami C, Siriwardena CM, Martin JL (2011) Functional landscape heterogeneity and animal biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecol Lett 14:101–112
Filippi-Codaccioni O, Devictor V, Bas Y, Clobert J, Julliard R (2010) Specialist response to proportion of arable land and pesticide input in agricultural landscapes. Biol Conserv 143:883–890. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2009.12.035
Flick T, Feagan S, Fahrig L (2012) Effects of landscape structure on butterfly species richness and abundance in agricultural landscapes in eastern Ontario, Canada. Agric Ecosyst Environ 156:123–133
Flohre A, Fischer C, Aavik T et al (2011) Agricultural intensification and biodiversity partitioning in European landscapes comparing plants, carabids, and birds. Ecol Appl 21:1772–1781. doi:10.1890/10-0645.1
Fuller RJ, Hinsley SA, Swetnam RD (2004) The relevance of non-farmland habitats, uncropped areas and habitat diversity to the conservation of farmland birds. Ibis 146:22–31. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.2004.00357.x
Gabriel D, Roschewitz I, Tscharntke T, Thies C (2006) Beta diversity at different spatial scales: plant communities in organic and conventional agriculture. Ecol Appl 16:2011–2021. doi:10.1890/1051-0761(2006)016%5B2011:BDADSS%5D2.0.CO;2
Gilroy JJ, Anderson GQA, Grice PV, Vickery JA, Sutherland WJ (2010) Mid-season shifts in the habitat associations of Yellow Wagtails Motacilla flava breeding in arable farmland. Ibis 152:90–104. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.2009.00988.x
Gregory RD, van Strien A, Vorisek P, Meyling AWG, Noble DG, Foppen RP, Gibbons DW (2005) Developing indicators for European birds. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360:269–288. doi:10.1098/rstb.2004.1602
Guerrero I, Morales MB, Oñate JJ, Geiger F, Berendse F, Snoo G de, Eggers S, Pärt T, Bengtsson J, Clement LW, Weisser WW, Olszewski A, Ceryngier P, Hawro V, Liira J, Aavik T, Fischer C, Flohre A, Thies C, Tscharntke T (2012) Response of ground-nesting farmland birds to agricultural intensification across Europe: landscape and field level management factors. Biol Conserv 152:74–80. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2012.04.001
Haslem A, Bennett AF (2008) Birds in agricultural mosaics: the influence of landscape pattern and countryside heterogeneity. Ecol Appl 18:185–196. doi:10.1890/07-0692.1
Henderson I, Holt C, Vickery J (2007) National and regional patterns of habitat association with foraging Barn Swallows Hirundo rustica in the UK. Bird Study 54:371–377. doi:10.1080/00063650709461497
Henderson IG, Ravenscroft N, Smith G, Holloway S (2009) Effects of crop diversification and low pesticide inputs on bird populations on arable land. Agric Ecosyst Environ 129:149–156
Hendrickx F, Maelfait J-P, Van Wingerden W et al (2007) How landscape structure, land-use intensity and habitat diversity affect components of total arthropod diversity in agricultural landscapes. J Appl Ecol 44:340–351. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2006.01270.x
Herzon I, O’Hara RB (2007) Effects of landscape complexity on farmland birds in the Baltic States. Agric Ecosyst Environ 118:297–306. doi:10.1016/j.agee.2006.05.030
Hiron M, Berg Å, Pärt T (2012) Do skylarks prefer autumn sown cereals? Effects of agricultural land use, region and time in the breeding season on density. Agric Ecosyst Environ 150:82–90
Hiron M, Berg Å, Eggers S, Pärt T (2013) Are farmsteads over-looked biodiversity hotspots in intensive agricultural ecosystems? Biol Conserv 159:332–342. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2012.11.018
Ihse M (1995) Swedish agricultural landscapes—patterns and changes during the last 50 years, studied by aerial photos. Landsc Urban Plann 31:21–37. doi:10.1016/0169-2046(94)01033-5
Kleijn D, Baquero RA, Clough Y et al (2006) Mixed biodiversity benefits of agri-environment schemes in five European countries. Ecol Lett 9:243–254. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2005.00869.x
Kleijn D, Rundlöf M, Scheper J, Smith HG, Tscharntke T (2011) Does conservation on farmland contribute to halting the biodiversity decline? Trends Ecol Evol 26:474–481. doi:10.1016/j.tree.2011.05.009
Krebs JR, Wilson JD, Bradbury RB, Siriwardena GM (1999) The second silent spring? Nature 400:611–612. doi:10.1038/23127
Legendre P, Borcard D, Peres-Neto PR (2005) Analyzing beta diversity: partitioning the spatial variation of community composition data. Ecol Monogr 75:435–450. doi:10.1890/05-0549
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Law R, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol Lett 7:601–613. doi:10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00608.x
Moorcroft D, Wilson JD, Bradbury RB (2006) Diet of nestling Linnets Carduelis cannabina on lowland farmland before and after agricultural intensification. Bird Study 53:156–162. doi:10.1080/00063650609461428
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos PM, Henry H, Stevens HH, Wagner H (2011) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0-1.http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Pasher J, Mitchell SW, King DJ, Fahrig L, Smith AC, Lindsay KE (2013) Optimizing landscape selection for estimating relative effects of landscape variables on ecological responses. Landscape Ecol 28:371–383. doi:10.1007/s10980-013-9852-6
Pickett SRA, Siriwardena GM (2011) The relationship between multi-scale habitat heterogeneity and farmland bird abundance. Ecography 34:955–969. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2011.06608.x
Piha M, Tiainen J, Holopainen J, Vepsäläinen V (2007) Effects of land-use and landscape characteristics on avian diversity and abundance in a boreal agricultural landscape with organic and conventional farms. Biol Conserv 140:50–61
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org/
Robertson JG, Eknert B, Ihse M (1990) Habitat analysis from infra-red aerial photographs and the conservation of birds in Swedish agricultural landscapes. Ambio 19:195–203
Roschewitz I, Gabriel D, Tscharntke T, Thies C (2005) The effects of landscape complexity on arable weed species diversity in organic and conventional farming. J Appl Ecol 42:873–882. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2005.01072.x
Siriwardena GM, Crick HQP, Baillic SR, Wilson JD (2000) Agricultural land-use and the spatial distribution of granivorous lowland farmland birds. Ecography 23:702–719. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0587.2000.tb00314.x
Stoate C, Boatman N, Borralho R, Carvalho CR, De Snoo GR, Eden P (2001) Ecological impacts of arable intensification in Europe. J Environ Manag 63:337–365. doi:10.1006/jema.2001.0473
Tucker GM, Evans MI (1997) Habitats for birds in Europe: a conservation strategy for the wider environment. BirdLife International, Cambridge
Vickery JA, Bradbury RB, Henderson IG, Eaton MA, Grice PV (2004) The role of agri-environment schemes and farm management practices in reversing the decline of farmland birds in England. Biol Conserv 119:19–39. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2003.06.004
Whittingham MJ (2007) Will agri-environment schemes deliver substantial biodiversity gain, and if not why not? J Appl Ecol 44:1–5
Whittingham MJ (2011) The future of agri-environment schemes: biodiversity gains and ecosystem service delivery? J Appl Ecol 48:509–513. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2011.01987.x
Whittingham MJ, Evans KL (2004) The effects of habitat structure on predation risk of birds in agricultural landscapes. Ibis 146:210–220. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.2004.00370.x
Wilson JD, Evans J, Browne SJ, King JR (1997) Territory distribution and breeding Success of skylarks Alauda arvensis on organic and intensive farmland in southern England. J Appl Ecol 34:1462–1478. doi:10.2307/2405262
Wilson JD, Whittingham MJ, Bradbury RB (2005) The management of crop structure: a general approach to reversing the impacts of agricultural intensification on birds? Ibis 147:453–463. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919x.2005.00440.x
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the many fieldworkers, farmers and landowners who made this study possible. Comments from two reviewers greatly improved this manuscript. This project was financed by FORMAS (Grant 215-2007-518 to TP and Grant 215 – 2010 – 612 to SE) and Carl Tryggers´ Stiftelse (Grant CTS 10:79 to SE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hiron, M., Berg, Å., Eggers, S. et al. The relationship of bird diversity to crop and non-crop heterogeneity in agricultural landscapes. Landscape Ecol 30, 2001–2013 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0226-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0226-0