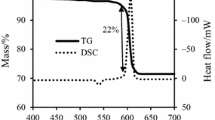
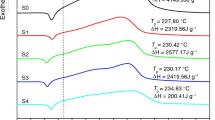
Abstract
The purpose of this research is to analyze the thermal behavior and kinetics of the pyrotechnic compositions including Al + KClO4, Mg + KClO4, Al + Mg + KClO4, MgAl + KClO4 and Al + MgAl + KClO4 mixtures. The differential scanning calorimeter coupled with thermogravimetry analysis was employed to illustrate the reaction process of these pyrotechnic compositions. Moreover, the bomb calorimetry was utilized to compare experimental and theoretical heats of reaction. The apparent activation energy (E a), frequency factor (A), the critical ignition temperature of thermal explosion and the self-accelerating decomposition temperature (T SADT), were calculated using Kissinger approach. The results showed that the composition containing MgAl had the highest activation energy and frequency factor; however, the critical ignition temperature of their oxidation reaction was lowest value. In agreement with the theoretical value, the highest experimental heat of reaction for the composition MgAl/KClO4 corresponds to the more complete combustion of metastable MgAl as an alloying mixture of Aluminum and Magnesium with equal proportions. These results suggest that benchmark values for an optimum designation and issues pertinent to the storage and handling of pyrotechnics containing Mg, Al and KClO4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoenitz M, Dreizin EL. Structure and properties of Al–Mg mechanical alloys. J Mater Res. 2003;18:1827–36.
Aly Y, Schoenitz M, Dreizin EL. Ignition and combustion of mechanically alloyed Al–Mg powders with customized particle sizes. Combust Flame. 2013;160:835–42.
Shoshin YL, Mudryy RS, Dreizin EL. Preparation and characterization of energetic Al–Mg mechanical alloy powders. Combust Flame. 2002;128:259–69.
Chan ML, Reed R, Ciaramitaro DA. Advances in solid propellant formulations. Solid propellant chemistry, combustion, and motor interior ballistics(A 00-36332 09-28), Reston, VA, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. Prog Astronaut Aeronaut. 2000;185:185–206.
Dreizin E. Phase changes in metal combustion. Prog Energ Combust Sci. 2000;26:57–78.
Yetter RA, Risha GA, Son SF. Metal particle combustion and nanotechnology. Proc Combust Inst. 2009;32:1819–38.
Wang Y, Jiang W, Zhang X, Liu H, Liu Y, Li F. Energy release characteristics of impact-initiated energetic aluminum–magnesium mechanical alloy particles with nanometer-scale structure. Thermochim Acta. 2011;512:233–9.
Palaszewski B, Powell R. Launch vehicle performance using metallized propellants. J Propuls Power. 1994;10:828–33.
Palaszewski B. Metallized propellants for the human exploration of Mars. J Propuls Power. 1992;8:1192–9.
Singh D, Suryanarayana C, Mertus L, Chen R-H. Extended homogeneity range of intermetallic phases in mechanically alloyed Mg–Al alloys. Intermetallics. 2003;11:373–6.
Schoenitz M, Dreizin EL, Shtessel E. Constant volume explosions of aerosols of metallic mechanical alloys and powder blends. J Propuls Power. 2003;19:405–12.
Dreizin EL, Shoshin YL, Mudryy RS, Hoffmann VK. Constant pressure flames of aluminum and aluminum–magnesium mechanical alloy aerosols in microgravity. Combust Flame. 2002;130:381–5.
Zhu C-G, Wang H-Z, Min L. Ignition temperature of magnesium powder and pyrotechnic composition. J Energ Mater. 2014;32:219–26.
Stern KH. High temperature properties and thermal decomposition of inorganic salts with oxyanions. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2000.
Lee J-S, Hsu C-K, Jaw K-S. The thermal properties of KClO4 with different particle size. Thermochim Acta. 2001;367:381–5.
Kang X, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Du K, Tang Y. Studies on ignition and afterburning processes of KClO4/Mg pyrotechnics heated in air. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;109:1333–40.
Mei-shuai Z, Xiao-yan G, Rong-jie Y, Long-xin Q, Zhi-hong C. Effect of oxidizers in magnesium fuel-rich propellant for water-ramjet engine. J Propuls Technol. 2010;6:018.
Lee J-S, Hsu C-K. The DSC studies on the phase transition, decomposition and melting of potassium perchlorate with additives. Thermochim Acta. 2001;367:367–70.
Furuichi R, Ishii T, Kobayashi K. Phenomenological study of the catalytic thermal decomposition of potassium perchlorate by iron(II) oxides with different preparing histories. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1974;6:305–20.
Danali S, Palaiah R, Raha K. Developments in pyrotechnics (review paper). Def Sci J. 2010;60:152–8.
Conkling JA, Mocella C. Chemistry of pyrotechnics: basic principles and theory. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2010.
Conkling JA. Pyrotechnics. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; 1996.
Pourmortazavi S, Hajimirsadeghi S, Hosseini S. Characterization of the aluminum/potassium chlorate mixtures by simultaneous TG-DTA. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2006;84:557–61.
Pourmortazavi S, Fathollahi M, Hajimirsadeghi S, Hosseini S. Thermal behavior of aluminum powder and potassium perchlorate mixtures by DTA and TG. Thermochim Acta. 2006;443:129–31.
Hosseini SG, Eslami A. Thermoanalytical investigation of relative reactivity of some nitrate oxidants in tin-fueled pyrotechnic systems. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2010;101:1111–9.
Ilunga K, Del Fabbro O, Yapi L, Focke WW. The effect of Si–Bi2O3 on the ignition of the Al–CuO thermite. Powder Technol. 2011;205:97–102.
Dreizin EL. Metal-based reactive nanomaterials. Prog Energ Combust Sci. 2009;35:141–67.
Fathollahi M, Pourmortazavi S, Hosseini S. The effect of the particle size of potassium chlorate in pyrotechnic compositions. Combust Flame. 2004;138:304–6.
Wharton R, Barratt A. Observations on the reactivity of pyrotechnic compositions containing potassium chlorate and thiourea. Propell Explos Pyrot. 1993;18:77–80.
Brown M. Some thermal studies on pyrotechnic compositions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2001;65:323–34.
Anandprakash K. Effect of Tammann temperature and relative humidity on lead chromate and magnesium-based compositions. Def Sci J. 2013;48:303–8.
Kissinger HE. Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Anal Chem. 1957;29:1702–6.
Augis J, Bennett J. Calculation of the Avrami parameters for heterogeneous solid state reactions using a modification of the Kissinger method. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1978;13:283–92.
Chrissafis K. Kinetics of thermal degradation of polymers. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95:273–83.
Barral L, Cano J, Lopez J, Lopez-Bueno I, Nogueira P, Ramirez C, et al. Thermogravimetric study of tetrafunctional/phenol novolac epoxy mixtures cured with a diamine. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1998;51:489–501.
Khawam A, Flanagan DR. Solid-state kinetic models: basics and mathematical fundamentals. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:17315–28.
Pickard JM. Critical ignition temperature. Thermochim Acta. 2002;392:37–40.
Rong L, Binke N, Yuan W, Zhengquan Y, Rongzu H. Estimation of the critical temperature of thermal explosion for the highly nitrated nitrocellulose using non-isothermal DSC. J Therm Anal Calorim. 1999;58:369–73.
Fathollahi M, Mohammadi B, Mohammadi J. Kinetic investigation on thermal decomposition of hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) nanoparticles. Fuel. 2013;104:95–100.
Roduit B, Hartmann M, Folly P, Sarbach A, Brodard P, Baltensperger R. Determination of thermal hazard from DSC measurements. Investigation of self-accelerating decomposition temperature (SADT) of AIBN. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;117:1017–26.
Liu R, Yang L, Zhou Z, Zhang T. Thermal stability and sensitivity of RDX-based aluminized explosives. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115:1939–48.
Tonglai Z, Rongzu H, Yi X, Fuping L. The estimation of critical temperatures of thermal explosion for energetic materials using non-isothermal DSC. Thermochim Acta. 1994;244:171–6.
Association NFP. Standard system for the identification of the hazards of materials for emergency response. Quincy: National Fire Protection Association; 2001.
Ando T, Fujimoto Y, Morisaki S. Analysis of differential scanning calorimetric data for reactive chemicals. J Hazard Mater. 1991;28:251–80.
Ouyang D, Pan G, Guan H, Zhu C, Chen X. Effect of different additives on the thermal properties and combustion characteristics of pyrotechnic mixtures containing the KClO4/Mg–Al alloy. Thermochim Acta. 2011;513:119–23.
Acknowledgements
Authors are very indebted to Research Committee of the University of Tehran due to its authorities for financial support during the tenure of which work was completed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fathollahi, M., Behnejad, H. A comparative study of thermal behaviors and kinetics analysis of the pyrotechnic compositions containing Mg and Al. J Therm Anal Calorim 120, 1483–1492 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4433-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4433-3