Abstract
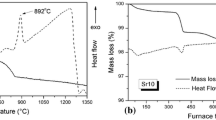
Calcium phosphate bioactive glasses (BG) and some ceramics are candidates for implantation due to their excellent bonding to bone. Silver is a bactericidal element and can be easily introduced in glasses and ceramics. In this work, nanometer-sized bioactive glass particles doped with silver were produced and characterized by Thermal Gravimetric analysis (TG), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). Water hygroscopy was reduced with increasing silver content. The increase in the amount of silver caused an increase in quartz and metallic silver crystallization while reducing the BG transformation into hydroxyapatite. It was observed the silver reduction leading to metallic silver formation for bioactive glasses containing high amount of silver.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa HS, Rocha MF, Andrade GI, Barbosa-Stancioli EF, Pereira MM, Orefice RL, et al. Sol-gel derived composite from bioactive glass-polyvinyl alcohol. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;43:494–502.
Hench LLJ. The story of Bioglass®. Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17:967–78.
Chatzistavrou X, Zorba T, Chrissafis K, Kaimakami G, Kontonasaki E, Koidis P, et al. Influence of particle size on the crystallization process and the bioactive behavior of a bioactive glass system. J Therm Anal Cal. 2006;85:253–9.
Du RL, Chang J, Ni SY, Zhai WY. Characterization and in vitro bioactivity of zinc-containing bioactive glass and glass-ceramics. J Biomater Appl. 2006;20:341–60.
Aina V, Perardi A, Bergandi L, Malavasi G, Menabue L, Morterra C, et al. Cytotoxicity of zinc-containing bioactive glasses in contact with human osteoblasts. Chemico-Biol Interact. 2007;167:207–18.
Monem AS, Elbatal HA, Khalil EMA, Azooz MA, Hamdy YM. In vivo behavior of bioactive phosphate glass-ceramics from the system P2O5–Na2O–CaO containing TiO2. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19:1097–108.
James PF. Glass ceramic: new compositions and uses. J Non-Cryst Solids. 1995;181:1–15.
Navarro M, Ginebra MP, Clement J, Salvador M, Gloria A, Planell JA. Physicochemical degradation of titania-stabilized soluble phosphate glasses for medical applications. J Am Ceram Soc. 2003;86:1345–52.
Balamurugan A, Balossier G, Michel J, Kannan S, Benhayoune H, Rebelo AHS, et al. Sol gel derived SiO2–CaO–MgO–P2O5 bioglass system-preparation and in vitro characterization. J Biomed Mater Res B. 2007;83:546–53.
Efflandt SE, Magne P, Douglas WH, Francis LF. Interaction between bioactive glasses and human dentin. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2002;13:557–65.
Ning J, Yao A, Wang D, Huang W, Fu H, Liu X, et al. Synthesis and in vitro bioactivity of a borate-based bioglass. Mater Lett. 2007;61:5223–6.
Marion NW, Liang W, Reilly G, Day DE, Rahaman MN, Mao JJ. Borate glass supports the in vitro osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Mech Adv Mater Struct. 2005;12:239–46.
Huang W, Day DE, Kittiratanapiboon K, Rahaman MN. Kinetics and mechanisms of the conversion of silicate (45S5), borate, and borosilicate glasses to hydroxyapatite in dilute phosphate solutions. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17:583–96.
Munukka E, Leppäranta O, Korkeamäki M, Vaahtio M, Peltola T, Zhang D, et al. Bactericidal effects of bioactive glasses on clinically important aerobic bacteria. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19:1927–32.
Bellantone M, Coleman NJ, Hench LL. Bacteriostatic action of a novel four-component bioactive glass. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51:484–90.
Clupper DC, Hench LL. Bioactive response of Ag-doped tape cast Bioglass® 45S5 following heat treatment. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2001;12:917–21.
Carta D, Knowles JC, Smith ME. Synthesis and structural characterization of P2O5–CaO–Na2O sol–gel materials. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2007;352:1141–9.
Aguiara H, Solla EL, Serra J, González P, León B, Almeida N, et al. Orthophosphate nanostructures in SiO2–P2O5–CaO–Na2O–MgO bioactive glasses. J Non-Cryst Solids. 2008;354:4075–80.
Cieciñska M. Thermal analysis of gel-derived bioactive phospho-silicate glasses. J Therm Anal Cal. 2003;72:199–207.
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by FINEP, CNPq, FUNDECT, and by UFMS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delben, J.R.J., Pimentel, O.M., Coelho, M.B. et al. Synthesis and thermal properties of nanoparticles of bioactive glasses containing silver. J Therm Anal Calorim 97, 433–436 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0086-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-009-0086-4