Abstract
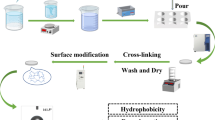
The silica aerogels based on the fly ash acid sludge were successfully synthesized using ethanol (EtOH)/trimethylchlorosilane (TMCS)/n-hexane as surface modification agent via ambient pressure drying. The surface modification of hydrogels was a crucial step during the processing which preserved mesopores structure in ambient pressure drying. It was found that the structure and physical properties of silica aerogels dependent on the TMCS/hydrogel volume ratio. The results indicated that the specific density decreased with an increase in the TMCS/hydrogel volume ratio. The silica aerogels modified with TMCS (volume ratio = 1) presented good performance with the specific surface area (830 m2/g), bulk density (0.072 g/cm3), contact angle (146°), and the average pore size (10.7 nm).
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kocon L, Despetis F, Phalippou J (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 22:96–100
Kim GS, Hyun SH (2003) J Non-Cryst Solids 320:125–132
Rao AV, Bhagat SD (2004) Solid State Sci 6:945–952
Bhagat SD, Kim YH, Ahn YS, Yeo JG (2007) Appl Surf Sci 25:33231–33236
Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (2011) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York
Rassy HEL, Pierre AC (2005) J Non-Cryst Solids 351:1603–1610
da Pinto da Cunha J, Neves F, Lopes MI (2000) Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res A 452:401–421
Yoldas BE, Annen MJ, Bostaph J (2000) Chem Mater 12:2475–2484
Smirnova I, Suttiruengwong S, Arlt W (2004) J Non-Cryst Solids 350:54–60
Tamon H, Kitamura T, Okazaki M (1998) J Colloid Interface Sci 197:353–359
Schmidt M, Schwertfeger F (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:364–368
Rao AV, Kulkarni MM, Amalnerkar DP, Seth T (2003) Appl Surf Sci 206:262–270
Rassy HEL, Buisson P, Bouali B, Perrard A, Pierre AC (2003) Langmuir 19:358–363
Rao AV, Pajonk GM, Nadargi DY, Koebel MM (2011) In: Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (eds) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York, pp 21–45
Schwertfeger F, Frank D, Schmidt M (1998) J Non-Cryst Solids 225:24–29
Lee CJ, Kim GS, Hyun SH (2002) J Mater Sci 37:2237–2241
Rao AV, Rao AP, Kulkarni MM (2004) J Non-Cryst Solids 350:224–229
Bhagat SD, Kim YH, Ahn YS, Yeo JG (2006) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 96:237–244
Rao AV, Pajonk GM, Bangi UK, Rao AP, Koebel MM (2011) In: Aegerter MA, Leventis N, Koebel MM (eds) Aerogels handbook. Springer, New York, pp 103–124
Wu K (1994) J Henan Urban Constr Jr Coll 3:85–88
Wei CD, Luo F, Jiang YS, Xue B, Sun YB, Li FF, Gao Q (2012) CN 201210288939.3
Prassas M, Phalippou J, Zarzycki J (1984) J Mater Sci 19:1656–1665
Li WC, Lu AH, Guo SC (2002) J Colloid Interface Sci 254:153–157
Bhagat SD, Kim YH, Suh KH, Ahn YS, Yeo JG, Han JH (2008) Microporous Mesoporous Mater 112:504–509
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41472035 and 51304080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Li, N. & Wei, C. Effect of the TMCS/hydrogel volume ratio on physical properties of silica aerogels based on fly ash acid sludge. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 78, 279–284 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3954-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3954-3