Abstract
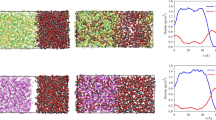
The distribution coefficient of Cs is estimated using dibenzo-21-crown-7 (DB21C7) and di-benzo-18-crown-6 (DB18C6) in 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bis (trifluroromethanesulphonyl) imide (BMIMTF2N) ionic liquid by performing solvent extraction experiments. In addition, molecular dynamics studies on the extraction of cesium (Cs+) ion transfer from the aqueous phase to the BMIMTF2N phase is reported. The experimental findings gave a cesium distribution coefficient of 0.218 and 0.326, which agrees closely with the values of 0.2 and 0.5 obtained from MD simulation for the ionophores DB18C6 and DB21C7, respectively. Thus MD simulation may be helpful in screening the solvents prior to the experiments.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chun S, Dzyuba SV, Bartsch RA (2001) Influence of structural variation in room-temperature ionic liquids on the selectivity and efficiency of competitive alkali metal salt extraction by a crown ether. Anal Chem 73:3737–3741
Cocalia VA, Jensen MP, Holbrey JD, Spear SK, Stepinski DC, Rogers RD (2005) Identical extraction behavior and coordination of trivalent or hexavalent f-element cations using ionic liquid and molecular solvents. Dalton Trans 11:1966–1971
Dai S, Ju YH, Barnes CE (1999) Solvent extraction of strontium nitrate by a crown ether using room-temperature ionic liquids [dagger]. Dalton Trans 8:1201–1202
Luo H, Dai S, Bonnesen PV, Buchanan AC, Holbrey JD, Bridges NJ, Rogers RD (2004) Extraction of cesium ions from aqueous solutions using calix[4]arene-bis(tert-octylbenzo-crown-6) in ionic liquids. Anal Chem 76:3078–3083
Visser AE, Jensen MP, Laszak I, Nash KL, Choppin GR, Rogers RD (2003) Uranyl coordination environment in hydrophobic ionic liquids: an in situ investigation. Inorg Chem 42:2197–2199
Visser AE, Swatloski RP, Reichert WM, Griffin ST, Rogers RD (2000) Traditional extractants in nontraditional solvents: groups 1 and 2 extraction by crown ethers in room-temperature ionic liquids. Ind Eng Chem Res 39:3596–3604
Nakashima K, Kubota F, Maruyama T, Goto M (2005) Feasibility of ionic liquids as alternative separation media for industrial solvent extraction processes. Ind Eng Chem Res 44:4368–4372
Pedersen CJ (1967) Cyclic polyethers and their complexes with metal salts. J Am Chem Soc 89:7017–7036
Gutsche CD, Dhawan B, No KH, Muthukrishnan R (1981) Calixarenes 4 the synthesis, characterization, and properties of the calixarenes from p-tert-butylphenol. J Am Chem Soc 103:3782–3792
Xu C, Yuan L, Shen X, Zhai M (2010) Efficient removal of caesium ions from aqueous solution using a calix crown ether in ionic liquids: mechanism and radiation effect. Dalton Trans 39:3897–3902
Levitskaia TG, Macdonald DM, Lamb JD, Moyer BA (2000) Prediction of the carrier-mediated cation flux through polymer inclusion membranes via fundamental thermodynamic quantities: complexation study of bis(dodecyloxy)calix[4]arene-crown-6 with alkali metal cations. Phys Chem Chem Phys 2:1481–1491
Huddleston J, Rogers R (1998) Room temperature ionic liquids as novel media for ‘clean’liquid–liquid extraction. Chem Commun 16:1765–1766
Breneman CM, Wiberg KB (1990) Determining atom-centered monopoles from molecular electrostatic potentials. The need for high sampling density in formamide conformational analysis. J Comput Chem 11:361–373
Huddleston JG, Visser AE, Reichert WM, Willauer HD, Broker GA, Rogers RD (2001) Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem 3:156–164
Leeuw SWD, Perram JW, Smith ER (1983) Simulation of electrostatic systems in periodic boundary conditions. III. Further theory and applications. Proc R Soc Lond A 388:177–193
Sieffert N, Wipff G (2006) Comparing an ionic liquid to a molecular solvent in the cesium cation extraction by a calixarene: a molecular dynamics study of the aqueous interfaces. J Phys Chem B 110:19497–19506
Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin EG, Martínez JM (2009) PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 30:2157–2164
Kalé L, Skeel R, Bhandarkar M, Brunner R, Gursoy A, Krawetz N, Phillips J, Shinozaki A, Varadarajan K, Schulten K (1999) NAMD2: greater scalability for parallel molecular dynamics. J Comput Phys 151:283–312
Canongia Lopes JN, Pádua AA (2006) Molecular force field for ionic liquids III: imidazolium, pyridinium, and phosphonium cations; chloride, bromide, and dicyanamide anions. J Phys Chem B 110:19586–19592
Canongia Lopes JN, Deschamps J, Pádua AA (2004) Modeling ionic liquids using a systematic all-atom force field. J Phys Chem B 108:2038–2047
Canongia Lopes JN, Pádua AA (2004) Molecular force field for ionic liquids composed of triflate or bistriflimide anions. J Phys Chem B 108:16893–16898
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD, Impey RW, Klein ML (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935
Joung IS, Cheatham TE III (2008) Determination of alkali and halide monovalent ion parameters for use in explicitly solvated biomolecular simulations. J Phys Chem B 112:9020–9041
Sahu P, Ali SM, Singh JK (2014) Structural and dynamical properties of Li+-dibenzo-18-crown-6 (DB18C6) complex in pure solvents and at the aqueous-organic interface. J Mol Model 20:1–12
Weiner SJ, Kollman PA, Nguyen DT, Case DA (1986) An all atom force field for simulations of proteins and nucleic acids. J Comput Chem 7:230–252
Vranes M, Dozic S, Djeric V, Gadzuric S (2012) Physicochemical characterization of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium and 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis (trifluoromethylsulfonyl) imide. J Chem Eng Data 57:1072–1077
Sieffert N, Wipff G (2006) The [BMI][Tf2N] ionic liquid/water binary system: a molecular dynamics study of phase separation and of the liquid–liquid interface. J Phys Chem B 110:13076–13085
Ali SM, Joshi J, Deb AS, Boda A, Shenoy K, Ghosh S (2014) Dual mode of extraction for Cs+ and Na+ ions with dicyclohexano-18-crown-6 and bis (2-propyloxy) calix [4] crown-6 in ionic liquids: density functional theoretical investigation. RSC Adv 4:22911–22925
Allen MP, Tildesley DJ (1989) Computer simulation of liquids. Oxford University Press, New York
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Board of Research in Nuclear Sciences (BRNS, Government of India) vide scheme no. 2013/36/30-BRNS/2352, dated: 26 November 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
The formation of the Cs–DB18C6 complex from the starting configuration (t = 0 ns) to its end i.e. t = 40 ns is provided as a part of Supplementary material. Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 8631 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biswas, R., Pasumarthi, V., Banerjee, T. et al. Interfacial insights on the dibenzo-based crown ether assisted cesium extraction in [BMIM][Tf2N]–water binary system. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 311, 427–438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5050-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-016-5050-8