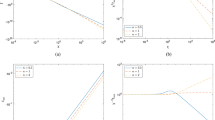
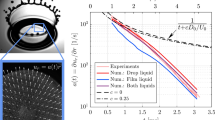
Abstract
We study the Poiseuille flow of a soft-glassy material above the jamming point, where the material flows like a complex fluid with Herschel–Bulkley rheology. Microscopic plastic rearrangements and the emergence of their spatial correlations induce cooperativity flow behavior whose effect is pronounced in presence of confinement. With the help of lattice Boltzmann numerical simulations of confined dense emulsions, we explore the role of geometrical roughness in providing activation of plastic events close to the boundaries. We probe also the spatial configuration of the fluidity field, a continuum quantity which can be related to the rate of plastic events, thereby allowing us to establish a link between the mesoscopic plastic dynamics of the jammed material and the macroscopic flow behaviour.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
For the Voronoi analysis we used the tools included in the voro++ libraries available at http://math.lbl.gov/voro++/.
References
Mason, T.G., Bibette, J., Weitz, D.: Yielding and flow of monodisperse emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 179, 439–448 (1996)
Katgert, G., Tighe, B.P., Van Hecke, M.: The jamming perspective on wet foams. Soft Matter 9, 9739 (2013)
Kamrin, K., Koval, G.: Nonlocal constitutive relation for steady granular flow. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 178301 (2012)
Larson, R.G.: The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids. Oxford University Press, New York (1999)
Goyon, J., Colin, A., Ovarlez, G., Ajdari, A., Bocquet, L.: Spatial cooperativity in soft glassy flows. Nature 454, 84–87 (2008)
Goyon, J., Colin, A., Bocquet, L.: How does a soft glassy material flow: finite size effects, nonlocal rheology, and flow cooperativity. Soft Matter 6, 2668–2678 (2010)
Jop, P., Mansard, V., Chaudhuri, P., Bocquet, L., Colin, A.: Microscale rheology of a soft glassy material close to yielding. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 148301 (2012)
Katgert, G., Tighe, B.P., Möbius, M.E., Van Hecke, M.: Couette flow of two-dimensional foams. Europhys. Lett. 90, 54002 (2010)
Bocquet, L., Colin, A., Ajdari, A.: Kinetic theory of plastic flow in soft glassy materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 036001 (2009)
Geraud, B., Bocquet, L., Barentin, C.: Confined flows of a polymer microgel. Eur. Phys. J. E 36, 30 (2013)
Amon, A., Nguyen, V.B., Bruand, A., Crassous, J., Clément, E.: Hot spots in an athermal system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 135502 (2012)
Mansard, V., Colin, A., Chaudhuri, P., Bocquet, L.: A molecular dynamics study of non-local effects in the flow of soft jammed particles. Soft Matter 9, 7489–7500 (2013)
Dollet, B., Scagliarini, A., Sbragaglia, M.: Plastic flow of foams and emulsions in a channel. arXiv:1406.2686
Mansard, V., Colin, A., Bocquet, L.: Boundary conditions for soft glassy flows: slippage and surface fluidization. Soft Matter 10, 6984–6989 (2014)
Benzi, R., Sbragaglia, M., Succi, S., Bernaschi, M., Chibbaro, S.: Mesoscopic lattice Boltzmann modeling of soft-glassy systems: theory and simulations. J. Chem. Phys. 131, 104903 (2009)
Benzi, R., Bernaschi, M., Sbragaglia, M., Succi, S.: Herschel-Bulkley rheology from lattice kinetic theory of soft glassy materials. Europhys. Lett. 91, 14003 (2010)
Sbragaglia, M., Benzi, R., Bernaschi, M., Succi, S.: The emergence of supramolecular forces from lattice kinetic models of non-ideal fluids: applications to the rheology of soft glassy materials. Soft Matter 8, 10773–10782 (2012)
Benzi, R., Bernaschi, M., Sbragaglia, M., Succi, S.: Rheological properties of soft-glassy flows from hydro-kinetic simulations. Europhys. Lett. 104, 48006 (2013)
Sbragaglia, M., Benzi, R., Biferale, L., Succi, S., Sugiyama, K., Toschi, F.: Generalized lattice Boltzmann method with multirange pseudopotential. Phys. Rev. E 75, 026702 (2007)
Falcucci, G., Bella, G., Chiatti, G., Chibbaro, S., Sbragaglia, M., Succi, S.: Lattice Boltzmann models with mid-range interactions. Commun. Comput. Phys. 2, 1071–1084 (2007)
Bastea, S., Esposito, R.: Hydrodynamics of binary fluid phase segregation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 235701 (2002)
Shan, X., Chen, H.: Lattice Boltzmann Model for simulating flows with multiple phases and components. Phys. Rev. E 47, 1815 (1993)
Seul, M., Andelman, D.: Domain shapes and patterns: the phenomenology of modulated phases. Science 267, 476–483 (1995)
Sbragaglia, M., Shan, X.: Consistent pseudopotential interactions in lattice Boltzmann models. Phys. Rev. E 84, 036703 (2011)
Shan, X.: Pressure tensor calculation in a class of nonideal gas lattice Boltzmann models. Phys. Rev. E 77, 066702 (2008)
Sbragaglia, M., Belardinelli, D.: Interaction pressure tensor for a class of multicomponent lattice Boltzmann models. Phys. Rev. E 88, 013306 (2013)
Wolf-Gladrow, D.: Lattice-Gas Cellular Automata and Lattice Boltzmann Models. Springer, New York (2000)
Scagliarini, A., Sbragaglia, M., Bernaschi, M.: unpublished
Bernaschi, M., Benzi, R., Rossi, L., Sbragaglia, M., Succi, S.: Graphics processing unit implementation of lattice Boltzmann models for flowing soft systems. Phys. Rev. E 80, 066707 (2009)
Weaire, D., Hutzler, S.: The Physics of Foams. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1999)
Rycroft, C.H., Grest, G.S., Landry, J.W., Bazant, M.Z.: Analysis of granular flow in a pebble-bed nuclear reactor. Phys. Rev. E 74, 021306 (2006)
Sbragaglia, M., Prosperetti, A.: Effective velocity boundary condition at a mixed slip surface. J. Fluid. Mech. 578, 435–451 (2007)
Benzi, R., Sbragaglia, M., Perlekar, P., Bernaschi, M., Succi, S., Toschi, F.: Direct evidence of plastic events and dynamic heterogeneities in soft-glasses. Soft Matter 10, 4615–4624 (2014)
Einzel, D., Panzer, P., Liu, M.: Boundary-condition for fluid flow—curved or rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 2269 (1990)
Panzer, P., Liu, M., Einzel, D.: The effects of boundary curvature on hydrodynamic fluid flow—calculation of slip lengths. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 6, 3251 (1992)
Varagnolo, S., Ferraro, D., Fantinel, P., Pierno, M., Mistura, G., Amati, G., Biferale, L., Sbragaglia, M.: Stick-slip sliding of water drops on chemically heterogeneous surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 066101 (2013)
Seemann, R., Brinkmann, M., Pfohl, T., Herminghaus, S.: Droplet based microfluidics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 75, 016601 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors kindly acknowledge funding from the European Research Council under the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013)/ERC Grant Agreement No. 279004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scagliarini, A., Sbragaglia, M. & Bernaschi, M. Mesoscopic Simulation Study of Wall Roughness Effects in Micro-channel Flows of Dense Emulsions. J Stat Phys 161, 1482–1495 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-015-1374-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-015-1374-y