Abstract
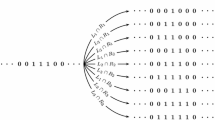
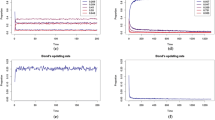
We describe a real-space renormalisation scheme for non-equilibrium probabilistic cellular automata (PCA) models, and apply it to a two-dimensional binary PCA. An exact renormalisation scheme is rare, and therefore we provide a method for computing the stationary probability distribution of states for such models with which to weight the renormalisation, effectively minimising the error in the scale transformation. While a mean-field approximation is trivial, we use the principle of maximum entropy to incorporate nearest-neighbour spin-correlations in the steady-state probability distribution. In doing so we find the fixed point of the renormalisation is modified by the steady-state approximation order.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balzter, H., Braun, P.W., Küohler, K.: Cellular automata models for vegetation dynamics. Ecol. Model. 107(2–3), 113–125 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(97)00202-0. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304380097002020
Burraston, D., Edmonds, E.: Cellular automata in generative electronic music and sonic art: a historical and technical review. Digit. Creat. 16(3), 165–185 (2005a). doi:10.1080/14626260500370882
De Oliveira, M.J., Satulovsky, J.E.: Renormalization group of probabilistic cellular automata with one absorbing state. Phys. Rev. E 55(6), 6377 (1997). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.55.6377
Edlund, E., Nilsson Jacobi, M.: Renormalization of cellular automata and self-similarity. J. Stat. Phys. 139(6), 972–984 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10955-010-9974-z
Hinrichsen, H.: Non-equilibrium phase transitions. Phys. A 369(1), 1–28 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.physa.2006.04.007. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S037843710600402X
Ilachinski, A.: Zane, Cellular Automata: A Discrete Universe. World Scientific Publishing Co., Inc, River Edge (2001)
Nagel, K., Schreckenberg, M.: A cellular automaton model for freeway traffic. J. Phys. I 2(12), 2221–2229 (1992). doi:10.1051/jp1:1992277
Toméand, T., de Oliveira, M.J., Tomé, T.: Renormalization group of the Domany–Kinzel cellular automaton. Phys. Rev. E 55(4), 4000–4004 (1997). doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.55.4000
Vespignani, A., Zapperi, S., Loreto, V.: Renormalization of nonequilibrium systems with critical stationary states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77(22), 4560–4563 (1996). doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.77.4560
Weaver, I.S., Prügel-Bennett, A.: Renormalization group approach to 1D cellular automata with large updating neighborhoods. Complexity (2014). doi:10.1002/cplx.21557
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by an EPSRC Doctoral Training Centre Grant (EP/G03690X/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weaver, I.S., Prügel-Bennett, A. Renormalisation of 2D Cellular Automata with an Absorbing State. J Stat Phys 159, 211–220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-014-1142-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-014-1142-4