Abstract
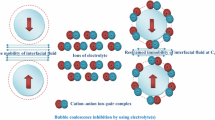
The physical properties of concentrated salt solutions are an important aspect of many industrial processes. The effects of different salts on the inhibition of bubble coalescence have raised some unexpected observations, because some salts inhibit coalescence while others have no effect over a wide concentration range. Fortunately, many common salts inhibit bubble coalescence and although the mechanism is not fully understood, this effect allows the construction of bubble column evaporators (BCEs) for the efficient transfer of both vapor and heat. In this study the BCE process has been used under steady state conditions to determine the latent heat (enthalpy) of vaporization (ΔH vap) of concentrated solutions of several common salts. In addition, it was found that under non-steady state conditions using high inlet gas temperatures, the rate of vapor transfer, and hence thermal desalination, could be increased using the BCE process. Some new observations on the fundamental mechanism of the bubble coalescence phenomenon are also reported.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grover, G.S., Eisa, M.A.R., Holland, F.A.: Thermodynamic design data for absorption heat pump systems operating on water–lithium chloride—part one. Cool. Heat. Recover. Syst. CHP 8, 33–41 (1988)
Patil, K.R., Kim, M.N., Eisa, M.A.R., Holland, F.A.: Experimental evaluation of aqueous lithium halides as single- and double-salt systems in absorption heat-pumps. Appl. Energy 34(2), 99–111 (1989)
Mandani, F., Ettouney, H., El-Dessouky, H.: LiBr–H2O absorption heat pump for single-effect evaporation desalination process. Desalination 128, 161–176 (2000)
Post, J.W., Veerman, J., Hamelers, H.V., Euverink, G.J., Metz, S.J., Nymeijer, K., Buisman, C.J.: Salinity-gradient power: evaluation of pressure-retarded osmosis and reverse electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 288, 218–230 (2007)
Achilli, A., Cath, T.Y., Childress, A.E.: Power generation with pressure retarded osmosis: an experimental and theoretical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 343, 42–52 (2009)
Cath, T.Y., Childress, A.E., Elimelech, M.: Forward osmosis: principles, applications, and recent developments. J. Membr. Sci. 281, 70–87 (2006)
McGinnis, R.L., Elimelech, M.: Energy requirements of ammonia–carbon dioxide forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 207, 370–382 (2007)
Craig, V., Ninham, B., Pashley, R.: Effect of electrolytes on bubble coalescence. Nature 364(6435), 317–319 (1993)
Leifer, I., Patro, R.K., Bowyer, P.: A study on the temperature variation of rise velocity for large clean bubbles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 17, 1392–1402 (2000)
Francis, M., Pashley, R.: Application of a bubble column for evaporative cooling and a simple procedure for determining the latent heat of vaporization of aqueous salt solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 113, 9311–9315 (2009)
Atkins, R.C.: Evaporative Cooling System for Buildings. USA patent US5146762 (1992)
Shahid, M., Pashley, R., Mohklesur, R.A.: Use of a high density, low temperature, bubble column for thermally efficient water sterilization. Desalin. Water Treat. 52(22–24), 4444–4452 (2014)
Francis, M., Pashley, R.: Thermal desalination using a non-boiling bubble column. Desalin. Water Treat. 12(1–3), 155–161 (2009)
Klassen, V.I., Mokrousov, V.A.: An Introduction to the Theory of Flotation. Butterworths, London (1963)
Craig, V.S.: Bubble coalescence and specific-ion effects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 9, 178–184 (2004)
Craig, V.S.: Do hydration forces play a role in thin film drainage and rupture observed in electrolyte solutions? Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 16, 597–600 (2011)
Horn, R.G., Del Castillo, L.A., Ohnishi, S.: Coalescence map for bubbles in surfactant-free aqueous electrolyte solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 168(1), 85–92 (2011)
Browne, C., Tabor, R.F., Chan, D.Y., Dagastine, R.R., Ashokkumar, M., Grieser, F.: Bubble coalescence during acoustic cavitation in aqueous electrolyte solutions. Langmuir 27, 12025–12032 (2011)
Al-Shorachi, H.N., Hashim, E.T.: Prediction of the heat of vaporization from the heat of vaporization at normal boiling point. Pet. Sci. Technol. 25, 1527–1530 (2007)
Fish, L.W., Lielmezs, J.: General method for predicting the latent heat of vaporization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 14, 248–256 (1975)
Godts, P., Dupont, D., Leclercq, D.: Direct measurement of the latent heat of evaporation by flowmetric method. Instrum. Meas. IEEE Trans. 54, 2364–2369 (2005)
Kuwairi, B., Maddox, R.N.: Generalized method for calculation latent heat of vaporization. Chem. Eng. Commun. 29, 337–351 (1984)
Torquato, S., Stell, G.: Latent heat of vaporization of a fluid. J. Phys. Chem. 85, 3029–3030 (1981)
Torquato, S., Stell, G.R.: An equation for the latent heat of vaporization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 21(3), 202–205 (1982)
Zhong, X.U.: An improved generalized Watson equation for prediction of latent heat of vaporization. Chem. Eng. Commun. 29(1–6), 257–269 (1984)
Lunnon, R.G.: The latent heat of evaporation of aqueous salt solutions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 25, 180–191 (1912)
Lide, D.R., Bruno, T.J.: CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton (2012)
Kestin, J.: Viscosity of liquid water in the range −8 °C to −150 °C. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 7, 941–948 (1978)
Kestin, J., Khalifa, H.E., Abe, Y., Grimes, C.E., Sookiazian, H., Wakeham, W.A.: Effect of pressure on the viscosity of aqueous sodium chloride solutions in the temperature range 20–150 °C. J. Chem. Eng. Data 23, 328–336 (1978)
Craig, V.S., Ninham, B.W., Pashley, R.M.: The effect of electrolytes on bubble coalescence in water. J. Phys. Chem. 97, 10192–10197 (1993)
Clift, R., Grace, J., Weber, M.: Bubbles, Drops and Particles, p. 346. Academic Press, New York (1978)
Hunter, J.B., Bliss, H.: Thermodynamic properties of aqueous salt solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 36, 945–953 (1944)
Chou, J., Rowe, A.M.: Enthalpies of aqueous sodium chloride solutions from 32–350 F. Desalination 6, 105–115 (1969)
Topor, N., Logasheva, A., Tsoy, G.: Determination of the heat of evaporation of pure substances and of aqueous solutions of inorganic salts with the derivatograph. J. Therm. Anal. 17, 427–433 (1979)
Gurovich, B.M., Zyuzin, R.A., Mezheritskii, S.M.: Experimental determination of the heat of vaporization of aqueous salt solutions at atmospheric pressure. Chem. Pet. Eng 24, 599–600 (1988)
Clarke, E.C.W., Glew, D.N.: Evaluation of the thermodynamic functions for aqueous sodium chloride from equilibrium and calorimetric measurements below 154 °C. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 14, 489–610 (1985)
Hubert, N., Gabes, Y., Bourdet, J.-B., Schuffenecker, L.: Vapor pressure measurements with a nonisothermal static method between 293.15 and 363.15 K for electrolyte solutions. Application to the H2O + NaCl System. J. Chem. Eng. Data 40, 891–894 (1995)
Patil, K.R., Tripathi, A.D., Pathak, G., Katti, S.S.: Thermodynamic properties of aqueous electrolyte solutions. 2. Vapor pressure of aqueous solutions of sodium bromide, sodium iodide, potassium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium iodide, rubidium chloride, cesium chloride, cesium bromide, cesium iodide, magnesium chloride, calcium chloride, calcium bromide, calcium iodide, strontium chloride, strontium bromide, strontium iodide, barium chloride, and barium bromide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 36, 225–230 (1991)
Sako, T., Hakuta, T., Yoshitome, H.: Vapor pressures of binary (water–hydrogen chloride,–magnesium chloride, and–calcium chloride) and ternary (water–magnesium chloride–calcium chloride) aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 30, 224–228 (1985)
Frankel, S.P., Myseis, K.J.: On the “dimpling” during the approach of two interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 66, 190–191 (1962)
Shibue, Y.: Vapor pressures of aqueous NaCl and CaCl2 solutions at elevated temperatures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 213, 39–51 (2003)
Sparrow, B.S.: Empirical equations for the thermodynamic properties of aqueous sodium chloride. Desalination 159(2), 161–170 (2003)
Shahid, M., Pashley, R.M.: The use of air bubbles to desalinate seawater without boiling. In: Aqua Incognita: Why Ice Floats on Water and Galileo 400 Years On. Connorcourt Publishing, Melbourne (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Australian Research Council for funding this project and Mr. Mark Freeman of Blackwater Treatment Systems (BTS) for supplying the air pumping systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Shahid, M. & Pashley, R.M. Studies on Bubble Column Evaporation in Various Salt Solutions. J Solution Chem 43, 1297–1312 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10953-014-0206-z