Abstract
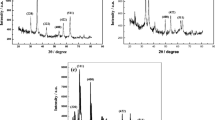
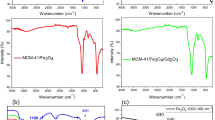
In the present work, we synthesize Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposite by sol-gel method using iron nitrate, ethylene glycol, zinc acetate dehydrate, and ammonium carbonate as precursors. Amorphous matrix and crystalline grains were formed in composite as well. The nanostructural properties of the nanocomposite were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), atomic force microscopy (AFM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), and colloidal stability was checked out by Zeta potential. The biological effects of Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposite were investigated by microculture tetrazolium test (MTT) against MCF-7 breast cancer cells as usage in medicine. Crystallite size, lattice strain, and dislocation density of the nanoparticles were estimated with Williamson-Hall method. The obtained results show that the highest death rate of Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7) cancer cells was for Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposite with the molar ratio is 1:10 in the lower concentration (49 μ g/ml). Therefore, these nanocomposites due to their small size, colloidal stability, magnetic properties, and nontoxicity can be a good candidate as option in medicine application.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shahmiri, M.R., Bahari, A., Karimi-Maleh, H., Hosseinzadeh, R., Mirnia, N.: Ethynylferrocene–NiO/MWCNT nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode as a novel voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of glutathione and acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 177, 70–77 (2013)
Kong, W., Abd-Shukor, R.: Enhanced electrical transport properties of nano NiFe2O4-added (Bi1.6Pb0.4) Sr2Ca2Cu3O10 superconductor. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 23(2), 257–263 (2010)
Chinnaraj, K., Manikandan, A., Ramu, P., Antony, S.A., Neeraja, P.: Comparative studies of microwave-and sol-gel-assisted combustion methods of Fe3O4 nanostructures: structural, morphological, optical, magnetic, and catalytic properties. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 28(1), 179–190 (2015)
Bahari, A., Roeinfard, M., Ramzannezhad, A.: Characteristics of Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposite as a possible gate dielectric of nanoscale transistors in the field of cyborg. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(9), 9363–9369 (2016)
Singh, M., Sviridenkova, N., Timur, N., Savchenko, A., Shetinin, I., Majouga, A.: Synthesis and characterization of stable iron oxide nanoparticle with amino covalent binding on the surface for biomedical application. J. Clust. Sci. 27(4), 1383–1393 (2016)
Liu, A.P., Li, X., Duan, L.H., Qin, G.P., Guo, H.H.: Study of Fe3O4 nano-magnetic ferrofluid by atomic force microscope. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 23(6), 967–970 (2010)
Tse, B.W.C., Cowin, G.J., Soekmadji, C., Jovanovic, L., Vasireddy, R.S., Ling, M.T., Russell, P.J.: PSMA-targeting iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles enhance MRI of preclinical prostate cancer. Nanomedicine 10(3), 375–386 (2015)
Wolf, S.A., Awschalom, D.D., Buhrman, R.A., Daughton, J.M., Von Molnar, S., Roukes, M.L., Treger, D.M.: Spintronics: a spin-based electronics vision for the future. Science 294(5546), 1488–1495 (2001)
Hornyak, G.L., Moore, J.J., Tibbals, H.F., Dutta, J.: Fundamentals of nanotechnology. CRC 5, 204–233 (2008)
Vinogradov, S., Wei, X.: Cancer stem cells and drug resistance: the potential of nanomedicine. Nanomedicine 7(4), 597–615 (2012)
Zhou, J., Xu, N.S., Wang, Z.L.: Dissolving behavior and stability of ZnO wires in biofluids: a study on biodegradability and biocompatibility of ZnO nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 18(18), 2432–2435 (2006)
Wahab, R., Siddiqui, M.A., Saquib, Q., Dwivedi, S., Ahmad, J., Musarrat, J., Shin, H.S.: ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 117, 267–276 (2014)
Ostrovsky, S., Kazimirsky, G., Gedanken, A., Brodie, C.: Selective cytotoxic effect of ZnO nanoparticles on glioma cells. Nano Res. 2(11), 882–890 (2009)
Wan, J., Li, H., Chen, K.: Synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4@ZnO core-shell structured nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114(1), 30–32 (2009)
Shal, A.A., Jafari, A.: Study of structural and magnetic properties of superparamagnetic Fe3O4–ZnO core–shell nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 27(6), 1531–1538 (2014)
Choi, K., Chae, W., Kim, E., Jun, J., Jung, J., Kim, Y.: A facile fabrication of Fe3O4/ZnO core-shell submicron particles with controlled size. October 47(10), 3369–3372 (2011)
Beltran Huarac, J.C., Singh, S.P., Tomar, M.S., Pena, S., Rivera, L., Perales-Perez, O.: Synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO core-shell nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications. MRS Online Proc. Libr. Arch. 1257, O06–04 (2010)
Gordon, T., Perlstein, B., Houbara, O., Felner, I., Banin, E., Margel, S.: Synthesis and characterization of zinc/iron oxide composite nanoparticles and their antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 374(1–3), 1–8 (2011)
Singh, S.P.: Multifunctional magnetic quantum dots for cancer theranostics. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 7(1), 95–97 (2011)
Rahman, M.F., Wang, J., Patterson, T.A., Saini, U.T., Robinson, B.L., Newport, G.D., Ali, S.F.: Expression of genes related to oxidative stress in the mouse brain after exposure to silver-25 nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 187(1), 15–21 (2009)
Prabhu, Y.T., Rao, K.V., Kumar, V.S.S., Kumari, B.S.: X-ray analysis by Williamson-Hall and size-strain plot methods of ZnO nanoparticles with fuel variation. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 4(01), 21 (2014)
Shintani, T., Murata, Y.: Evaluation of the dislocation density and dislocation character in cold rolled Type 304 steel determined by profile analysis of X-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 59(11), 4314–4322 (2011)
Uvarov, V., Popov, I.: Metrological characterization of X-ray diffraction methods for determination of crystallite size in nano-scale materials. Mater. Charact. 58(10), 883–891 (2007)
Franklin, N.M., Rogers, N.J., Apte, S.C., Batley, G.E., Gadd, G.E., Casey, P.S.: Comparative toxicity of nanoparticulate ZnO, bulk ZnO, and ZnCl2 to a freshwater microalga (Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata): the importance of particle solubility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 41(24), 8484–8490 (2007)
Huarac, J.C.B., Singh, S.P., Tomar, M.S., Pena, S., Rivera, L., Perales-Perez, O.: Synthesis of Fe3O4/ZnO core-shell nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy applications. MRS Proc. 1257, 1257–O06 (2010)
Nanse, G., Papirer, E., Fioux, P., Moguet, F., Tressaud, A.: Fluorination of carbon blacks: an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study: I. A literature review of XPS studies of fluorinated carbons. XPS investigation of some reference compounds. Carbon 35(2), 175–194 (1997)
Biesinger, M.C., Payne, B.P., Grosvenor, A.P., Lau, L.W., Gerson, A.R., Smart, R.S.C.: Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(7), 2717–2730 (2011)
Gammon, W.J., Kraft, O., Reilly, A.C., Holloway, B.C.: Experimental comparison of N (1s) X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy binding energies of hard and elastic amorphous carbon nitride films with reference organic compounds. Carbon 41(10), 1917–1923 (2003)
Bahari, A., Nik, A.S., Roodbari, M., Mirnia, N.: Investigation the Al–Fe–Cr–Ti nano composites structures with using XRD and AFM techniques. Sadhana 37(6), 657–664 (2012)
Win, K.Y., Feng, S.S.: Effects of particle size and surface coating on cellular uptake of polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 26(15), 2713–2722 (2005)
Premanathan, M., Karthikeyan, K., Jeyasubramanian, K., Manivannan, G.: Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 7(2), 184–192 (2011)
Hanley, C., Layne, J., Punnoose, A., Reddy, K.M., Coombs, I., Coombs, A., Wingett, D.: Preferential killing of cancer cells and activated human T cells using ZnO nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 19(29), 295103 (2008)
Wahab, R., Siddiqui, M.A., Saquib, Q., Dwivedi, S., Ahmad, J., Musarrat, J., Shin, H.S.: ZnO nanoparticles induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in HepG2 and MCF-7 cancer cells and their antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 117, 267–276 (2014)
Hanaor, D., Michelazzi, M., Leonelli, C., Sorrell, C.C.: The effects of carboxylic acids on the aqueous dispersion and electrophoretic deposition of ZrO2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 32(1), 235–244 (2012)
Greenwood, R., Kendall, K.: Selection of suitable dispersants for aqueous suspensions of zirconia and titania powders using acoustophoresis. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 19(4), 479–488 (1999)
Bahari, A.: Characteristics of Fe3O4, α-Fe2O3, and γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles as suitable candidates in the field of nanomedicine. J Supercond Nov Magn, 1–10 (2017)
Kievit, F.M., Zhang, M.: Surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Accounts Chem. Res. 44(10), 853–862 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roeinfard, M., Bahari, A. Nanostructural Characterization of the Fe3O4/ZnO Magnetic Nanocomposite as an Application in Medicine. J Supercond Nov Magn 30, 3541–3548 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4154-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4154-x