Abstract
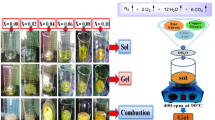
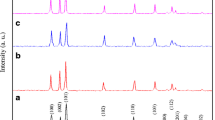
Ferromagnetic oxide semiconductor of pure and (Mn, Co) codoped CuO nanocrystals were synthesized by a chemical coprecipitation method. The phase structure, morphology and room temperature ferromagnetism were investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). Results of XRD demonstrated that both the undoped and (Mn, Co) codoped CuO samples have single phase of CuO monoclinic structure and no secondary phases were detected, suggesting the incorporation of Mn and Co dopants in CuO lattice. The FTIR spectra of all samples showed three main absorption bands attributed to stretching vibrations of Cu–O bond. The morphology of the pure CuO was found to change from nanoparticle to nanorod structure after codoping with Mn and Co ions. The diameter and length of the nanorods were nearly 28–60 and 130–550 nm, respectively. The obtained magnetic hysteresis loops at room temperature confirmed the ferromagnetic nature of all the prepared samples, which was enhanced after the incorporation of Mn and Co ions into CuO lattice. The effect of the codoped ions on the structure and ferromagnetism are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dietl, T.: Why ferromagnetic semiconductor? Postêpy Fizyki 52 (Suppl.) (2001), presented at the IV International School and Symposium on Physics in Materials, Jaszowiec, Poland, Sept. 23-29, 2001, and at the 34th Meeting of the Polish Physicists, Toruñ, Sept. 17–20.
Kalyani, V.L., Agrawal, V.: Spintronics—a vision for future in electronics and computers. J. Manag. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2, 30–36 (2015).
Rahi, S.B., Rastogi, P.: A review report for next generation of CMOS technology as spintronics: fundamentals, applications and future. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 6, 696–702 (2013).
Zunger, A., Lany, S., Raebiger, H.: The quest for dilute ferromagnetism in semiconductors: guides and misguides by theory. Physics. 3, 53 (2010).
Xu, Y.B., Ahmad, E., Claydon, J.S., Lu, Y.X., Hassan, S.S.A., Will, I.G., Cantor, B.: Hybrid magnetic/semiconductor spintronic materials and devices. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 304, 69–74 (2006).
Gautam, A.: Spintronics—a new hope for the digital world. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2, 1–5 (2012).
Chambers, S.A., Droubay, T.C., Wang, C.M., Rosso, K.M., Heald, S.M., Schwartz, D.A., Kittilstved, K.R., Gamelin, D.R.: Ferromagnetism in oxide semiconductors. Materials Today. 9, 28–35 (2006).
Yu-Feng, T., Shu-Jun, H., Shi-Shen, Y., Liang-Mo, M.: Oxide magnetic semiconductors: materials, properties, and devices. Chin. Phys. B. 22, 088505–1: 088505-19 (2013).
Dietl, T., Ohno, H., Matsukura, F., Cibert, J., Ferrant, D.: Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science. 287, 1019–1022 (2000).
Matsumoto, Y., Murakami, M., Shono, T., Hasegawa, T., Fukumora, T., Kawasaki, M., Ahmet, P., Chikyow, T., Koshihara, S., Koinuma, H.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in transparent transition metal-doped titanium dioxide. Science. 291, 854–856 (2001).
Kaushal, A., Bansal, P., Vishnoi, R., Choudhary, N., Kaur, D.: Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Sn 1−xMn x O 2 nanocrystalline thin films prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Physica B. 404, 3732–3738 (2009).
El-Hilo, M., Dakhel, A.A., Ali-Mohamed, A.Y.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in nanocrystalline Ni-doped ZnO synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2279–2283 (2009).
Raja, S.P., Joseph, D.P., Venkateswaran, C.: Analysis on Cu 0.95Mn 0.05O for ferromagnetic ordering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 67–70 (2009).
Sundaresan, A., Rao, C.N.R.: Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of inorganic nanoparticles. Nano Today. 4, 96–106 (2009).
Guo, T., Zhang, Y., Luo, Y., Nan, C.-W., Lin, Y.-H.: Magnetical behaviors observed in nanostructured ZnO with different morphologies. Mater. Lett. 108, 273–275 (2013).
Khan, G.G., Ghosh, S., Mandal, K.: Origin of room temperature d 0 ferromagnetism and characteristic photoluminescence in pristine SnO 2 nanowires: a correlation. J. Solid State Chem. 186, 278–282 (2012).
Das, S., Majumdar, S., Giri, S.: Room temperature weak ferromagnetism and magnetoconductance in functional CuO film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 10775–10779 (2011).
Xu, Q., Gao, D., Zhang, J., Yang, Z., Zhang, Z., Rao, J., Xue, D.: Observation of room temperature ferromagnetism in pure La 2 O 3 nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A. 116, 1293–1298 (2014).
Gao, D., Li, J., Li, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Shi, H., Xue, D.: Defect-mediated magnetism in pure CaO nanopowders. J. Phys. Chem. C. 114, 11703–11707 (2010).
Qian, X., Wei-Peng, W., Zheng, X., Peng, Z., Zheng-Cao, L., Zheng-Jun, Z.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in un-doped amorphous HfO 2 nano-helix arrays. Chin. Phys. B. 24, 057503–1: 057503-6 (2015).
Okabayashi, J., Nomura, K., Kono, S., Yamada, Y.: Magnetization enhancement in room-temperature ferromagnetic Fe–Mn co-doped SnO 2. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 023003–1: 023003-4 (2012).
Issa, B., Obaidat, I.M., Albiss, B.A., Haik, Y.: Magnetic nanoparticles: surface effects and properties related to biomedicine applications. Int J Mol Sci. 14, 21266–21305 (2013).
Köseoğlu, Y.: Rapid synthesis of room temperature ferromagnetic Fe and Co co-doped ZnO DMS nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41, 11655–11661 (2015).
Chang, Y., Wang, P., Sun, Q., Wang, Y., Long, Y.: Room temperature ferromagnetism of (Mn, Fe) codoped ZnO nanowires synthesized by chemical vapor deposition. J. Nanomater. 2011, 1–6 (2011).
Manikandan, D., Murugan, R.: Room temperature dilute magnetism in nanoscale Co and Zn co-doped SnO 2. Superlattices Microstruct. 89, 7–14 (2016).
Gülena, Y., Bayansal, F., Şahin, B., H.A., Çetinkara, H., Gü, der S.: Fabrication and characterization of Mn-doped CuO thin films by the SILAR method. Ceram. Int. 39, 6475–6480 (2013).
Basith, N.M., Vijaya, J.J., Kennedy, L.J., Bououdina, M., Hussain, S.: Optical and magnetic properties of co-doped CuO flower/plates/particles-like nanostructures. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 2577–2583 (2014).
Mageshwari, K., Sathyamoorthy, R.: Lower-shaped CuO nanostructures: synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 909–914 (2013).
Erdogan, I.Y., Gullu, O.: Optical and structural properties of CuO nanofilm: its diode application. J. Alloy. Compd. 492, 378–383 (2010).
Ethiraj, A. S., Kang, D. J.: Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanowires by a simple wet chemical method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 70 (2012).
Radhakrishnan, A.A., Beena, B.B.: Structural and optical absorption analysis of CuO nanoparticles. Indian J. Adv. Chem. Sci. 2, 158–161 (2014).
Ali, A.G., Dejene, F.B., Swart, H.C.: Effect of Mn doping on the structural and optical properties of sol-gel derived ZnO nanoparticles. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 10, 478–484 (2012).
Kisan, B., Alagarsamy, P.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in finite sized ZnO nanoparticles. Physica B. 448, 115–119 (2014).
Shi, S., Gao, D., Xu, Q., Yang, Xue, Z., D.: Singly-charged oxygen vacancy-induced ferromagnetism in mechanically milled SnO 2 powders. RSC Adv. 4, 45467–45472 (2014).
Gao, D., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Qi, J., Zhang, Z., Sui, W., Shi, H., Xue, D.: Vacancy-mediated magnetism in pure copper oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 769–772 (2010).
Zhao, J.G., Liu, S.J., Yang, S.H., Yang, S.G.: Hydrothermal synthesis and ferromagnetism of CuO nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 9678–9681 (2011).
Shang, D., Yu, K., Zhang, Y., Xu, J., Wu, J., Xu, Y., Li, L., Zhu, Z.: Magnetic and field emission properties of straw-like CuO nanostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 4093–4096 (2009).
Zou, C.W., Wang, J., Liang, F., Xie, W., Shao, L.X., Fu, D.J.: Large-area aligned CuO nanowires arrays: synthesis, anomalous ferromagnetic and CO gas sensing properties. Curr. Appl. Phys. 12, 1349–1354 (2012).
Chandra, S.: Comprehensive inorganic chemistry. New Age International Pvt Ltd (2006).
Yu, X., Meng, D., Liu, C., He, X., Wang, Y., Xie, J.: Structure and ferromagnetism of Fe-doped and Fe-and Co-codoped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by homogeneous precipitation method. Mater. Lett. 86, 112–114 (2012).
Huang, X., Li, G., Duan, L., Li, L., Dou, X., Zhang, L.: Formation of ZnO nanosheets with room-temperature ferromagnetism by co-doping with Mn and Ni. Scr. Mater. 60, 984–987 (2009).
Subramanyam, K., Sreelekha, N., Reddy, D. A., Murali, G., Poornaprakash, B., Ramu, S., Vijayalakshmi, R.P.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of chromium and manganese co-doped SnO 2 nanoparticles. Solid State Sci. 39, 74–81 (2015).
Duan, L.B., Rao, G.H., Wang, Y.C., Yu, J., Wang, T.: Magnetization and Raman scattering studies of (Co, Mn) codoped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 104, 013909–1: 013909-5 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yakout, S.M., El-Sayed, A.M. Structural, Morphological and Ferromagnetic Properties of Pure and (Mn, Co) Codoped CuO Nanostructures. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 2961–2968 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3641-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3641-9