Abstract
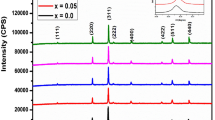
High-purity Mn-doped Ni x Zn0.9−x Fe2 O 4 particles were fabricated by conventional ceramic processing. The ac conductivity reveals a temperature-dependent behavior at low frequencies and temperature-independent behavior at high frequencies which could be an indication of ionic conductivity because of activated frequency ranges. The dc conductivities of Mn-substituted Ni-Zn spinel ferrites [Ni x Zn0.9−x Mn0.1:Fe2 O 4 (where 0.3 ≤x≤ 0.7)] are found to obey the Arrhenius plot with activation energies between 016 and 0.18 eV. The electrical characterization confirms that ac conductivity is found to be almost independent of frequency at lower frequencies up to 10 kHz and however increases with temperature elevation. Additionally, the imaginary component of dielectric function obeys the power law of frequency while it possesses temperature dependency as well. This can be attributed to the molecular interatomic interactions among Mn-substituted Ni-Zn spinel ferrites. Functional analysis of the electrical conductivities and dielectric permittivity suggests that ionic motions are strongly coupled within the spinel ferrite nanocomposites because of the stimulated frequency ranges








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deligöz, H., et al.: Synthesis, structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Co1 - xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.2) nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 48(2), 646–654 (2013)
Köseoğlu, Y.: Structural, magnetic, electrical and dielectric properties of MnxNi1 - xFe2O4 spinel nanoferrites prepared by PEG assisted hydrothermal method. Ceram. Int. 39(4), 4221–4230 (2013)
Anwar, H., Maqsood, A.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of Cu substituted Mn–Zn soft nanoferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25(6), 1913–1920 (2012)
Gabal, M.A., et al.: Influence of Al-substitution on structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Mn–Zn ferrites nanopowders prepared via the sol–gel auto-combustion method. Polyhedron 57, 105–111 (2013)
Genç, F., Turhan, E., Kavas, H., Topal, U., Baykal, A., Sözeri, H.: Submitted to J. of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetisim as a proceeding of ICSM 2014 “International Conference on Superconductivity and Magnetism” in Antalya, Turkey
Wejrzanowski, T., et al.: Quantitative methods for nanopowders characterization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 253(1 SPEC. ISS.), 204–208 (2006)
Sertkol, M., et al.: Synthesis and magnetic characterization of Zn0.6Ni0.4Fe2O4 nanoparticles via a polyethylene glycol-assisted hydrothermal route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(3), 157–162 (2009)
Kavas, H., et al.: Cation distribution and magnetic properties of Zn doped NiFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by PEG-assisted hydrothermal route. J. Alloys Compd. 479(1–2), 49–55 (2009)
Sertkol, M., et al.: Microwave synthesis and characterization of Zn-doped nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 486(1–2), 325–329 (2009)
Kumar, A., et al.: Finite size effect on Ni doped nanocrystalline NixZn1-xFe2O4 (0.1 =x= 0.5). Thin Solid Films 519(3), 1056–1058 (2010)
Shen, Y.F., et al.: Manganese oxide octahedral molecular sieves: preparation, characterization, and applications. Science 260(5107), 511–515 (1993)
Unal, B., et al.: Synthesis, conductivity and dielectric characterization of salicylic acid–Fe3O4 nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 123(1), 184–190 (2010)
Macdonald, J.R.: Comparison of the universal dynamic response power-law fitting model for conducting systems with superior alternative models. Solid State Ionics 133(1–2), 79–97 (2000)
Zhang, C.S., Yang, L.: Preparation and magnetic properties of the conductive Co(1 - x)NixFe2O4/polyaniline microsphere composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(8), 1469–1472 (2012)
Kurtan, U., et al.: The electrical properties of polyaniline (PANI)–Co0.5Mn0.5Fe2O4 nanocomposite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 23(5), 1089–1096 (2013)
Zhong-ai, H., et al.: The preparation and characterization of quadrate NiFe2O4/polyaniline nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci: Mater. Electron. 17(11), 859–863 (2006)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by TUBITAK (The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey) with Project number 213M174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Genc, F., Ünal, B., Baykal, A. et al. Electrical Properties of Mn-Doped Ni x Zn0.9−x Fe2O4 Particles. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 1055–1064 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2833-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2833-4