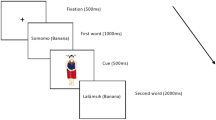
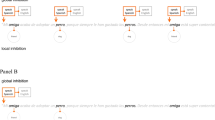
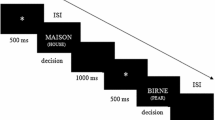
Abstract
This study reports two metalinguistic parameters that constitute the schematic control of lateral inhibitory links between translation equivalents within the bilingual lexico-semantic system of Green’s (Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1:67–81, 1998a, Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1:100–104, 1998b, The bilingualism reader, Routledge, London, 2007) inhibitory control (IC) model. Building on Green’s postulation that the bilingual lexico-semantic system is controlled by a hierarchy of schemas under a supervisory attentional system, the bilingual unconsciously filters activated lemmas during fluent spontaneous codeswitching, such that lemmas that are semantico-syntactically versatile or morphosyntactically transparent are likely to reach a threshold of activation first while other lemmas are inhibited. To investigate the issue, we collected code-paired naturalistic and elicited data with a focus on code-switched determiner phrases from 140 Mandarin-English simultaneous bilinguals who were post-secondary students in Singapore. We found that the semantico-syntactic and morpho-syntactic dissimilarities between Mandarin and English activated both filters. As most Mandarin determiners are economical vis-à-vis their English counterparts, their lemmas were selected frequently while English lemmas were largely inhibited. It was also found that our participants preferred English nouns in filling the lexical category for their interpretable feature of number, a feature that is normally absent in Mandarin nouns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abutalebi J., Green D. W. (2007) The neurocognition of bilingual speech production. Journal of Neurolinguistics 20: 242–275
Abutalebi J., Green D. W. (2008) Control mechanisms in bilingual language production: Neural evidence from language switching studies. Language and Cognitive Processes 23: 557–582
Bialystok E. (1988) Levels of bilingualism and levels of linguistic awareness. Developmental Psychology 88: 560–567
Bialystok E., Majumder S. (1998) The relationship between bilingualism and the development of cognitive processes in problem-solving. Applied Psycholinguistics 19: 69–85
Bussman, H. (1996). Routledge dictionary of language and linguistics (3rd ed., G. P. Trauth & K. Kazzazi, Trans.). London: Routledge.
Chao Y. R. (1948) Mandarin primer: An intensive course in spoken Chinese. Harvard University Press, Cambridge
Chao Y. R. (1968) A grammar of spoken Chinese. University of California Press, Berkeley, CA
Chen, J. J. (1992). Lun xin jia po hua yu zhong yu ma jia za xian xiang (Code-mixing in Singapore Mandarin). Unpublished B.A. (Honors) thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
Cheng L., Sybesma R. (1999) Bare and not-so-bare nouns and the structure of NP. Linguistic Inquiry 30: 509–542
Chong, H. M. (2001). Xin jia po hua yu yu ma jia za zhong de dan ci (Code-mixed single words in Singapore Mandarin conversation). Unpublished B.A. (Honors) thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
Chu C. C. (1983) A reference grammar of Mandarin Chinese for English speakers. Peter Lang, New York
Clyne M. (1991) Community languages: The Australian experience. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Codó E. (2008) Interviews and questionnaires. In: Li W., Moyer M. G. (eds) The Blackwell guide to research methods in bilingualism and multilingualism. Blackwell Publishing, Oxford, pp 158–176
Colomé A. (2001) Lexical activation in bilinguals’ speech production: Language-specific or language-independent?. Journal of Memory and Language 45: 721–735
Creswell J. W. (2003) Research design: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches. (2nd ed.) Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks
Cummins J. (2000) Language, power and pedagogy. Multilingual Matters, Clevedon
de Bot K. (2007) A bilingual production model: Levelt’s “speaking” model adapted. In: Li W. (eds) The bilingualism reader. Routledge, London, pp 84–104
Department of Statistics. (2001). Census of population 2000 statistical release 2: Education, language and religion. Singapore: Ministry of Trade and Industry.
Edwards M., Gardner-Chloros P. (2007) Compound verbs in code-switching: Bilinguals making do?. International Journal of Bilingualism 11: 73–91
Faersch C., Kasper G. (1984) Two ways of defining communication strategies. Language Learning 34: 45–63
Francis N. (2004) The components of bilingual proficiency. International Journal of Bilingualism 8: 167–189
Gao Q. (1994) Chinese NP structure. Linguistics 32: 475–510
Green D. W. (1998a) Mental control of the bilingual lexico-semantic system. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1: 67–81
Green D. W. (1998b) Schemas, tags and inhibition: Reply to commentators. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1: 100–104
Green D. W. (2007) Control, activation and resource: A framework and a model for the control of speech in bilinguals. In: Li W. (eds) The bilingualism reader. Routledge, London, pp 371–383
Green D. W., Crinion J., Price C. J. (2006) Convergence, degeneracy and control. Language Learning 56(Special Issue 1): 99–125
Grosjean F. (1997) Processing mixed languages: Issues, findings and models. In: de Groot A., Kroll J. F. (eds) Tutorials in bilingualism: Psycholinguistic perspectives. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah NJ, pp 225–254
Grosjean F. (2001) The bilingual’s language modes. In: Nicol J. (eds) One mind, two languages. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 1–22
Gupta A. F. (1994) The step tongue: Children’s English in Singapore. Multilingual Matters, Clevedon, UK
Hirst G. (1999) What exactly are lexical concepts?. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 22: 45–46
Jay T. B. (2003) The psychology of language. Pearson, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Kamwangamalu N. M., Lee C. L. (1991) Chinese-English code-mixing: A case of matrix language assignment. World Englishes 10: 247–261
Krifka M. (1995) Common nouns: A contrastive analysis of Chinese and English. In: Carlson G., Pellertier J. (eds) The generic book. University of Chicago Press, Chicago, pp 398–411
Kuo L., Anderson R. C. (2007) Conceptual and methodological issues in comparing metalinguistic awareness across languages. In: Koda K., Zehler A. M. (eds) Learning to read across languages: Cross-linguistic relationships in first and second-language literacy development. Routledge, New York, pp 39–67
Lee, C. C. P. (2005). The role of code-switching in a communications skills classroom. Unpublished M.A. (Applied Linguistics) thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Lee C. L. (2003) Motivations of code-switching in multilingual Singapore. Journal of Chinese Linguistics 31: 145–176
Levelt W. J. M., Roeflofs A., Meyer A. S. (1999) A theory of lexical access in speech production. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 22: 1–76
Li C. N., Thompson S. A. (1981) Mandarin Chinese: A functional reference grammar. University of California Press, Berkeley
Li D. G. S. (1996) Issues in bilingualism and biculturalism: A Hong Kong case study. Peter Lang Publishing, New York
Li P. (1998) Mental control, language tags, and language nodes in bilingual lexical processing. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1: 92–93
Liceras J., Fuertes R. F., Perales S., Pérez-Tattam R., Spradlin K. T. (2008) Gender and gender agreement in bilingual native and non-native grammars: A view from child and adult functional-lexical mixings. Lingua 118: 827–851
Liceras J., Martinez C., Pérez-Tattam R., Perales S. (2006) L2 acquisition as a process of creolization: Insights from child and adult code-mixing. In: Lefebvre C., White L., Jourdan C. (eds) L2 acquisition and creole genesis: Dialogues. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 113–144
Liceras J., Spradlin K. T., Fuertes R. (2005) Bilingual functional-lexical mixing and the activation of formal features. International Journal of Bilingualism 9: 227–252
Lin H. (2001) A grammar of Mandarin Chinese. Lincom Europa, Muenchen
Liu J., Tindall E., Nisbet D. (2006) Chinese learners and English plural forms. The Linguistics Journal 1: 127–147
Lu J. Y. (1991) Code-switching between Mandarin and English. World Englishes 10: 139–151
MacSwan J. (1999) A minimalist approach to intrasentential code switching. Garland, New York
MacSwan J. (2000) The architecture of the bilingual language faculty: Evidence from intrasentential code-switching. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 3: 3–54
Myers-Scotton C. (2002) Contact linguistics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Myers-Scotton C. (2005) Duelling languages: Grammatical structure in codeswitching. Oxford University Press, Oxford UK
Poh, L. K. (2003). A comparative study of commonly used noun classifiers in Singapore Mandarin and Putonghua. Unpublished B.A. (Honors) thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore.
Pulvermüller F. (1999) Lexical access as a brain mechanism. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 22: 52–54
Ricciardelli L.A. (1992) Bilingualism and cognitive development in relation to threshold theory. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research 21: 301–316
Rodriguez-Fornells A., De Diego Balaguer R., Münte T. F. (2006) Executive control in bilingual language processing. Language Learning 56: 133–190
Saravanan V. (1999) Bilingual Chinese, Malay and Tamil children’s language choices in a multi-lingual society. Early Child Development and Care 152: 43–54
Schreuder R., Hermans D. (1998) Mental control and language selection. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1: 96–97
Tan P. T. (1988) A description of patterns of code-mixing and code-switching in a multilingual household. In: Foley J. A. (eds) New Englishes: The case of Singapore. Singapore University Press, Singapore, pp 70–99
Tan, Z. L. (2004). Xin jia po hua xiao xue sheng yu ma hun yong ge an yan jiu (A case study of code-mixing among Chinese primary school students in Singapore). Unpublished B.A. (Honors) thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Teo, E. H. (2000). Xin jia po hua yu hui hua zhong yu ma jia za mo shi de ya jiu (Patterns of code-mixing in Singapore Mandarin conversation: A case study). Unpublished B.A. (Honors) thesis, National University of Singapore, Singapore
Trefflers-Daller J. (1998) The IC model and code-switching. Bilingualism: Language and Cognition 1: 98–99
Wei L. (2002) The bilingual mental lexicon and speech production process. Brain and Language 81: 691–707
Wheatley T., Wegner D. M. (2001) Automaticity of action, psychology of. In: Smelser N. J., Baltes P. B. (eds) International encyclopedia of behavioral sciences. Elsevier, 1nd ed. New York, pp 991–993
Williamson H. R. (1947) Teach yourself Chinese. English Universities Press, London
Xu D., Chew C. H., Chen S. (1998) Language use and language attitudes in the Singapore Chinese community. In: Gopinathan S., Pakir A., Ho W. K., Saravanan V. (eds) Language, society and education in Singapore. 2nd ed., Eastern Universities Press, Singapore, pp 133–154
Zhang L. J. (2002) Metamorphological awareness and EFL students’ memory, retention, and retrieval of English adjectival lexicons. Perceptual and Motor Skills 95: 934–944
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ong, K.K.W., Zhang, L.J. Metalinguistic Filters Within the Bilingual Language Faculty: A Study of Young English-Chinese Bilinguals. J Psycholinguist Res 39, 243–272 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9137-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-009-9137-z