Abstract
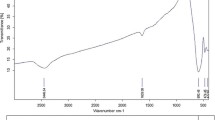
Adsorption characteristics of four different dyes Safranin O (cationic), Neutral Red (neutral), Congo Red (anionic) and Reactive Red 2 (anionic) on Si-MCM-41 material having very high surface area are reported. The surface morphology of Si-MCM-41 material before and after adsorbing dye molecules are characterised by FTIR, HRXRD, nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms, FESEM, and HRTEM. The adsorption capacities of Si-MCM-41 for the dyes followed a decreasing order of NR > SF > CR > RR2. The adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic parameters are investigated in detail for these dyes using calcined Si-MCM-41. The kinetics and isotherm data showed that both SF and NR adsorb more rapidly than CR and RR2, in accordance with pseudo-second-order kinetics model as well as intraparticle diffusion kinetics model and Langmuir adsorption isotherm model respectively. The thermodynamic data suggest that the dye uptake process is spontaneous. The high adsorption capacities of dyes on Si-MCM-41 (qm = 275.5 mg g−1 for SF, qm = 288.2 mg g−1 for NR) is explained on the basis of electrostatic interactions as well as H-bonding interactions between adsorbent and adsorbate molecules. Good regeneration capacity is another important aspect of the material that makes it potent for the uptake of dyes from aqueous solution.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- qm :
-
Adsorption capacity
- MW :
-
Molecular weight
- C0 and Ce :
-
Initial and equilibrium concentrations of adsorbate solutions (mg L−1)
- V:
-
The volume of the dye solution
- W:
-
The weight of the adsorbent
- E = hv:
-
Plank equation
- S:
-
The pore size dependent on the assumed pore geometry
- Vp :
-
The mesoporous volume
- ρ:
-
The pore wall density (i.e. 2.2 cm3/g for siliceous materials)
- d:
-
The XRD interplanar spacing
- R2 :
-
Correlation coefficient
- χ2 :
-
Correction factor
- RL :
-
Separation factor
- ΔG°:
-
The change in Gibbs free energy (J Mol−1)
- ΔH°:
-
The change in enthalpy (J Mol−1)
- ΔS°:
-
The change in entropy (J Mol−1 K−1)
References
M.A. Al-Ghouti, M. Khraisheh, S.J. Allen, M.N. Ahmad, The removal of dyes from textile wastewater: a study of the physical characteristics and adsorption mechanisms of diatomaceous earth. J. Environ. Manage. 69, 229–238 (2003)
S. Ray, M. Takafuji, H. Ihara, Peptide-based surface modified silica particles: adsorption materials for dye-loaded wastewater treatment. RSC Adv. 3, 23664–23672 (2013)
H.A. Mekkawy, M.O. Ali, A.M. El-Zawahry, Toxic effect of synthetic and natural food dyes on renal and hepatic functions in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 95, 155 (1998)
C.K. Lee, S.S. Liu, L.C. Jaung, C.C. Wang, K.S. Lin, M.D. Lyu, Application of MCM-41 for dyes removal from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 147, 997–1005 (2007)
D. Pokhrel, T. Viraraghavan, Treatment of pulp and paper mill wastewater—a review. Sci. Total Environ. 333, 37–58 (2004)
O. Tunay, I. Kabdasli, G. Eremektar, D. Orhon, Color removal from textile wastewaters. Water Sci. Technol. 34, 9–16 (1996)
A. Cassano, R. Molinari, M. Romano, E. Drioli, Treatment of aqueous effluents of the leather industry by membrane processes: a review. J. Membr. Sci. 181, 111–126 (2001)
K. Srinivasan, M.M. Bhargava, Hepatic binding proteins translocating azo dye carcinogen metabolites from cytoplasm into nucleus in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 42, 503–508 (2004)
E. Forgacs, T. Cserhati, G. Oros, Removal of synthetic dyes from wastewaters: a review. Environ. Int. 30, 953–971 (2004)
G. Crini, Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 1061–1085 (2006)
E.N. El Qada, S.J. Allen, G.M. Walker, Adsorption of Methylene Blue onto activated carbon produced from steam activated bituminous coal: a study of equilibrium adsorption isotherm. Chem. Eng. J. 124, 103–110 (2006)
Z.X. Wu, D.Y. Zhao, Ordered mesoporous materials as adsorbents. Chem. Commun. 47, 3332–3338 (2011)
O.G. Rhys, Adsorption on activated carbon-solution to dye waste problems. J. Soc. Dyers Colour 94, 293–297 (1978)
K.R. Ramakrishna, T. Viraraghavan, Dye removal using low cost adsorbents. Water Sci. Technol. 36, 189–196 (1997)
M. Doğan, M. Alkan, Adsorption kinetics of methyl violet onto perlite. Chemosphere 50, 517–528 (2003)
C.C. Wang, L.C. Juang, T.C. Hsu, C.K. Lee, J.F. Lee, F.C. Huang, Adsorption of basic dyes onto montmorillonite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 273, 80–86 (2004)
C. Namasivayam, R.T. Yamuna, Adsorption of direct red 12B by biogas residual slurry: equilibrium and rate processes. Environ. Pollut. 89, 1–7 (1995)
S. Netpradit, P. Thiravetyan, S. Towprayoon, Application of ‘waste’ metal hydroxide sludge for adsorption of azo reactive dyes. Water Res. 37, 763–772 (2003)
T. Robinson, B. Chandran, P. Nigam, Removal of dyes from an artificial textile dye effluent by two agricultural waste residues, corncob and barley husk. Environ. Int. 28, 29–33 (2002)
G. Annadurai, R.S. Juang, D.J. Lee, Use of cellulose-based wastes for adsorption of dyes from aqueous solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. 92, 263–274 (2002)
Y. Al-Degs, M.A.M. Khraisheh, S.J. Allen, M.N. Ahmad, Effect of carbon surface chemistry on the removal of reactive dyes from textile effluent. Water Res. 34, 927–935 (2000)
A.G. Espantaleon, J.A. Nieto, M. Fernandez, A. Marsal, Use of activated clays in the removal of dyes and surfactants from tannery waste waters. Appl. Clay Sci. 24, 105–110 (2003)
J.S. Beck, C. Vartuli, W.J. Roth, M.E. Leonowicz, C.T. Kresge, K.D. Scmmitt, C.T.-W. Chu, D.H. Olson, E.W. Sheppard, S.B. McCullen, J.B. Higgins, J.L. Schlenker, A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 114, 10834–10843 (1992)
L. Zhou, C. Gao, W. Xu, Magnetic dendritic materials for highly efficient adsorption of dyes and drugs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2, 1483–1491 (2010)
S. Qadri, A. Ganoe, Y. Haik, Removal and recovery of acridine orange from solutions by use of magnetic nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 169, 318–323 (2009)
A. Afkhami, R. Moosavi, Adsorptive removal of Congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye, from aqueous solutions by maghemite nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 174, 398–403 (2010)
Y. Yu, Y.Y. Zhuang, Z.H. Wang, M.Q. Qiu, Adsorption of water-soluble dyes onto resin NKZ. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 42, 6898–6903 (2003)
J. Huh, D. Song, Y. Jeon, Sorption of phenol and alkylphenols from aqueous solution onto organically modified montmorillonite and applications of dual-mode sorption model. Sep. Sci. Technol. 35, 243–259 (2000)
H. Zhao, K.L. Nagy, Dodecyl sulfate–hydrotalcite nanocomposites for trapping chlorinated organic pollutants in water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 274, 613–624 (2004)
A. Sayari, S. Hamoudi, Y. Yang, Applications of pore-expanded mesoporous silica. 1. Removal of heavy metal cations and organic pollutants from wastewater. Chem. Mater. 17, 212–216 (2005)
R. Liu, P. Liao, J. Liu, P. Feng, Responsive polymer-coated mesoporous silica as a pH-sensitive nanocarrier for controlled release. Langmuir 27, 3095–3099 (2011)
L.C. Juang, C.C. Wang, C.K. Lee, Adsorption of basic dyes onto MCM-41. Chemosphere 64, 1920–1928 (2006)
X.S. Zhao, G.Q. Lu, G.J. Millar, Advances in mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 35, 2075–2090 (1996)
J. Wloch, M. Rozwadowski, M. Lezanska, K. Erdmann, Analysis of the pore structure of the MCM-41 materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 191, 368–374 (2002)
N.A. Oladoja, A.K. Akinlabi, Congo red biosorption on palm kernel seed coat. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 48, 6188–6196 (2009)
S. Chatterjee, M.W. Lee, S.H. Woo, Adsorption of congo red by chitosan hydrogel beads impregnated with carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 101, 1800–1806 (2010)
Z. Qiao, L. Zhang, M. Guo, Y. Liu, Q. Huo, Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles via controlled hydrolysis and condensation of silicon alkoxide. Chem. Mater. 21, 3823–3829 (2009)
S. Ghorai, A.K. Sarkar, A.B. Panda, S. Pal, Effective removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solution using modified xanthan gum/silica hybrid nanocomposite as adsorbent. Bioresour. Technol. 144, 485–491 (2013)
S. Ghorai, A. Sinhamahpatra, A. Sarkar, A.B. Panda, S. Pal, Novel biodegradable nanocomposite based on XG-g-PAM/SiO2: application of an efficient adsorbent for Pb2+ ions from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 119, 181–190 (2012)
M.S. Sajab, C.H. Chia, S. Zakaria, S.M. Jani, M.K. Ayob, K.L. Chee, P.S. Khiew, W.S. Chiu, Citric acid modified kenaf core fibres for removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 102, 7237–7243 (2011)
G. Crini, H.N. Peindy, F. Gimbert, C. Robert, Removal of C.I. basic green 4 (malachite green) from aqueous solutions by adsorption using cyclodextrin-based adsorbent: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Sep. Purif. Technol. 53, 97–110 (2007)
G. Gu, P.P. Ong, C. Chu, Thermal stability of mesoporous silica molecular sieve. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 60, 943–947 (1999)
M. Kruk, M. Jaroniec, A. Sayari, Structural and surface properties of siliceous and titanium-modified HMS molecular sieves. Micropor. Mater. 9, 173–182 (1997)
S. Legergren, About the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl. 24, 1–39 (1898)
Y.S. Ho, G. McKay, Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 34, 451–465 (1999)
Y.S. Ho, Second-order kinetic model for the sorption of cadmium onto tree fern: a comparison of linear and non-linear methods. Water Res. 40, 119–125 (2006)
W.J. Weber, J.C. Morris, Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J. San. Eng. Div. ASCE 89, 31–59 (1963)
A. Ozcan, A.S. Ozcan, Adsorption of acid red 57 from aqueous solutions onto surfactant-modified sepiolite. J. Hazard. Mater. 125, 252–259 (2005)
L. Ai, C. Zhang, L. Meng, Adsorption of methyl orange from aqueous solution on hydrothermal synthesized Mg–Al layered double hydroxide. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 4217–4225 (2011)
I. Langmuir, The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 38, 2221–2295 (1916)
H.M.F. Freundlich, Uber die adsorption in Losungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 57, 385–470 (1906)
M.J. Temkin, V. Pyzhev, Recent modifications to Langmuir isotherms. Acta. Physicochem. 12, 217–222 (1940)
M.M. Ayad, A.A. El-Nasr, Adsorption of cationic dye (methylene blue) fromwater using polyaniline nanotubes base. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 14377–14383 (2010)
S. Chowdhury, R. Mishra, P. Saha, P. Kushwaha, Adsorption thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption of Malachite green onto chemically modified rice husk. Desalination 265, 159–168 (2011)
X.F. Sun, S.G. Wang, X.W. Liu, W.X. Gong, N. Bao, B.Y. Gao, H.Y. Zhang, Biosorption of malachitegreen from aqueous solutions onto aerobic granules: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 3475–3483 (2008)
Y. Zhou, M. Zhang, X. Hu, X. Wang, J. Niu, T. Ma, Adsorption of cationic dyes on a cellulose-based multicarboxyl adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. Data 58, 413–421 (2013)
S. Ghorai, A. Sarkar, M. Raoufi, A.B. Panda, H. Schonherr, S. Pal, Enhanced removal of methylene blue and methyl violet dyes from aqueous solution using a nanocomposite of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide grafted xanthan gum and incorporated nanosilica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 4766–4777 (2014)
I.D. Mall, V.C. Srivastava, G.V.A. Kumar, I.M. Mishra, Characterization and utilization of mesoporous fertilizer plant waste carbon for adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution, colloids and surfaces A: physicochem. Eng. Aspects 278, 175–187 (2006)
A. Roy, S. Chakraborty, S.P. Kundu, B. Adhikari, S.B. Majumder, Lignocellulosic jute fiber as a bioadsorbent for the removal of azo dye from its aqueous solution: batch and column studies. J. Appl. Poly. Sci. 129, 15–27 (2013)
R.S. Blackburn, Natural polysaccharides and their interactions with dye molecules: applications in effluent treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 38, 4905–4909 (2004)
G.Z. Kyzas, M. Kostoglou, N.K. Lazaridis, Relating interactions of dye molecules with chitosan to adsorption kinetic data. Langmuir 26, 9617–9626 (2010)
H. Chaudhuri, S. Dash, A. Sarkar, Synthesis and use of SBA-15 adsorbent for dye-loaded wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 3, 2866–2874 (2015)
N.M. Mahmoodi, Equilibrium kinetics and thermodynamics of dye removal using alginate in binary systems. J. Chem. Eng. Data 56, 2802–2811 (2011)
C.P. Sekhar, S. Kalidhasan, V. Rajesh, N. Rajesh, Bio-polymer adsorbent for the removal of malachite green from aqueous solution. Chemosphere 77, 842–847 (2009)
H. Chaudhuri, S. Dash, S. Ghoari, S. Pal, A. Sarkar, SBA-16: application for the removal of neutral, cationic, and anionic dyes from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4, 157–166 (2016)
Acknowledgments
H.C is thankful to the Director, Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad for providing research fellowship. Authors would like to thank CRF at Indian School of Mines, Dhanbad for providing FESEM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhuri, H., Dash, S. & Sarkar, A. Adsorption of different dyes from aqueous solution using Si-MCM-41 having very high surface area. J Porous Mater 23, 1227–1237 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0181-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-016-0181-4