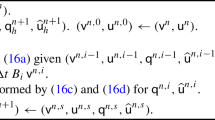Abstract
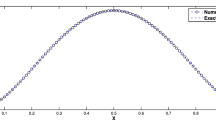
This work is concerned with the study of two-level penalty finite element method for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics equations. The new method is an interesting combination of the Newton iteration and two-level penalty finite element algorithm with two different finite element pairs \(P_{1}b\)-\(P_{1}\)-\(P_{1}b\) and \(P_{1}\)-\(P_{0}\)-\(P_{1}\). Moreover, the rigorous analysis of stability and error estimate for the proposed method are given. Numerical results verify the theoretical results and show the applicability and effectiveness of the presented scheme.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gunzburger, M., Meir, A., Peterson, J.: On the existence, uniquess and finite element approximation of solutions of the equations of sationary, incompressible magnetohydrodynamic. Math. Comput. 56, 523–563 (1991)
Moreau, R.: Magneto-hydrodynamics. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht (1990)
Cao, C., Wu, J.: Two regularity criteria for the 3D MHD equations. J. Differ. Equ. 248, 2263–2274 (2010)
He, C., Wang, Y.: On the regularity criteria for weak solutions to the magnetohydrodynamic equations. J. Differ. Equ. 238, 1–17 (2007)
Schonbek, M., Schonbek, T., Solli, E.: Large-time behaviour of solutions to the magnetohydrodynamics equations. Math. Ann. 304, 717–756 (1996)
Sermange, M., Temam, R.: Some mathematical questions related to the MHD equations. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 36, 635–664 (1983)
Salah, N., Soulaimani, A., Habashi, W.: A finite element method for magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 5867–5892 (2001)
Codina, R., Silva, N.: Stabilized finite element approximation of the stationary magnetohydrodynamics equations. Comput. Mech. 38, 344–355 (2006)
Sermange, M., Temam, R.: Some mathematical questions related to the MHD equations. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 36, 635–664 (1983)
Gerbeau, J.: A stabilized finite element method for the incompressible magnetohydrodynamic equations. Numer. Math. 87, 83–111 (2000)
Ravindran, S.: Linear feedback control and approximation for a system governed by unsteady MHD equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 524–541 (2008)
Salah, N., Soulaimani, A., Habashi, W.: A finite element method for magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190, 5867–5892 (2001)
Meir, A., Schmidt, P.: Analysis and numerical approximation of a stationary MHD flow problem with nonideal boundary. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 36, 1304–1332 (1999)
He, Y., Li, J.: Convergence of three iterative methods based on the finite element discretization for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1351–1359 (2009)
Xu, H., He, Y.: Some iterative finite element methods for steady Navier–Stokes equations with different viscosities. J. Comput. Phys. 232, 123–152 (2013)
Dong, X., He, Y., Zhang, Y.: Convergence analysis of three finite element iterative methods for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 276, 287–311 (2014)
Dong, X., He, Y.: Two-level Newton iterative method for the 2D/3D stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. J. Sci. Comput. 63, 426–451 (2015)
Su, H., Feng, X., Huang, P.: Iterative methods in penalty finite element discretization for the steady MHD equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 304, 521–545 (2016)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of some higher order projection and penalty-projection methods for Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Math. 62, 49–73 (1992)
Shen, J.: On error estimates of the penalty method for unsteady Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 32, 386–403 (1995)
He, Y.: Optimal error estimate of the penalty finite element method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 74, 1201–1216 (2005)
He, Y., Li, J., Yang, X.: Two-level penalized finite element methods for the stationary Navier–Stoke equations. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Sci. 2, 131–143 (2006)
Xu, J.: A novel two two-grid method for semilinear elliptic equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15, 231–237 (1994)
Xu, J.: Two-grid discretization techniques for linear and nonlinear PDEs. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 33, 1759–1777 (1996)
Layton, W., Lenferink, H., Peterson, J.: A two-level Newton finite element algorithm for approximating electrically conducting incompressible fluid flows. Comput. Math. Appl. 28, 21–31 (1994)
Layton, W., Meir, A., Schmidtz, P.: A two-level discretization method for the stationary MHD equations. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 6, 198–210 (1997)
Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., He, Y.: Two-level coupled and decoupled parallel correction methods for stationary incompressible magnetohydrodynamics. J. Sci. Comput. 65, 920–939 (2015)
He, Y.: Two-level method based on fnite element and Crank–Nicolson extrapolation for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41, 1263–1285 (2003)
Gerbeau, J., Le Bris, C., Lelièvre, T.: Mathematical Methods for the Magnetohydrodynamics of Liquid Metals, Numerical Mathematics and Scientific Computation. Oxford University Press, New York (2006)
He, Y.: Unconditional convergence of the Euler semi-implicit scheme for the 3D incompressible MHD equations. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 35, 767–801 (2014)
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank the editor and referees for their valuable comments and suggestions which helped us to improve the results of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Province (No. 2016D01C073).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, H., Feng, X. & Zhao, J. Two-Level Penalty Newton Iterative Method for the 2D/3D Stationary Incompressible Magnetohydrodynamics Equations. J Sci Comput 70, 1144–1179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0276-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0276-8
Keywords
- Magnetohydrodynamics equations
- Penalty finite element method
- Newton iteration
- Two-level method
- Inf-sup condition
- Error estimate