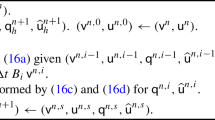Abstract
In this paper, we develop a high order semi-implicit time discretization method for highly nonlinear PDEs, which consist of the surface diffusion and Willmore flow of graphs, the Cahn–Hilliard equation and the Allen–Cahn/Cahn–Hilliard system. These PDEs are high order in spatial derivatives, which motivates us to develop implicit or semi-implicit time marching methods to relax the severe time step restriction for stability of explicit methods. In addition, these PDEs are also highly nonlinear, fully implicit methods will incredibly increase the difficulty of implementation. In particular, we can not well separate the stiff and non-stiff components for these problems, which leads to traditional implicit-explicit methods nearly meaningless. In this paper, a high order semi-implicit time marching method and the local discontinuous Galerkin (LDG) spatial method are coupled together to achieve high order accuracy in both space and time, and to enhance the efficiency of the proposed approaches, the resulting linear or nonlinear algebraic systems are solved by multigrid solver. Specially, we develop a first order fully discrete LDG scheme for the Allen–Cahn/Cahn–Hilliard system and prove the unconditional energy stability. Numerical simulation results in one and two dimensions are presented to illustrate that the combination of the LDG method for spatial approximation, semi-implicit temporal integration with the multigrid solver provides a practical and efficient approach when solving this family of problems.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassi, F., Rebay, S.: A high-order accurate discontinuous finite element method for the numerical solution of the compressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 131, 267–279 (1997)
Boscarino, S., Filbet, F., Russo, G.: High order semi-implicit schemes for time dependent partial differential equations. J. Sci. Comput. 66, 1–27 (2016). doi:10.1007/s10915-016-0168-y
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: TVB Runge–Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws II: general framework. Math. Comput. 52, 411–435 (1989)
Cockburn, B., Lin, S.-Y., Shu, C.-W.: TVB Runge–Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws III: one dimensional systems. J. Comput. Phys. 84, 90–113 (1989)
Cockburn, B., Hou, S., Shu, C.-W.: The Runge–Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws IV: the multidimensional case. Math. Comput. 54, 545–581 (1990)
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: The Runge–Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method for conservation laws V: multidimensional systems. J. Comput. Phys. 141, 199–224 (1998)
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: The local discontinuous Galerkin method for time-dependent convection-diffusion systems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 35, 2440–2463 (1998)
Deckelnick, K., Dziuk, G.: Error analysis of a finite element method for the Willmore flow of graphs. Interfaces Free Bound. 8, 21–46 (2006)
Dutt, A., Greengard, L., Rokhlin, V.: Spectral deferred correction methods for ordinary differential equations. BIT 40, 241–266 (2000)
Eyre, D.J.: Unconditionally gradient stable time marching the Cahn–Hilliard equation. In: Bullard, J.W., Kalia, R., Stoneham, M., Chen, L.Q. (eds.) Computational and Mathematical Models of Microstructural Evolution, vol. 53, pp. 1685–1712. Materials Research Society, Warrendale (1998)
Filbet, F., Jin, S.: An asymptotic preserving scheme for the ES-BGK model of the Boltzmann equation. J. Sci. Comput. 46(2), 204–224 (2011)
Filbet, F., Jin, S.: A class of asymptotic-preserving schemes for kinetic equations and related problems with stiff sources. J. Comput. Phys. 229(20), 7625–7648 (2010)
Guo, R., Xu, Y.: Efficient solvers of discontinuous Galerkin discretization for the Cahn–Hilliard equations. J. Sci. Comput. 58, 380–408 (2014)
Minion, M.L.: Semi-implicit spectral deferred correction methods for ordinary differential equations. Math. Sci. 1, 471–500 (2003)
Pareschi, L., Russo, G.: Implicit-Explicit Runge–Kutta Schemes for Stiff Systems of Differential Equations. Recent trends in numerical analysis, pp. 269–288, Adv. Theory Comput. Math. 3, Nova Sci. Publ. Huntington (2001)
Reed, W.H., Hill, T.R.: Triangular Mesh Method for the Neutron Transport Equation, Technical Report LA-UR-73-479. Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory, Los Alamos (1973)
Smereka, P.: Semi-implicit level set methods for curvature and surface diffusion motion. J. Sci. Comput. 19, 439–456 (2003)
Trottenberg, U., Oosterlee, C., Schüller, A.: Multigrid. Academic Press, New York (2005)
Xia, Y., Xu, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for the Cahn–Hilliard type equations. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 677–693 (2007)
Xia, Y., Xu, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Efficient time discretization for local discontinuous Galerkin methods. Discrete Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 8, 677–693 (2007)
Xia, Y., Xu, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Application of the local discontinuous Galerkin method for the Allen–Cahn/Cahn–Hilliard system. Commun. Comput. Phys. 5, 821–835 (2009)
Xia, Y.: A fully discrete stable discontinuous Galerkin method for the thin film epitaxy problem without slope selection. J. Comput. Phys. 280, 248–260 (2015)
Xu, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Local discontinuous Galerkin method for surface diffusion and Willmore flow of graphs. J. Sci. Comput. 40, 375–390 (2009)
Xu, Y., Shu, C.-W.: Local discontinuous Galerkin methods for high-order time-dependent partial differential equations. Commun. Comput. Phys. 7, 1–46 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research supported by NSFC Grant No. 11371342, 11426236.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, R., Filbet, F. & Xu, Y. Efficient High Order Semi-implicit Time Discretization and Local Discontinuous Galerkin Methods for Highly Nonlinear PDEs. J Sci Comput 68, 1029–1054 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0170-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0170-4