Abstract
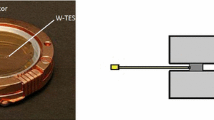
The goal of the Cryogenic wide-Area Light Detectors with Excellent Resolution project is the development of light detectors with large active area and noise energy resolution smaller than 20 eV RMS using phonon-mediated kinetic inductance detectors. The detectors are developed to improve the background suppression in large-mass bolometric experiments such as CUORE, via the double read-out of the light and the heat released by particles interacting in the bolometers. In this work, we present the design and the fabrication process, starting from the silicon wafer arriving to the single chip. The Al thin films (40 nm) are evaporated on high-quality, high-resistivity (>\(10\,\mathrm{k \Omega }\,\)cm) Si(100) substrates using an electron beam evaporator in a high-vacuum chamber. Detectors are patterned in direct-write mode, using electron beam lithography , positive tone resist poly-methyl methacrylate and lift-off process. Finally the wafer is diced into 20 \(\times \) 20 mm\(^2\) chips and assembled in a holder OFHC copper (oxygen-free high conductivity) using PTFE supports.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.S. Battistelli et al., CALDER - Neutrinoless double-beta decay identification in TeO\(_2\) bolometers with kinetic inductance detectors. Eur. Phys. J. C 75, 353 (2015). doi:10.1140/epjc/s10052-015-3575-6
J. Zmuidzinas et al., Superconducting microresonators: physics and applications. Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 3, 169–214 (2012). doi:10.1146/annurev-conmatphys-020911-125022
L.J. Swenson et al., High-speed phonon imaging using frequency-multiplexed kinetic inductance detectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 263511 (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3459142
L. Cardani et al., Energy resolution and efficiency of phonon-mediated kinetic inductance detectors for light detection. Appl. Phys. Lett. 107, 093508 (2015). doi:10.1063/1.4929977
H.G. Leduc et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 102509 (2010). doi:10.1063/1.3480420
M.R. Vissers et al., Proximity-coupled Ti/TiN multilayers for use in kinetic inductance detectors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 232603 (2013). doi:10.1063/1.4804286
A. Cruciani, et al. J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue
N. Casali, et al. J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue. doi:10.1007/s10909-015-1358-y
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the European Research Council (FP7/2007-2013) under contract CALDER No. 335359 and by the Italian Ministry of Research (FIRB 2012) under contract No. RBFR1269SL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colantoni, I., Bellini, F., Cardani, L. et al. Design and Fabrication of the KID-Based Light Detectors of CALDER. J Low Temp Phys 184, 131–136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1452-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1452-1