Abstract
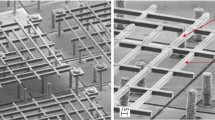
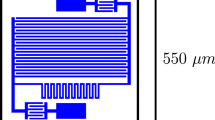
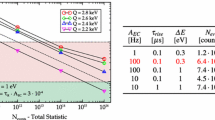
We present our current progress on the design and test of Ti/TiN multilayer for use in kinetic inductance detectors. Sensors based on sub-stoichiometric TiN film are commonly used in several applications. However, it is difficult to control the targeted critical temperature \(T_c\), to maintain precise control of the nitrogen incorporation process and to obtain a production uniformity. To avoid these problems we investigated multilayer Ti/TiN films that show a high uniformity coupled with high quality factor, kinetic inductance and inertness of TiN. These features are ideal to realize superconductive microresonator detectors for astronomical instruments application but also for the field of neutrino physics. Using pure Ti and stoichiometric TiN, we developed and tested different multilayer configurations, in terms of number of Ti/TiN layers and in terms of different interlayer thicknesses. The target was to reach a critical temperature \(T_c\) around \((1{\div } 1.5)\) K in order to have a low energy gap and slower recombination time (i.e. low generation–recombination noise). The results prove that the superconductive transition can be tuned in the \((0.5{\div } 4.6)\) K temperature range by properly choosing the Ti thickness in the \((0{\div } 15)\) nm range, and the TiN thickness in the \((5{\div } 100)\) nm range.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Standard cubic centimeters per minute, a flow measurement term.
References
P.K. Day et al., Nature 425, 817–821 (2003)
P.R. Maloney et al., Proc. SPIE 7741, 77410F (2010)
B.A. Mazin et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 222507 (2006)
T. Cecil et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 032601 (2012)
J. Zmuidzinas, Annual Review of Condensed Matter Physics 3, 169–214 (2012)
J. Gao et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 101, 142602 (2012)
J. Gao et al., NIMA 559, 585–587 (2006)
H.G. Leduc et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 102509 (2010)
M.R. Vissers et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, 232509 (2010)
M.R. Vissers et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 232603 (2013)
M. Faverzani et al., J. Low. Temp. Phys. 167, 10411047 (2012)
M. Faverzani et al., NIMA 167, 492494 (2013)
W. Silvert, Journal of Low Temperature Physics 20, 439 (1975)
N.R. Werthamer, Physical Review 132, 2440 (1963)
L. Yu, N. Newman, J.M. Rowell, IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity 12, 1795 (2002)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Fondazione Cariplo through the project Development of Microresonator Detectors for Neutrino Physics (Grant International Recruitment Call 2010, ref. 2010-2351).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giachero, A., Day, P., Falferi, P. et al. Critical Temperature Tuning of Ti/TiN Multilayer Films Suitable for Low Temperature Detectors. J Low Temp Phys 176, 155–160 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-1078-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-013-1078-0