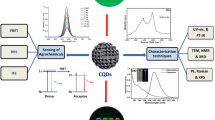
Abstract
In this paper, a rapid, simple and highly sensitive method with dual-readout (colorimetric and fluorometric) based on the nanometal surface energy transfer (NSET) between nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots (NCQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for detection of biothiols is described. Highly luminescent NCQDs were prepared via a simple one-step hydrothermal method by applying sucrose and glycine as carbon and nitrogen sources. The results showed the obtained NCQDs had an average particle diameter of 5 nm and highly luminescent. The maximum emission wavelength was 438 nm with an excitation wavelength of 360 nm. In this system, NCQDs and AuNPs were respectively treated as energy donors and energy acceptors, which enable the nanometal surface energy transfer (NSET) from the NCQDs to the AuNPs, quenching the fluorescence. However, biothiols was used as a competitor in the NSET by the strongly Au-S bonding to release NCQDs from the Au surface, which subsequently produces fluorescent signal recovery and the red-to-purple color change quickly. This probe showed rapid response, high selectivity and sensitivity for biothiols with dual colorimetric and fluorescent turn-on signal changes. The low detection limit was calculated as 20 nM by using L-cysteine acted as target melocules. The method was also successfully applied to the determination of biothiols in human serum samples, and the results were satisfying.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shahrokhian S (2001) Lead phthalocyanine as a selective carrier for preparation of a cysteine- selective electrode. Anal Chem 73:5972–5978
Wang WH, Rusin O, Xu XY, Kim KK, Escobedo JO, Fakayode SO, Fletcher KA, Lowry M, Schowalter CM, Lawrence CM, Fronczek FR, Warner IM, Strongin RM (2005) Detection of homocysteine and cysteine. J Am Chem Soc 127:15949–15958
Spataru N, Sarada BV, Popa E, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (2001) Voltammetric determination of l-cysteine at conductive diamond electrodes. Anal Chem 2001(73):514–519. doi:10.1021/ac000220v
Fei SD, Chen JH, Yao SZ, Deng GH, He DL, Kuang YF (2005) Electrochemical behavior of l-cysteine and its detection at carbon nanotube electrode modified with platinum. Anal Biochem 339:29–35
Shang L, Qin CJ, Wang T, Wang M, Wang LX, Dong SJ (2007) Fluorescent conjugated polymer-stabilized gold nanoparticles for sensitive and selective detection of cysteine. J Phys Chem C 111:13414–13417
Tseng KS, Chen LC, Ho KC (2006) Amperometric detection of cysteine at an In3+ stabilized indium hexacyanoferrate modified electrode. Electroanalysis 18:1306–1312
Sawuła W, Banecka-Majkutewicz Z, Kadziński L, Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka J, Wegrzyn G, Nyka W, Banecki B (2008) Improved HPLC method for total plasma homocysteine detection and quantification. Acta Biochim Pol 55:119–125
Tcherkas YV, Kartsova LA, Krasnova IN (2001) Analysis of amino acids in human serum by isocratic reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr A 913:303–308
Johnson JM, Strobel FH, Reed M, Pohl J, Jones DP (2008) A rapid LC-FTMS method for the analysis of cysteine, cystine and cysteine/cystine steady-state redox potential in human plasma. Clin Chim Acta 396:43–48
Yu H, Xu L, You TY (2013) Indirect electrochemiluminescence detection of lysine and histidine separated by capillary electrophoresis based on charge displacement. Luminescence 28:217–221
Yu LR, Li L, Ding YP, Lu YX (2016) A fluorescent switch sensor for glutathione detection based on Mn-doped CdTe quantum dots - methyl viologen nanohybrids. J Fluoresc 26:651–660
Vimal K, Bhardwaj HS, Singh N (2014) Ratiometric fluorescent probe for biothiol in aqueous medium with fluorescent organic nanoparticles. Talanta 129:198–202
Zhang QE, Deng T, Li JS, Xu WJ, Shen GL, Yu RQ (2015) Cyclodextrin supramolecular inclusion-enhanced pyrene excimer switching fortime-resolved fluorescence detection of biothiols in serum. Biosens Bioelectron 68:253–258
Zuo QP, Li B, Pei Q, Li ZJ, Liu SK (2010) A highly selective fluorescent probe for detection of biological samples thiol and its application in living cells. J Fluoresc 20:1307–1313
Fu X, Liu Y, Wu ZT, Zhang H (2014) Highly sensitive and naked eye dual-readout method for L-cysteine detection based on the NSET of fluorophore functionalized gold nanoparticles. Bull Kor Chem Soc 35:1159–1164
Hou J, Zhang FS, Yan X, Wang L, Yan J, Hong D, Ding L (2015) Sensitive detection of biothiols and histidine based on the recovered fluorescence of the carbon quantum dots–hg(II) system. Anal Chim Acta 859:72–78
Liu C, Wu T, Huang CZ (2010) Gold nanoparticles surface energy transfer and its application to highly selective and sensitive detection of cysteine. Sci Sin Chim 40:531–537
Saineelima B, Kasibabu B, D’souza SL, Jha S, Kailasa SK (2015) Imaging of bacterial and fungal cells using fluorescent carbon dots prepared from Carica papaya juice. J Fluoresc 25:803–810
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 49:6726–6744
Shan XY, Chai LJ, Ma JJ, Qian ZS, Chen JR, Feng H (2014) B-doped carbon quantum dots as a sensitive fluorescence probe for hydrogen peroxide and glucose detection. Analyst 139:2322–2325
Li Y, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Shi G, Deng L, Hou Y, Qu L (2011) An electrochemical avenue to green-luminescent graphene quantum dots as potential electron-acceptors for photovoltaics. Adv Mater 23:776–780
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang X, Routh P, Sana B, Lim S, Kim DH, Lim KH, Li J, Chen P (2014) Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv Funct Mater 24:3021–3026
Tian L, Ghosh D, Chen W, Pradhan S, Chang X, Chen S (2009) Nanosized carbon particles from natural gas soot. Chem Mater 21:2803–2809
Bourlinos AB, Stassinopoulos A, Anglos D, Zboril R, Georgakilas V, Giannelis EP (2008) Photoluminescent carbogenic dots. Chem Mater 20:4539–4541
Atienzar P, Primo A, Lavorato C, Molinari R, Garcia H (2013) Preparation of graphene quantum dots from Pyrolyzed alginate. Langmuir 29:6141–6146
Zhang B, Liu CY, Liu Y (2010) A novel one-step approach to synthesize fluorescent carbon nanoparticles. Eur J Inorg Chem 28:4411–4414
Wang J, Cheng C, Huang Y, Zheng B, Yuan H, Bo L, Zheng MW, Yang SY, Guo Y, Xiao D (2014) A facile large-scale microwave synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon dots from benzenediol isomers. J Mater Chem C 2:5028–5035
Liu DB, Chen WW, Wei JH, Li XB, Wang Z, Jiang XY (2012) A highly sensitive, dual-readout assay based on gold nanoparticles for organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. Anal Chem 84:4185
Zhang RZ, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens Bioelectron 55:83–90
Dai HC, Shi Y, Wang YL, Sun YJ, Hu JT, Ni PJ, Li Z (2014) A carbon dot based biosensor for melamine detection by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Sensors Actuators B 202:201–208
Wu HP, Huang CC, Cheng TL, Tseng WL (2008) Sodium hydroxide as pretreatment and fluororsurfactant-capped gold nanoparticles as sensor for the highly selective detection of cysteine. Talanta 76:347–352
Tang LB, Ji RB, Cao XK, Lin JY, Jiang HX, Li XM, Teng KS, Luk CM, Zeng SJ, Hao JH, Lau SP (2012) Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6:5102–5110
Chen X, Jin Q, Wu L, Tung C, Tang X (2014) Synthesis and unique photoluminescence properties of nitrogen-rich quantum dots and their applications. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12542–12547
Cui X, Zhu L, Wu J, Hou Y, Wang P, Wang Z, Yang M (2015) A fluorescent biosensor based on carbon dots-labeled oligodeoxyribonucleotide and graphene oxide for mercury(II) detection. Biosens Bioelectron 63:506–512
Zhai X, Zhang P, Liu C, Bai T, Li W, Dai L, Liu W (2012) Highly luminescent carbon nanodots by microwave-assisted pyrolysis. Chem Commun 48:7955–7957
Zhang Y, Cui PP, Zhang F, Feng XT, Wang YL, Yang YZ, Liu XG (2016) Fluorescent probes for “off–on” highly sensitive detection of Hg2+ and L-cysteine based on nitrogen-doped carbon dots. Talanta 152:288–300
Zhang H, Huang Y, Hu S, Huang Q, Wei C, Zhang W, Kang L, Huang Z, Hao A (2015) Fluorescent probes for "off-on" sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions and L-cysteine based on graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets. J Mater Chem C 3:2093–2100
Liu HL, Wang YH, Shen AG, Zhou XD, Hu JM (2012) Highly selective and sensitive method for cysteine detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between FAM-tagged ssDNA and graphene oxide. Talanta 93:330–335
Wei XY, Qi L, Tan JJ, Liu RG, Wang FY (2010) A colorimetric sensor for determination of cysteine by carboxymethyl cellulose-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 671:80–84
Liu ZN, Zhang HC, Hou SF, Ma HY (2012) Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical detection of L-cysteine using nanoporous gold. Microchim Acta 177:427–433
Amini N, Shamsipur M, Gholivanda MB, Barati A (2017) A glassy carbon electrode modified with carbon quantum dots and polyalizarin yellow R dyes for enhanced electrocatalytic oxidation and nanomolar detection of L-cysteine. Microchem J 131:9–14
Xu XZ, Qiao J, Li N, Qi L, Zhang SF (2015) Fluorescent probe for turn-on sensing of L-cysteine by ensemble of AuNCs and polymer protected AuNPs. Anal Chim Acta 879:97–103
Shiu HY, Chong HC, Leung YC, Wong MK, Che CM (2010) A highly selective FRET-based fluorescent probe for detection of cysteine and homocysteine. Chem-Eur J 16:3308–3313
Shen YM, Zhang XY, Zhang YY, Zhang CX, Jin JL, Li HT, Yao SZ (2016) A novel colorimetric/fluorescence dual-channel sensor based on NBD for the rapid and highly sensitive detection of cysteine and homocysteine in living cells. Anal Methods 8:2420–2426
Acknowledgments
The work is supported by Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (No. 2015JJ2039, No.14JJ3133), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (16B060).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, X., Gu, D., Zhao, S. et al. A Dual-Readout Method for Biothiols Detection Based on the NSET of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots–Au Nanoparticles System. J Fluoresc 27, 1597–1605 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2095-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-017-2095-1